Abstract
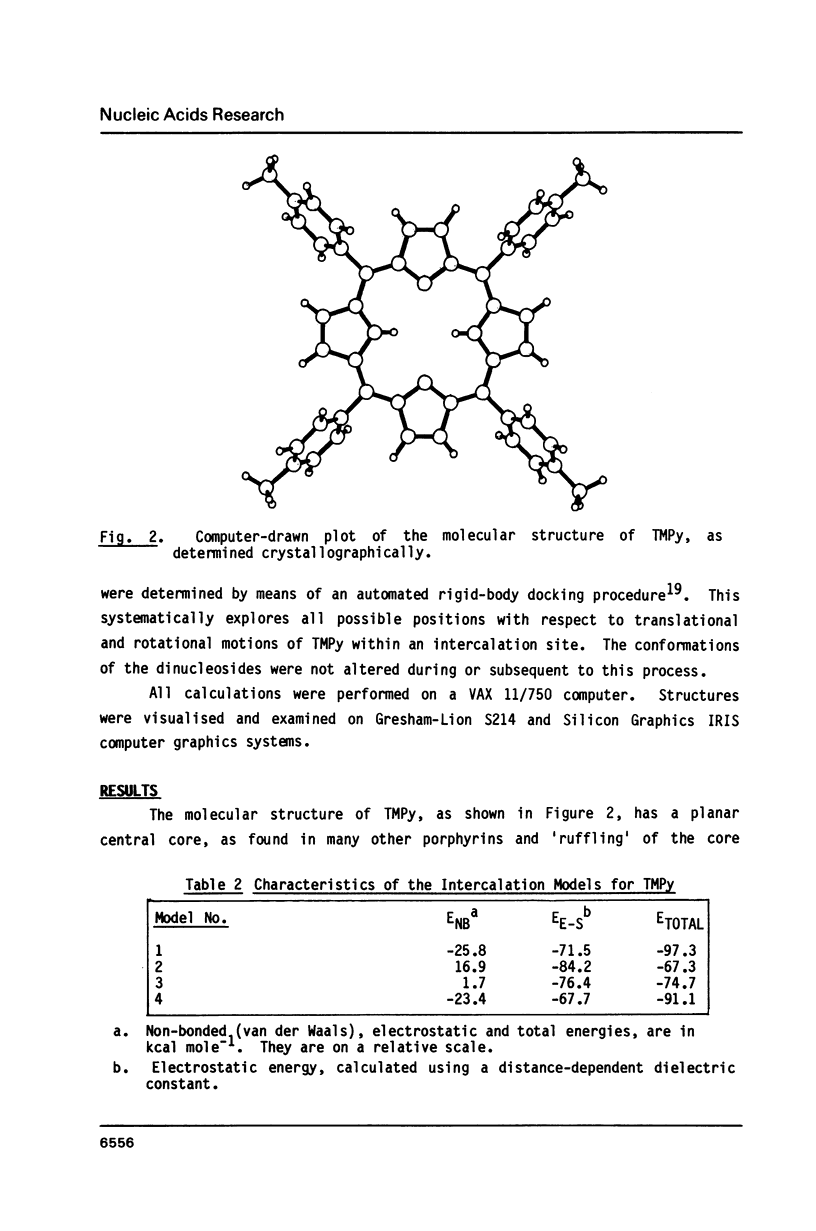
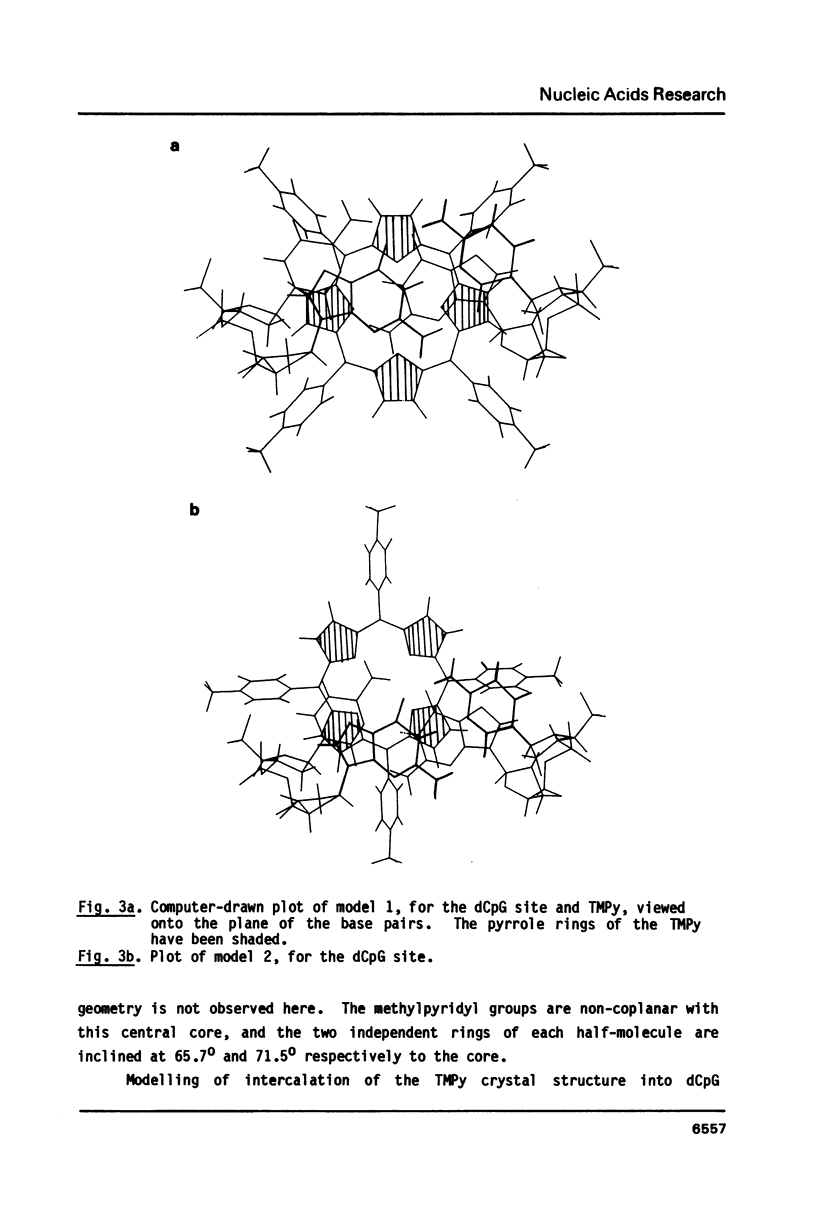
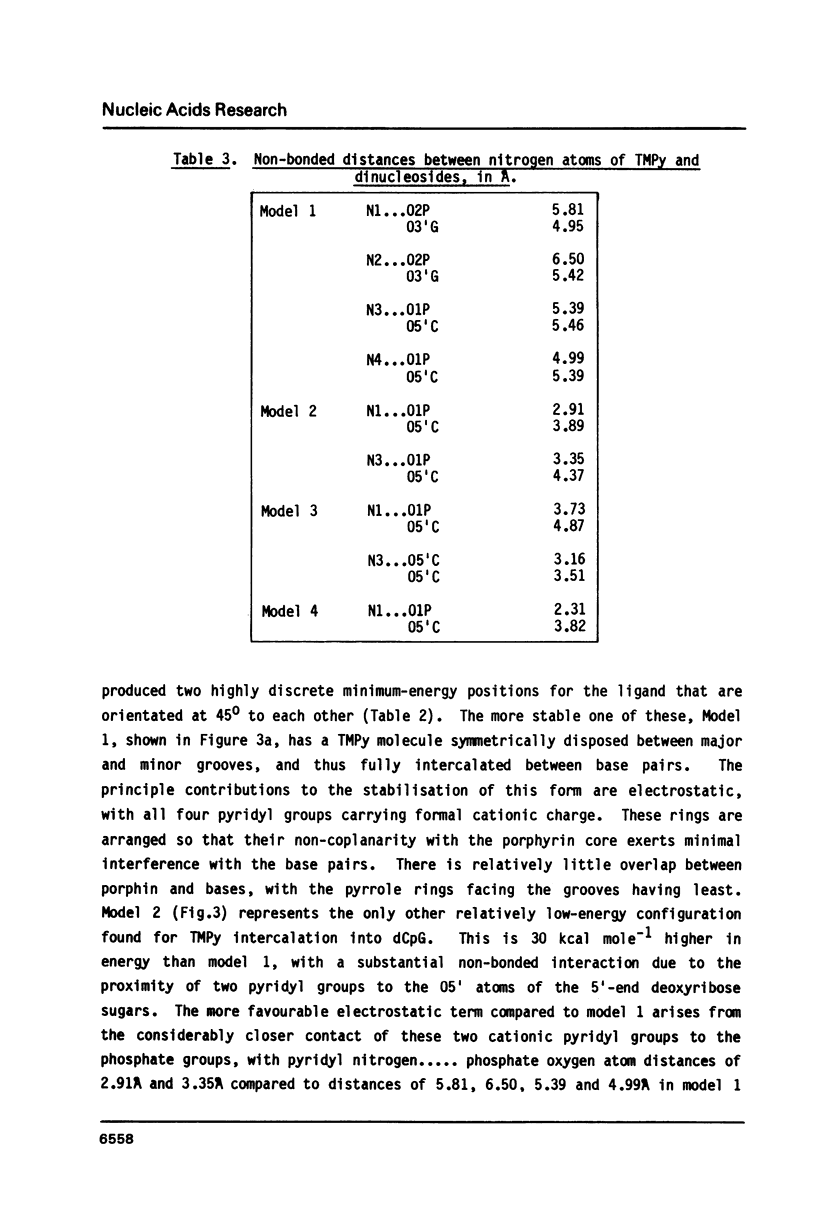
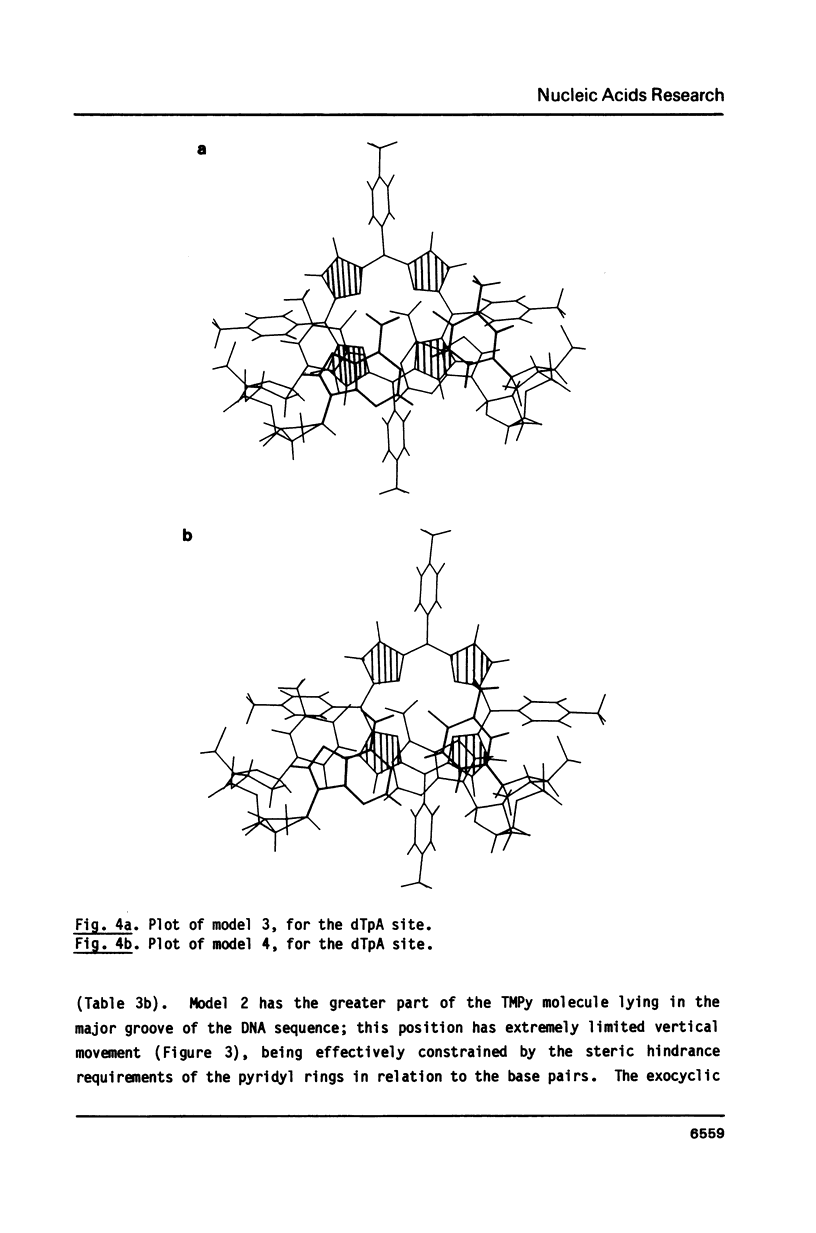
The molecular structure of the DNA-intercalating ligand tetra-(4-N-methylpyridyl) porphin has been determined by X-ray crystallography. The porphyrin has a precise centre of symmetry; the central core is planar, with the N-methylpyridyl groups inclined to it at angles of 66-72 degrees. Molecular modelling of this structure into TpA and CpG sites of intercalated DNA, has been performed, and approximate energetics calculated. It has been shown that only the CpG site can have full ligand intercalation, since the thymine methyl group sterically hinders such geometry at TpA sites. Modelling indicates the importance of electrostatic effects in the low-energy forms of intercalated and part-intercalated complexes at both sequences.
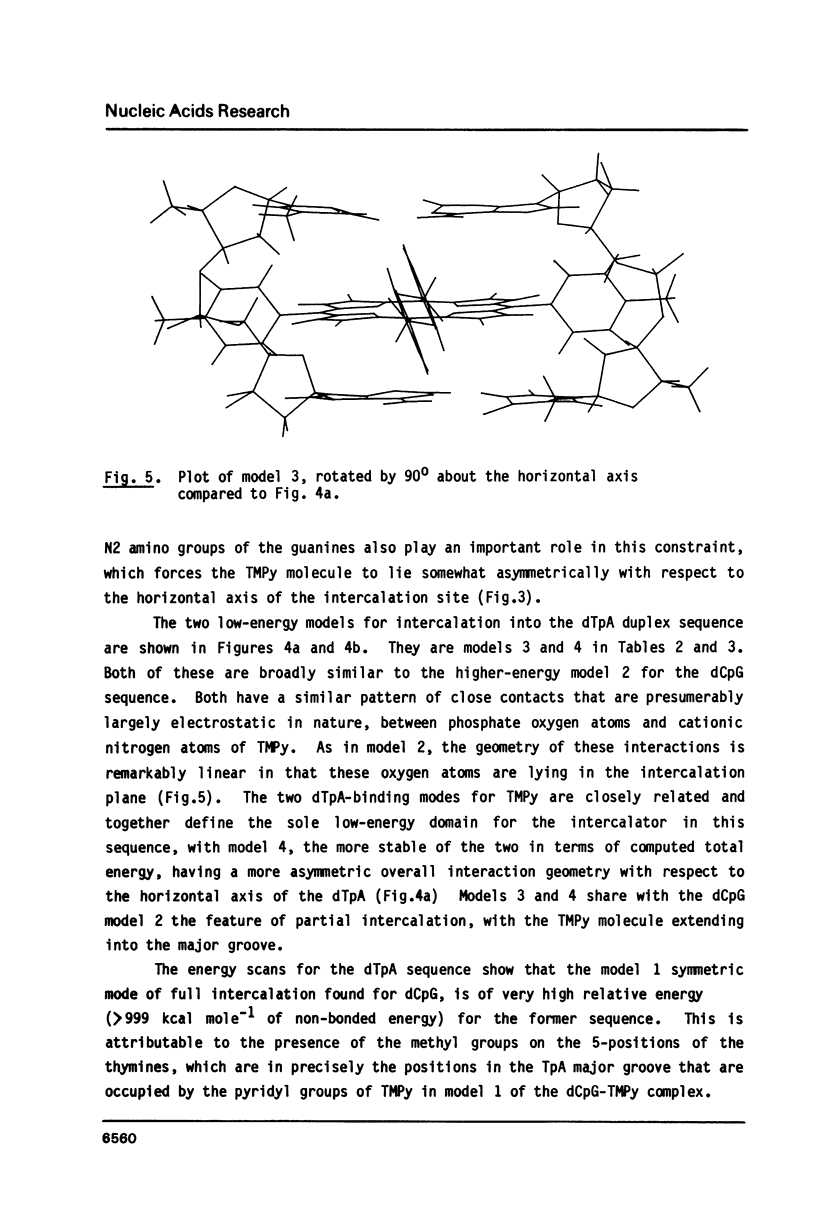
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banville D. L., Marzilli L. G., Strickland J. A., Wilson W. D. Comparison of the effects of cationic porphyrins on DNA properties: influence of GC content of native and synthetic polymers. Biopolymers. 1986 Oct;25(10):1837–1858. doi: 10.1002/bip.360251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banville D. L., Marzilli L. G., Wilson W. D. 31P NMR and viscometric studies of the interaction of meso-tetra(4-N-methylpyridyl) porphine and its Ni(II) and Zn(II) derivatives with DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 31;113(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley S. D., Ward B. W., Dabrowiak J. C. Cationic porphyrins as probes of DNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9133–9148. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvlin M. J., Mark E., Fiel R., Howard J. C. Intercalative and nonintercalative binding of large cationic porphyrin ligands to polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):6141–6154. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.6141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiel R. J., Howard J. C., Mark E. H., Datta Gupta N. Interaction of DNA with a porphyrin ligand: evidence for intercalation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3093–3118. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiel R. J., Munson B. R. Binding of meso-tetra (4-N-methylpyridyl) porphine to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2835–2842. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford K., Fox K. R., Neidle S., Waring M. J. DNA sequence preferences for an intercalating porphyrin compound revealed by footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2221–2234. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam S. A., Neidle S., Gandecha B. M., Partridge M., Patterson L. H., Brown J. R. Comparative computer graphics and solution studies of the DNA interaction of substituted anthraquinones based on doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. J Med Chem. 1985 Jul;28(7):857–864. doi: 10.1021/jm00145a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Pearl L. H., Skelly J. V. DNA structure and perturbation by drug binding. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2430001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Garrity P., Ehrlich B., Davis C. B., Gibbs E. J., Orloff G., Giartosio A., Turano C. The influence of ionic strength on the binding of a water soluble porphyrin to nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5919–5931. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Gibbs E. J., Villafranca J. J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2406–2414. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Gibbs E. J., Villafranca J. J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 8;22(23):5409–5417. doi: 10.1021/bi00292a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl L. H., Neidle S. Origins of stereospecificity in DNA damage by anti-benzo[a]pyrene diol-epoxides. A molecular modelling study. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh H. S., Berman H. M., Dabrow M., Neidle S. The structure of drug-deoxydinucleoside phosphate complex; generalized conformational behavior of intercalation complexes with RNA and DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):85–97. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B., Skorobogaty A., Dabrowiak J. C. DNA binding specificity of a series of cationic metalloporphyrin complexes. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7827–7833. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


