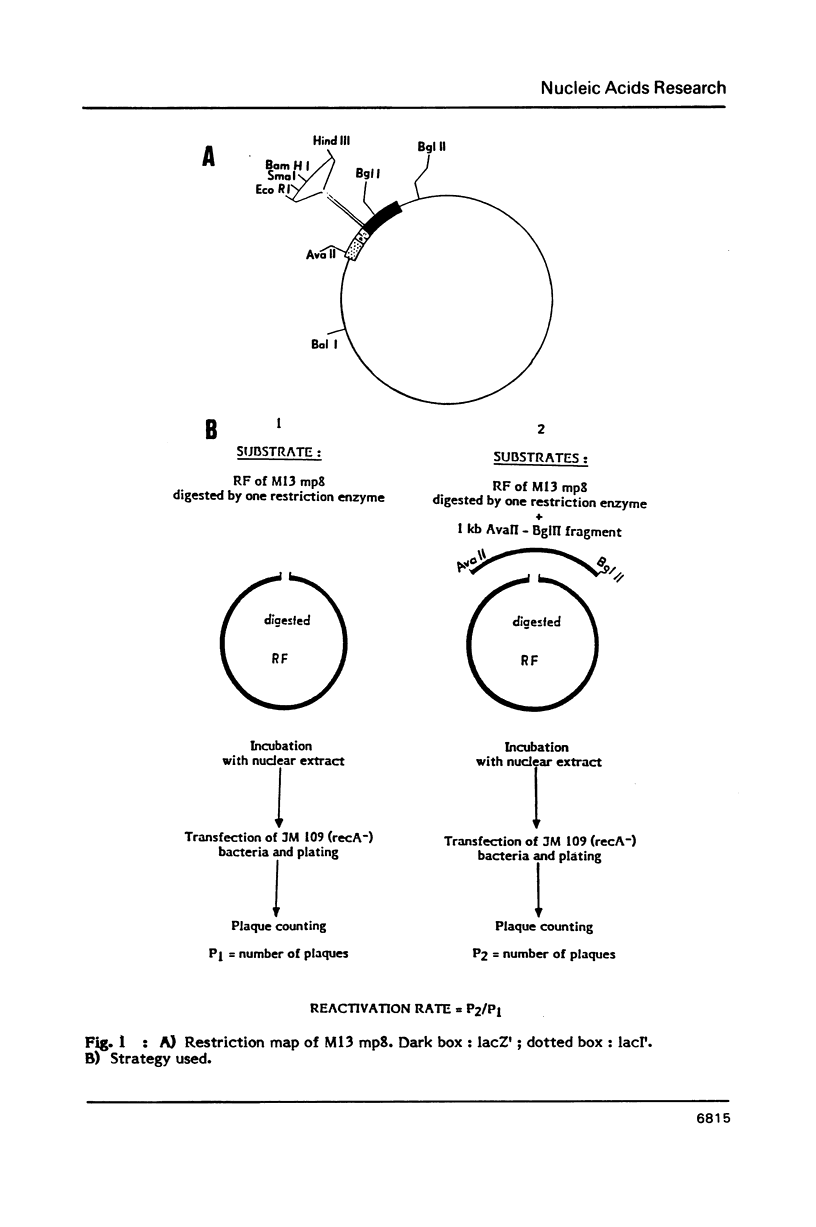
Abstract
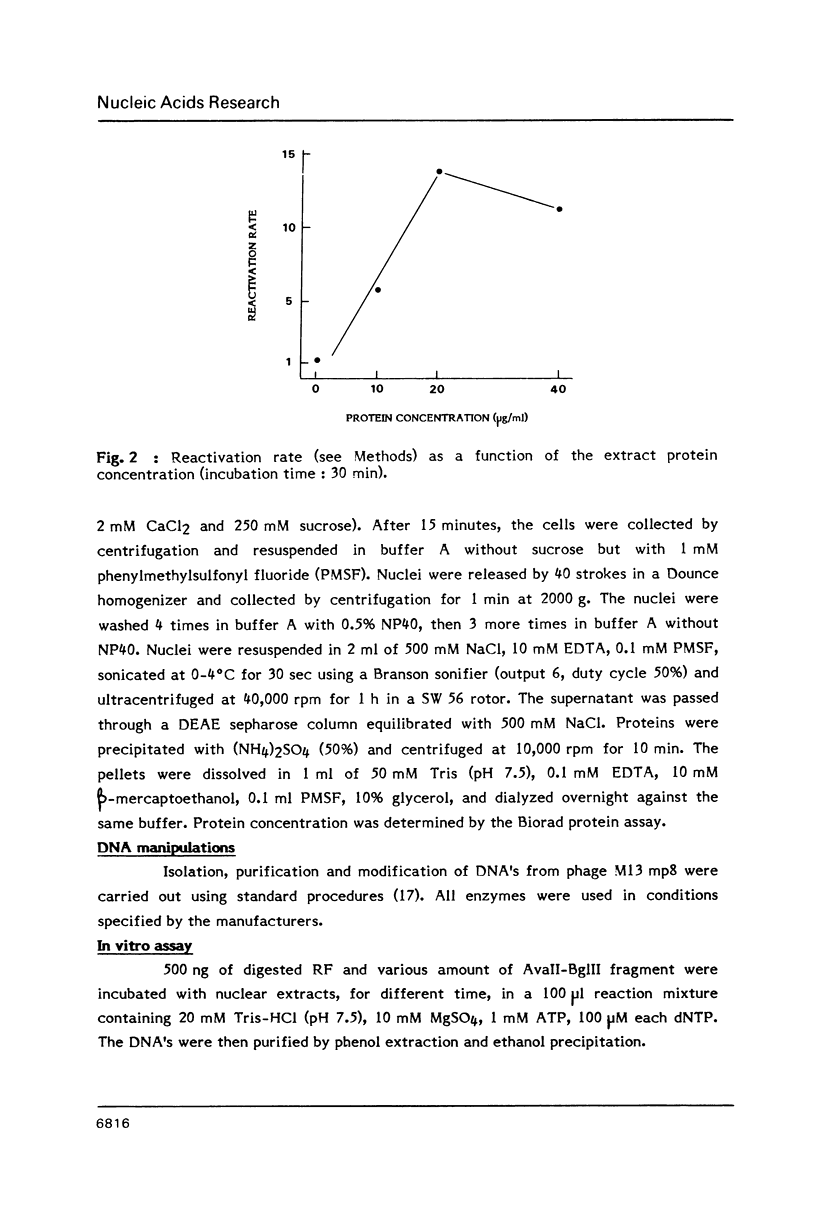
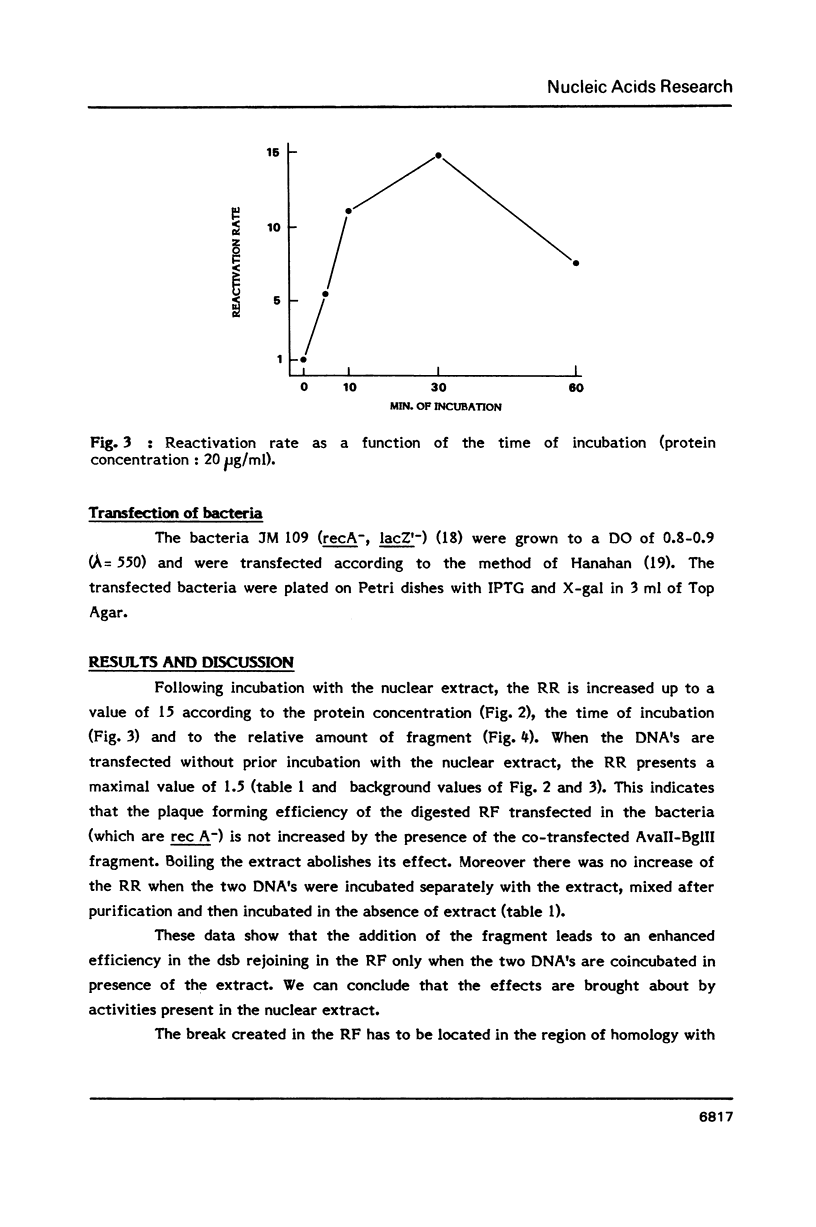
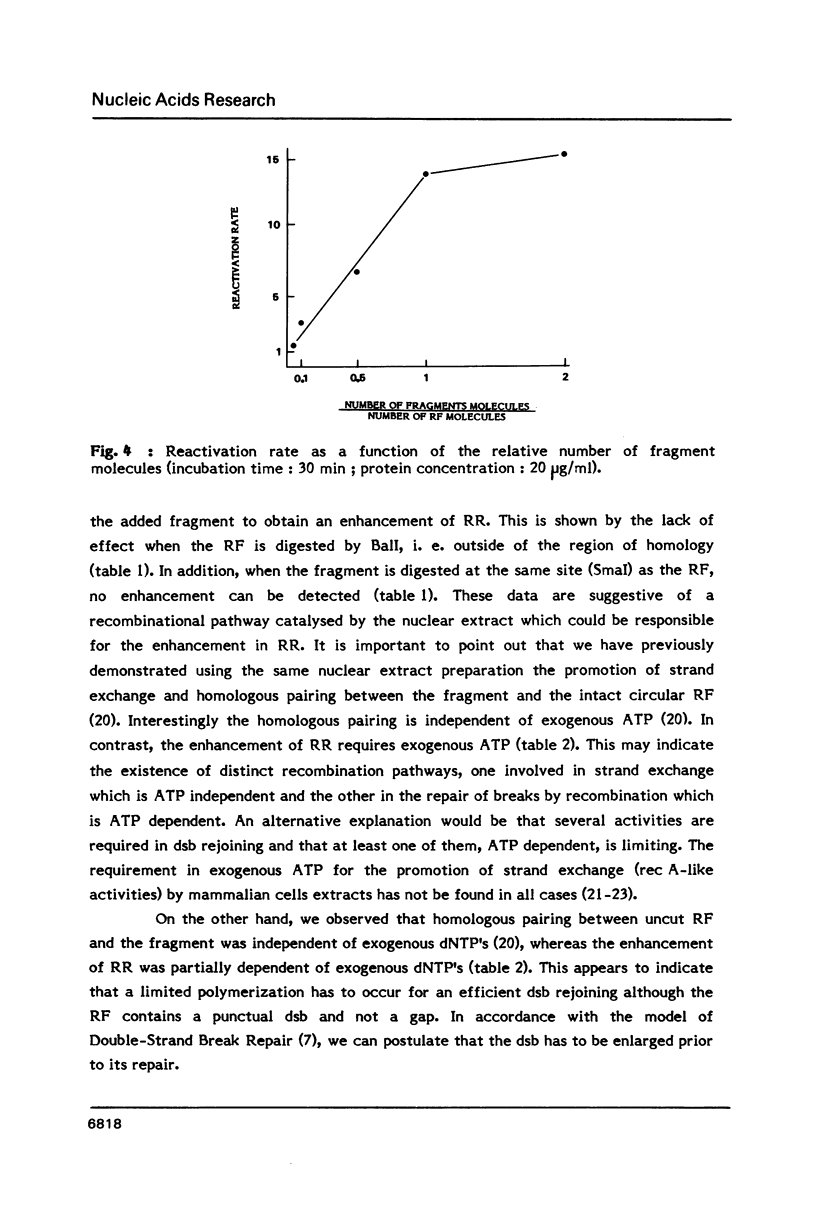
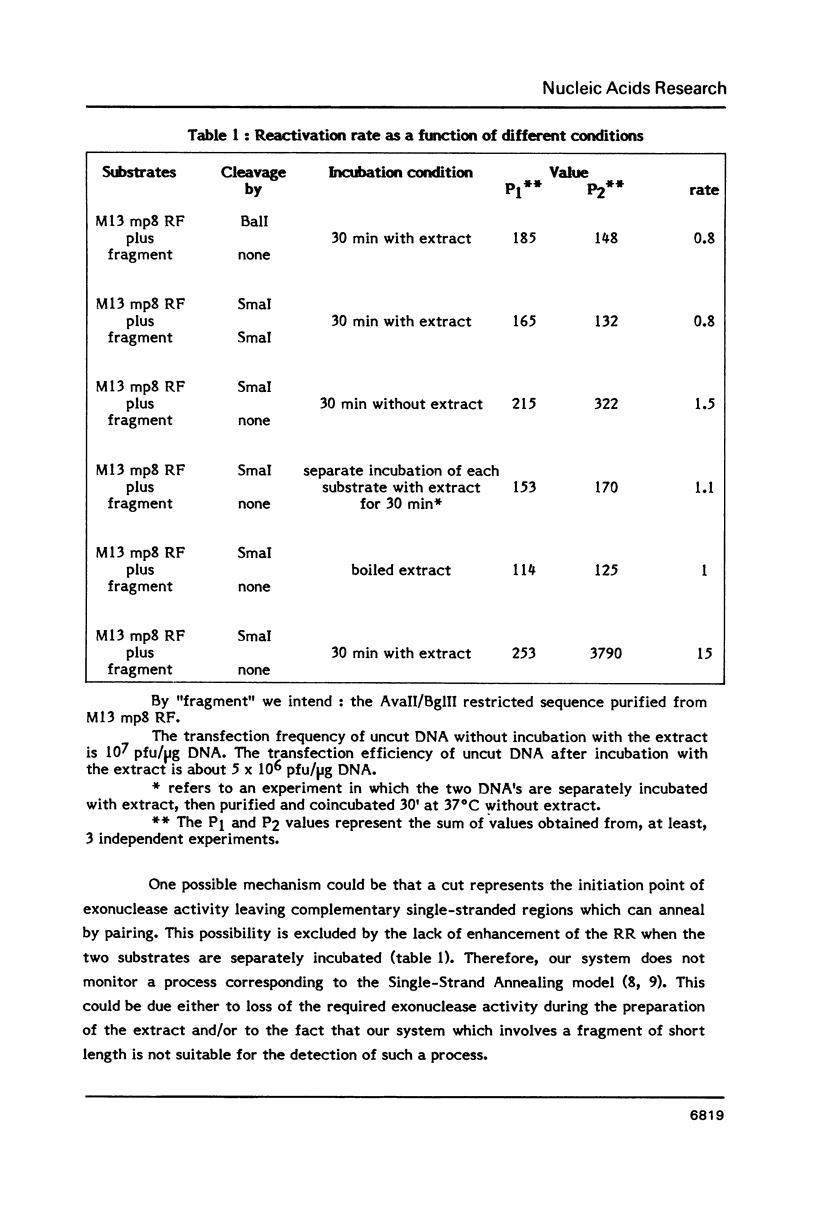
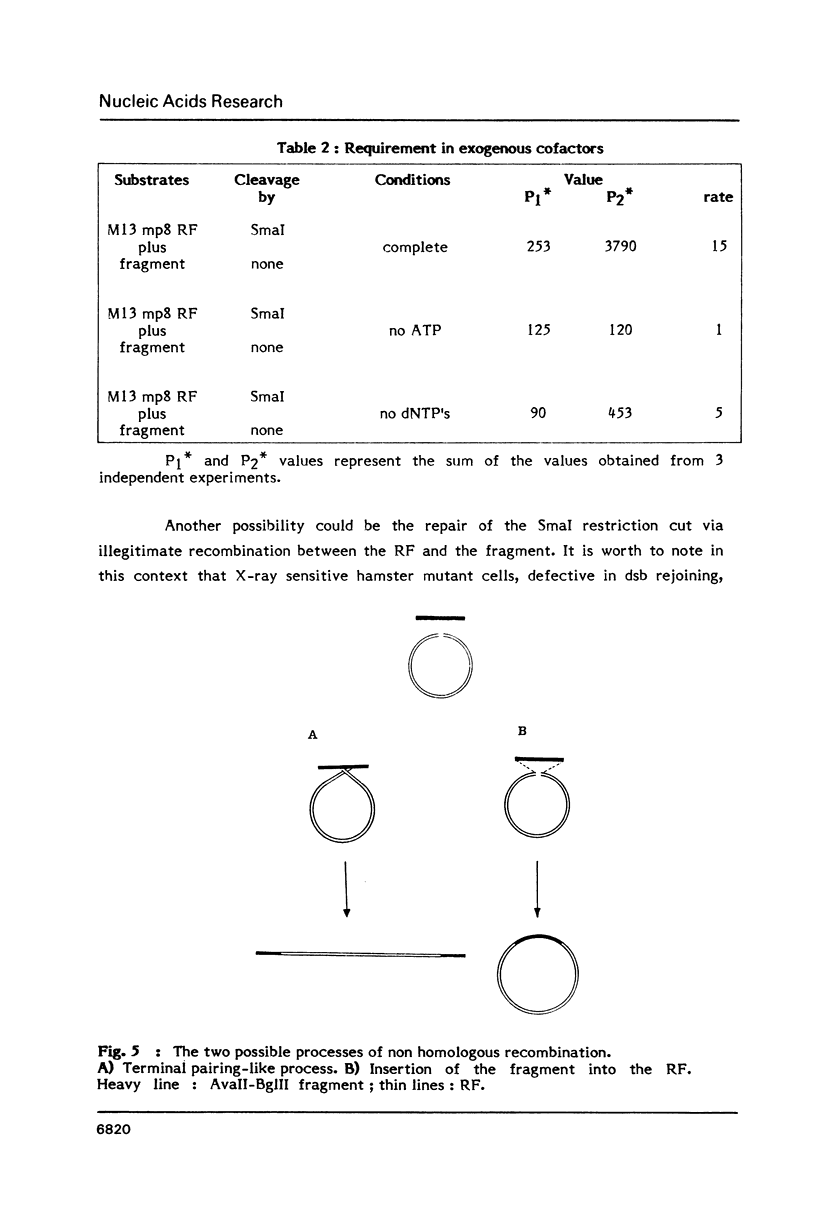
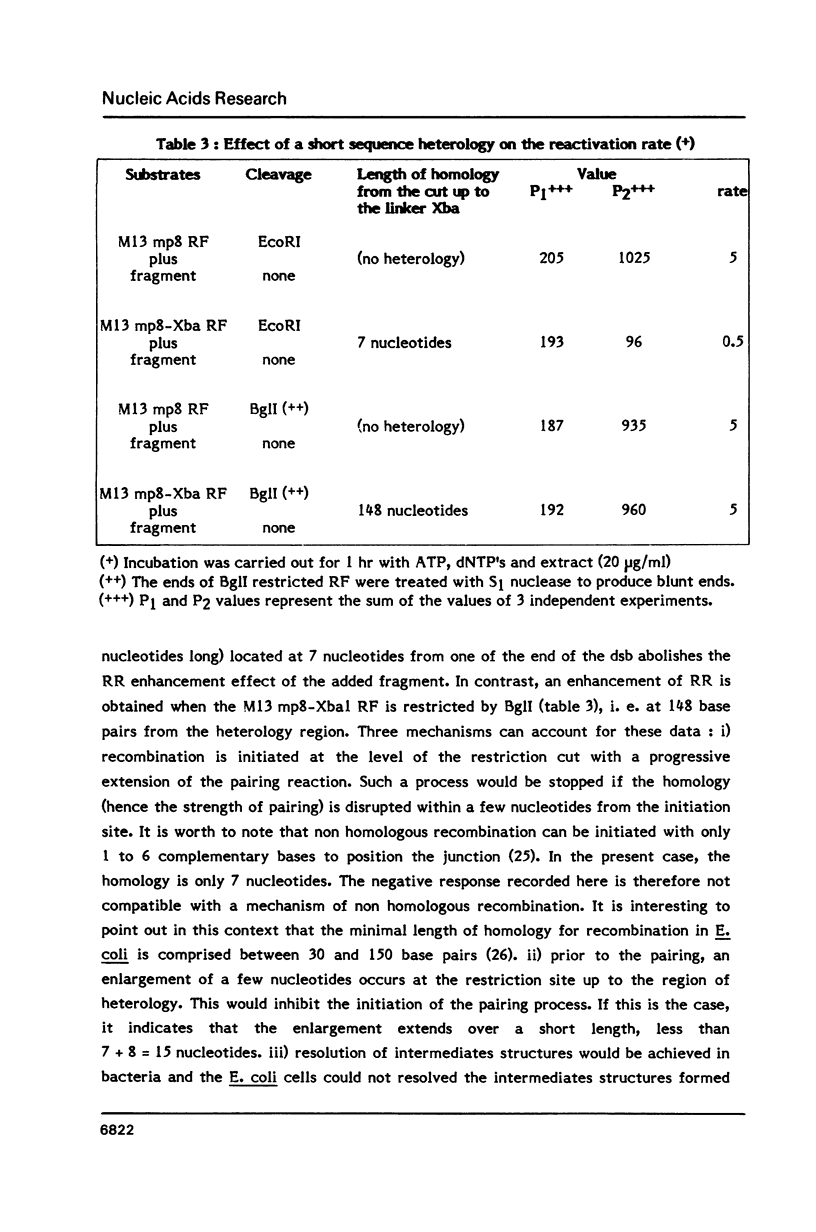
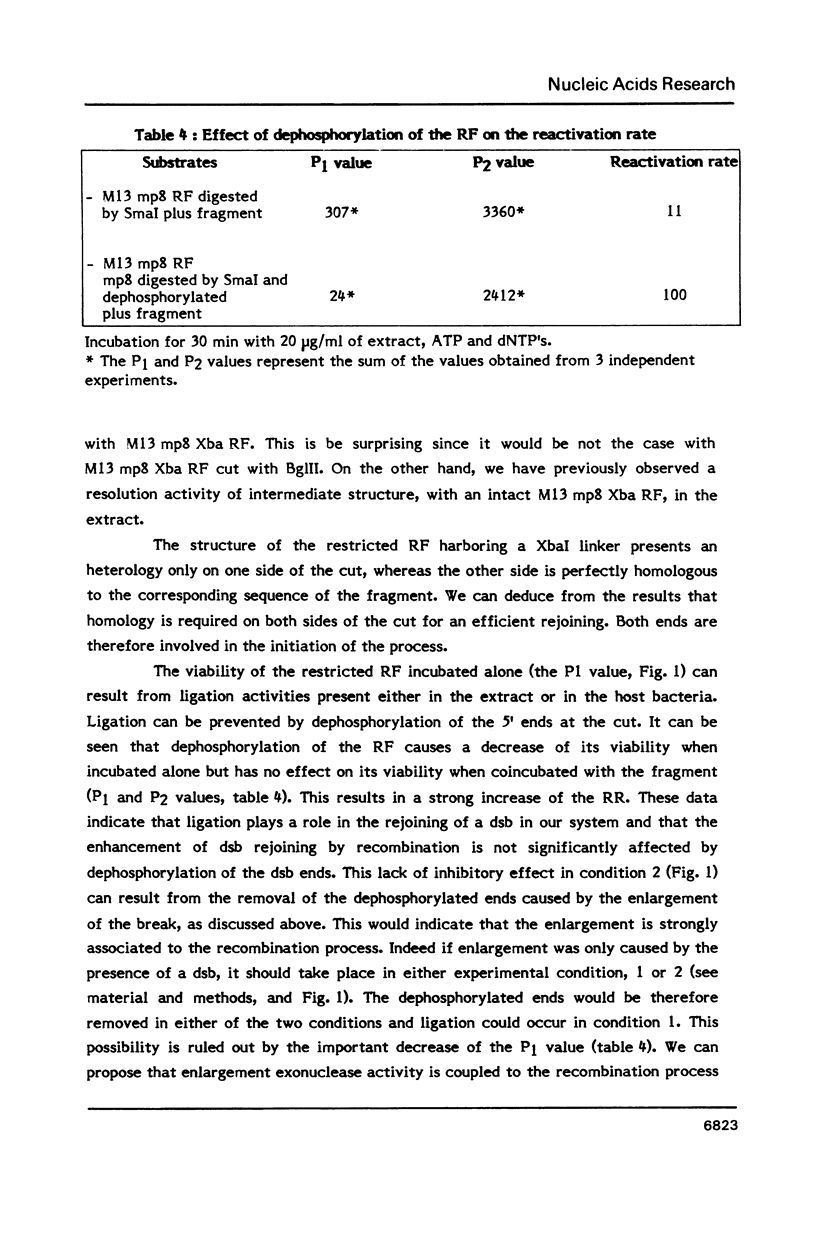
Parameters of DNA double strand break (dsb) repair catalysed by human nuclear extract were analysed using, as substrate, the replicative form (RF) of M13 mp8 in which a single double strand break (dsb) was introduced by restriction. After incubation with the extract, the dsb repair was estimated by the ability of the incubated RF to produce plaques following transfection into JM 109 (Rec A-) bacteria. The possibility of recombination with a purified fragment from M13 mp8 RF enhances up to 20 times the plaquing ability of the RF. The repair by recombination occurs under several conditions: i) the break in the RF must be located in the region of homology with the fragment. ii) the fragment has to be intact in the region corresponding to the break in the RF. iii) a minimal length of homology between the region surrounding the dsb in the RF, and the fragment is required. The in vitro reaction is ATP dependent and dNTP's partially dependent. Dephosphorylation of the free ends in the RF decreases the repair by ligation but is without effect on the recombination.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. A., Smigocki A. C., Camerini-Otero R. D. Double-strand gap repair results in homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1762–1766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Smigocki A. C., Camerini-Otero R. D. Effect of insertions, deletions, and double-strand breaks on homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):684–691. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. A., Thacker J. Gene recombination in X-ray-sensitive hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1409–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Tabata S., Bouchard R. A., Piñon R., Stern H. General recombination mechanisms in extracts of meiotic cells. Chromosoma. 1985;93(2):140–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00293161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne K., Ljungquist S. A DNA-recombinogenic activity in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3057–3068. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucherlapati R. S., Eves E. M., Song K. Y., Morse B. S., Smithies O. Homologous recombination between plasmids in mammalian cells can be enhanced by treatment of input DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3153–3157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K. M., Sternberg N. L. Extrachromosomal recombination in mammalian cells as studied with single- and double-stranded DNA substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):129–140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez B., Rousset S., Coppey J. Homologous recombination intermediates between two duplex DNA catalysed by human cell extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5643–5655. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. D., Song K. Y., Chekuri L., Wallace L., Kucherlapati R. S. Homologous recombination in a Chinese hamster X-ray-sensitive mutant. Mutat Res. 1986 Apr;160(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Martin P. The repair of double-strand breaks in the nuclear DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its genetic control. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jan 16;143(2):119–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00266917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick M. A., Moore P. D. Molecular recombination and the repair of DNA double-strand breaks in CHO cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3145–3160. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter M. A., Cleaver J. E., Tobias C. A. High-LET radiations induce a large proportion of non-rejoining DNA breaks. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):653–655. doi: 10.1038/266653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Berg P. Homologous recombination between defective neo genes in mouse 3T6 cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:171–181. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song K. Y., Chekuri L., Rauth S., Ehrlich S., Kucherlapati R. Effect of double-strand breaks on homologous recombination in mammalian cells and extracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3331–3336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W. Roles of double-strand breaks in generalized genetic recombination. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:169–194. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Effect of deletion and insertion on double-strand-break repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1300–1303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt V. M., Ingles C. J., Urdea M. S., Rutter W. J. Homology requirements for recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4768–4772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibezahn K. F., Coquerelle T. Radiation induced DNA double strand breaks are rejoined by ligation and recombination processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3139–3150. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibezahn K. F., Lohrer H., Herrlich P. Double-strand break repair and G2 block in Chinese hamster ovary cells and their radiosensitive mutants. Mutat Res. 1985 May;145(3):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibezahn K. F., Sexauer C., Coquerelle T. Negative pion irradiation of mammalian cells. III. A comparative analysis of DNA strand breakage, repair and cell survival after exposure to pi-mesons and X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1980 Oct;38(4):365–371. doi: 10.1080/09553008014551741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




