Abstract
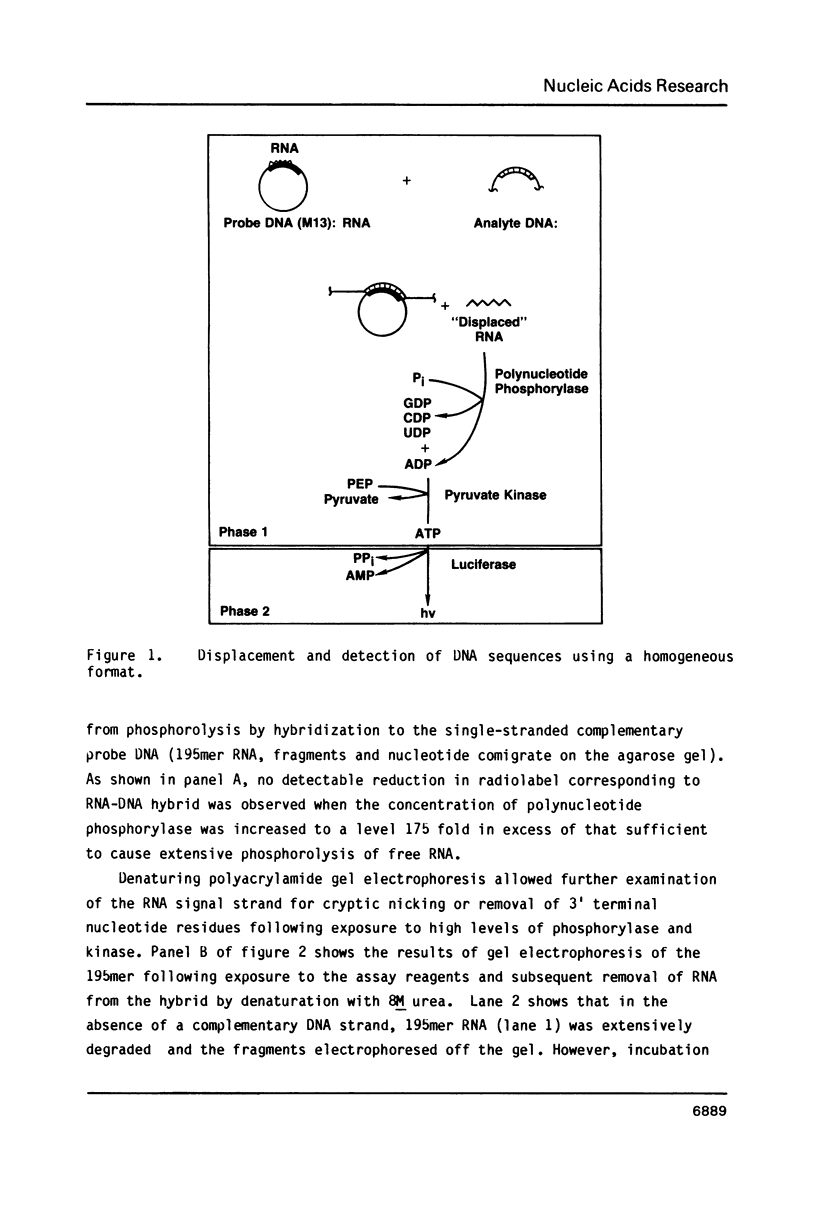
A homogeneous nucleic acid hybridization assay which is conducted in solution and requires no separation steps is described. The assay is based on the concept of strand displacement. In the strand displacement assay, an RNA "signal strand" is hybridized within a larger DNA strand termed the "probe strand", which is, in turn, complementary to the target nucleic acid of interest. Hybridization of the target nucleic acid with the probe strand ultimately results in displacement of the RNA signal strand. Strand displacement, therefore, causes conversion of the RNA from double to single-stranded form. The single-strand specificity of polynucleotide phosphorylase (EC 2.7.7.8) allows discrimination between double-helical and single-stranded forms of the RNA signal strand. As displacement proceeds, free RNA signal strands are preferentially phosphorolyzed to component nucleoside diphosphates, including adenosine diphosphate. The latter nucleotide is converted to ATP by pyruvate kinase(EC 2.7.1.40). Luciferase catalyzed bioluminescence is employed to measure the ATP generated as a result of strand displacement.
Full text
PDF







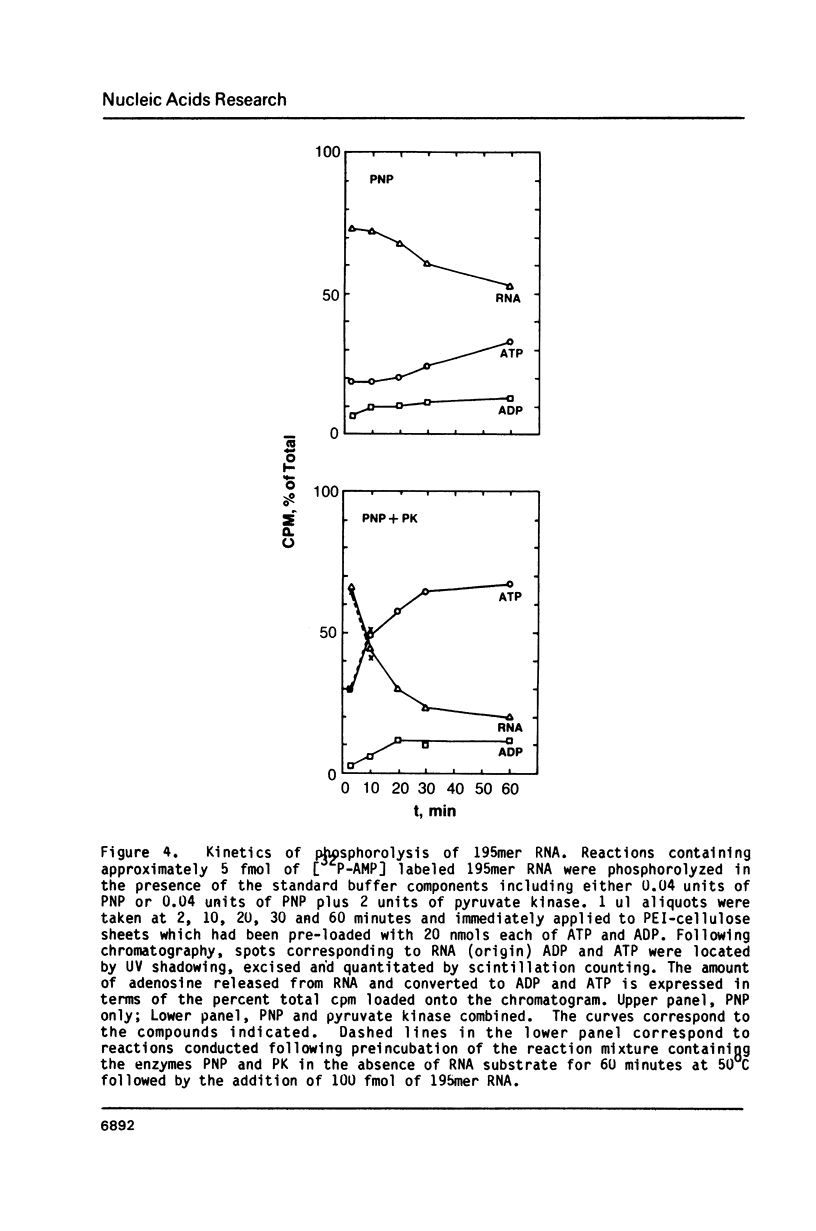
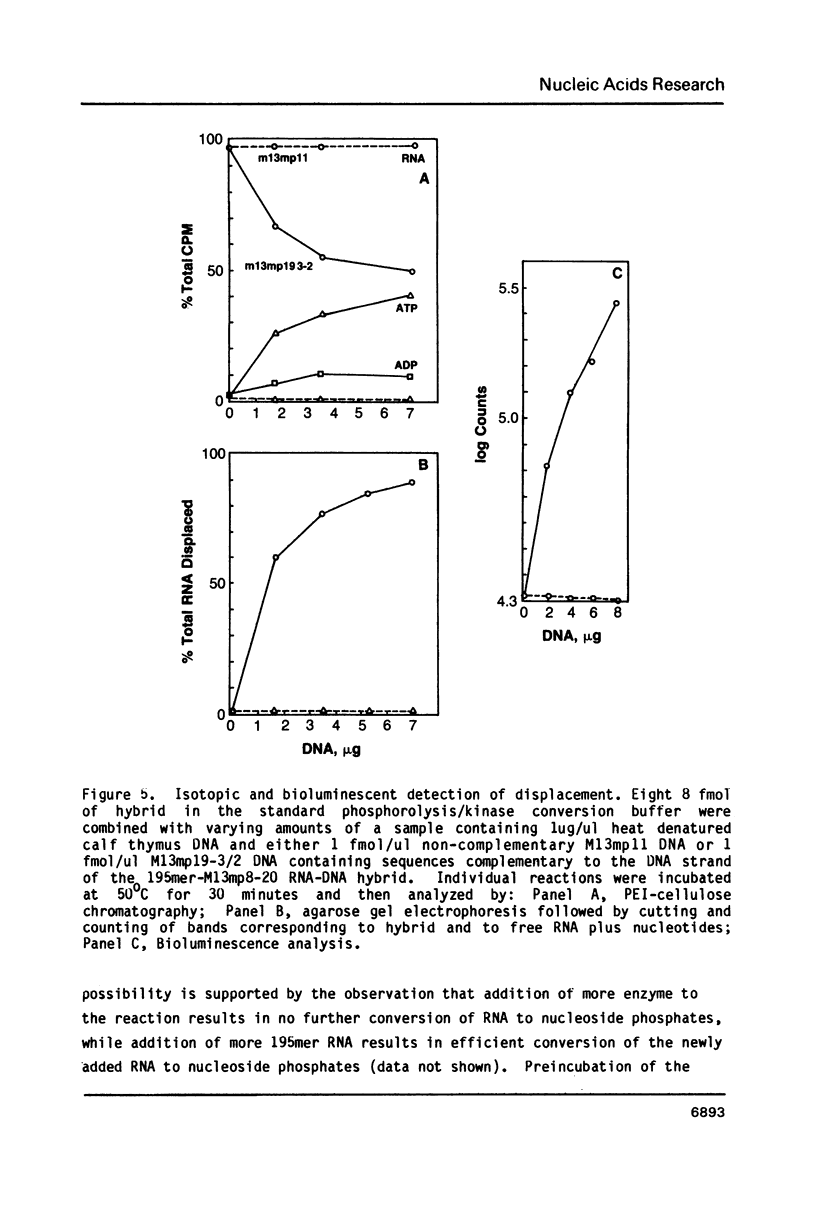




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambinder R. F., Charache P., Staal S., Wright P., Forman M., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. The vector homology problem in diagnostic nucleic acid hybridization of clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):16–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.16-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambinder R. F., Wingard J. R., Burns W. H., Hayward S. D., Saral R., Perry H. R., Santos G. W., Hayward G. S. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in mouthwashes by hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):353–356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.353-356.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann H. Immobilization of denatured DNA to macroporous supports: II. Steric and kinetic parameters of heterogeneous hybridization reactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7181–7196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. T., Fleming K. A., McGee J. O. Detection of sub-picogram quantities of specific DNA sequences on blot hybridization with biotinylated probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8083–8091. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M. S., Collins M., Fritsch E. F., Williams J. I., Diamond S. E., Brewen J. G. Strand displacement applied to assays with nucleic acid probes. Clin Chem. 1986 Sep;32(9):1631–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorus F., Schram E. Applications of bio- and chemiluminescence in the clinical laboratory. Clin Chem. 1979 Apr;25(4):512–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H. Amplification by enzymatic cycling. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Nov 20;32(3):135–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00227440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQUATE J. T., UTTER M. F. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of the pyruvic kinase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):2151–2157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molden D. P., Nakamura R. M., Suzuki H., Greer S., Pergolizzi R. G., Brakel C. L. Comparison of radio-labeled DNA probe with a nonisotopic probe for assay of serum hepatitis B virus DNA. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1985;3(4):174–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki M., Palva A., Virtanen M., Laaksonen M., Söderlund H. Sandwich hybridization as a convenient method for the detection of nucleic acids in crude samples. Gene. 1983 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saemundsen A. K., Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Sullivan J. L., Synnerholm A. C., Hanto D., Simmons R., Anvret M., Collins R., Klein G. Documentation of Epstein-Barr virus infection in immunodeficient patients with life-threatening lymphoproliferative diseases by Epstein-Barr virus complementary RNA/DNA and viral DNA/DNA hybridization. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4237–4242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto J., Hadchouel M., Hery C., Yvart J., Tiollais P., Brechot C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum by a simple spot hybridization technique: comparison with results for other viral markers. Hepatology. 1983 May-Jun;3(3):279–284. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Rua J. A., Spector D. H., McMillan R. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in clinical specimens by DNA-DNA hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):121–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Laaksonen M., Söderlund H. Fast quantification of nucleic acid hybrids by affinity-based hybrid collection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):5037–5048. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.5037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary C. P., McMahon F. J., Barbone F. P., Diamond S. E. Nonisotopic detection methods for strand displacement assays of nucleic acids. Clin Chem. 1986 Sep;32(9):1696–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





