Abstract
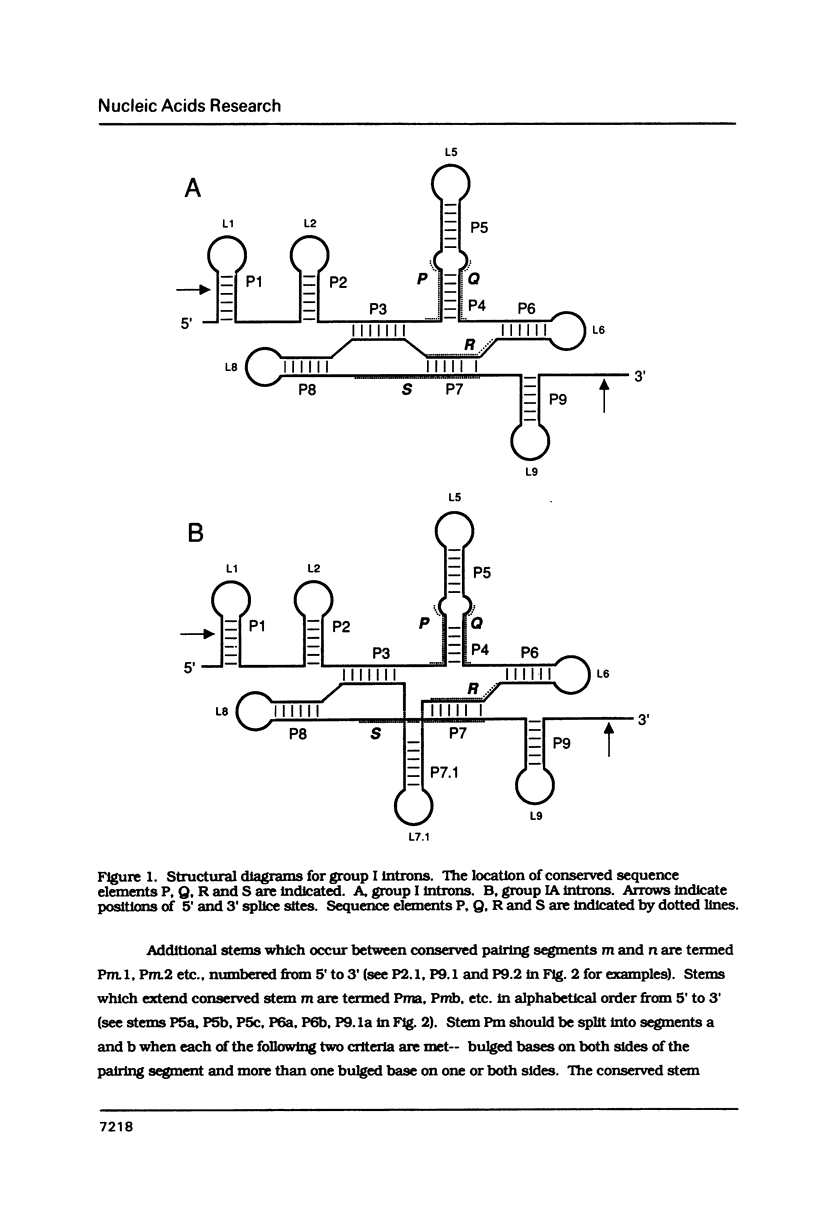
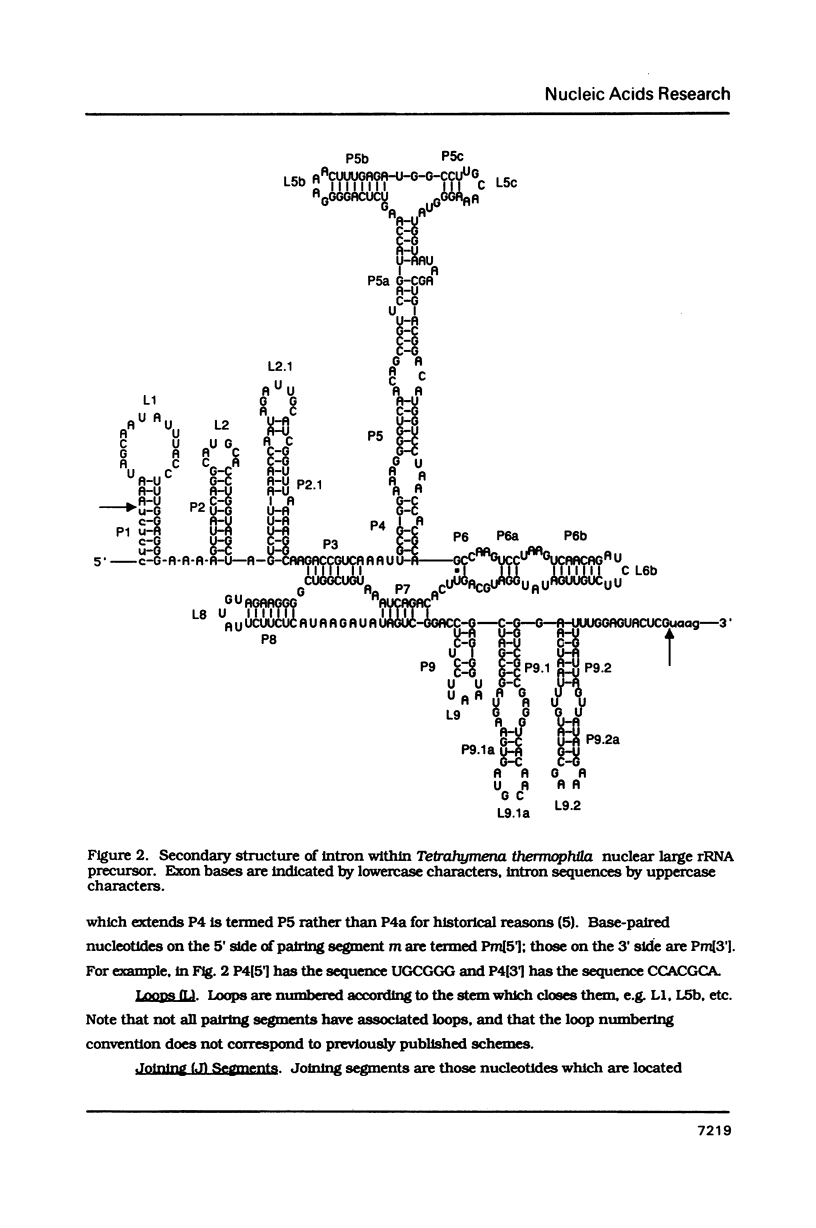
Conventions for nomenclature of structural elements and a standard secondary structure representation for group I introns have been established by workers in the field. These conventions are designed to facilitate effective communication of information concerning the structure and function of these self-splicing introns.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Irvine K. D., Kaneko K. J., Kerker B. J., Oettgen A. B., Tierney W. M., Williamson C. L., Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. Role of conserved sequence elements 9L and 2 in self-splicing of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA precursor. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Tanner N. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Weir B. R., Zuker M., Perlman P. S. Secondary structure of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA intervening sequence: structural homology with fungal mitochondrial intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The chemistry of self-splicing RNA and RNA enzymes. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1532–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.2438771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maley G. F., West D. K., Belfort M., Maley F. Characterization of the intron in the phage T4 thymidylate synthase gene and evidence for its self-excision from the primary transcript. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Salle H., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Critical sequences within mitochondrial introns: pleiotropic mRNA maturase and cis-dominant signals of the box intron controlling reductase and oxidase. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Rahire M., Michel F. The chloroplast ribosomal intron of Chlamydomonas reinhardii codes for a polypeptide related to mitochondrial maturases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):975–984. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Holl J., Schweyen R. J., Rödel G., Kaudewitz F. Processing of yeast mitochondrial RNA: involvement of intramolecular hybrids in splicing of cob intron 4 RNA by mutation and reversion. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


