Abstract
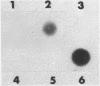
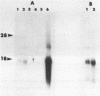
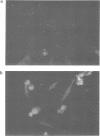
Lytic infection with herpes simplex virus results in transcriptional induction of a cellular gene encoding ubiquitin, causing increased accumulation of ubiquitin RNA and protein in the infected cell. This induction, which is dependent upon viral protein synthesis, does not occur in the HSV-1 mutant tsK which is defective in the gene encoding the viral protein ICP4. Transfected cells expressing the viral ICP4 protein exhibit higher levels of ubiquitin gene transcription than untransfected controls indicating that transcriptional induction can be mediated by the ICP4 protein alone.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann M., Falke D., Preuhs J., Schröder H. C., Pfeifer K., Müller W. E. Occurrence of novel small RNAs with concomitant inhibition of host cellular U small nuclear RNA synthesis in Vero cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2587–2594. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. T., Board P. G. The human ubiquitin gene family: structure of a gene and pseudogenes from the Ub B subfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):443–463. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):949–956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Activation of a Qa/Tla class I major histocompatibility antigen gene is a general feature of oncogenesis in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):756–760. doi: 10.1038/306756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Harland J. Three mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2: one lacking the genes US10, US11 and US12 and two in which Rs has been extended by 6 kb to 0.91 map units with loss of Us sequences between 0.94 and the Us/TRs junction. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charette M. F., Henderson G. W., Markovitz A. ATP hydrolysis-dependent protease activity of the lon (capR) protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4728–4732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. H., Goldberg A. L. The product of the lon (capR) gene in Escherichia coli is the ATP-dependent protease, protease La. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4931–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Activation of cellular promoters during herpes virus infection of biochemically transformed cells. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03880.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The products of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate early genes 1, 2 and 3 can activate HSV-1 gene expression in trans. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2507–2513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. The oncogenic potential of herpes simplex viruses: evidence for a 'hit-and-run' mechanism. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):21–24. doi: 10.1038/302021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Buchan A., Halliburton I. W., Watson D. H. Recombination and linkage between structural and regulatory genes of herpes simplex virus type 1: study of the functional organization of the genome. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):716–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.716-742.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis S. C. Inhibition of host protein synthesis and degradation of cellular mRNAs during infection by influenza and herpes simplex virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1644–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Brickell P. M., La Thangue N. B., Latchman D. S. Transcriptional induction of cellular gene expression during lytic infection with herpes simplex virus. Biosci Rep. 1986 Nov;6(11):945–951. doi: 10.1007/BF01114970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Preston C. M., Preston V. G., Latchman D. S. Cellular gene induction during herpes simplex virus infection can occur without viral protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9261–9270. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Sharp P. A. Transcription control by oncogenes. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaThangue N. B., Shriver K., Dawson C., Chan W. L. Herpes simplex virus infection causes the accumulation of a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S., Chan W. L., Leaver C. E., Patel R., Oliver P., La Thangue N. B. The human Mr 90,000 heat shock protein and the Escherichia coli Lon protein share an antigenic determinant. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1987;87(4):961–967. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(87)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Selective arrangement of ubiquitinated and D1 protein-containing nucleosomes within the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Simmons J. G., Hoyt E., D'Ercole A. J., Martin F., Van Wyk J. J. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding human ubiquitin reveals that ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7609–7613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab J. C., Orr A., La Thangue N. B. Cellular proteins expressed in herpes simplex virus transformed cells also accumulate on herpes simplex virus infection. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3223–3228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Transcripts regulated during normal embryonic development and oncogenic transformation share a repetitive element. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Requirement of protein synthesis for the degradation of host mRNA in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected wtih herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.619-627.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R., Chan W. L., Kemp L. M., La Thangue N. B., Latchman D. S. Isolation of cDNA clones derived from a cellular gene transcriptionally induced by herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5629–5640. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson R. H., Bacchetti S., Smiley J. R. Cells that constitutively express the herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP4 allow efficient activation of viral delayed-early genes in trans. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):414–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.414-421.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Jonak G. J., Galanti N., Floros J., Baserga R. Identification of an SV40 DNA sequence related to the reactivation of silent rRNA genes in human greater than mouse hybrid cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Latent herpes simplex virus and the nervous system,. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;70:31–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66101-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiborg O., Pedersen M. S., Wind A., Berglund L. E., Marcker K. A., Vuust J. The human ubiquitin multigene family: some genes contain multiple directly repeated ubiquitin coding sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):755–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]