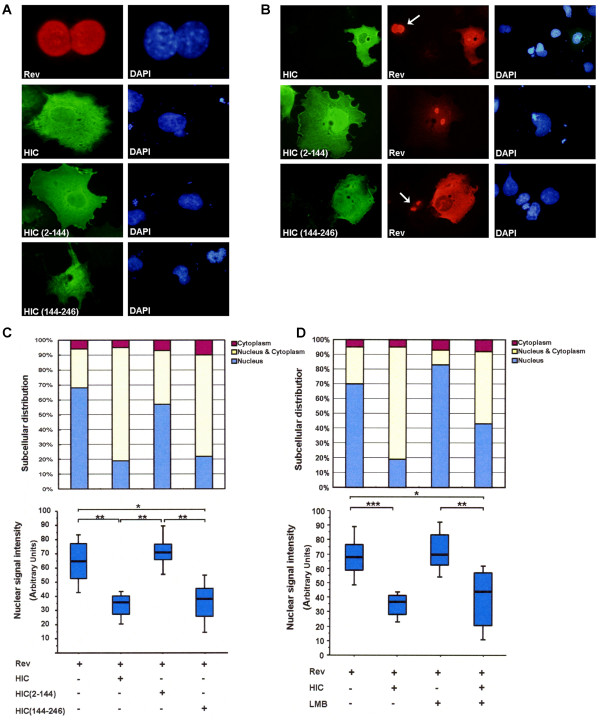
Figure 1.
HIC sequesters HIV-1 Rev in the cytoplasm by inhibiting its nuclear import in vivo. COS7 cells were transiently transfected with HA-Rev; pFLAG-HIC; pFLAG-HIC (2-144); pFLAG-HIC (144-246). Rev expression is shown in Red and HIC, HIC (2-144) and HIC (144-246) expression is shown in Green. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Blue). Representative images of transfected cells are shown. Arrows indicate cells expressing Rev only. (A) Localisation of Rev, HIC and its mutants in singly transfected COS7 cells. (B) Co-expression of HIV-1 Rev and HIC or HIC (144-246) results in the redistribution of Rev to the cytoplasm. (C) Quantitative analysis of Rev nuclear localization. Same conditions as described in B. Upper panel: quantitative analysis of Rev subcellular localisation. A minimum of 100 transfected cells was counted per well and results are expressed as a percentage of the total number of cells counted according to the classification: nucleus-dominant (blue), nucleus/cytoplasm-equivalent (yellow), or cytoplasm-dominant (red). Lower panel: quantitative analysis of Rev nuclear signal. Rev nuclear signal intensities were analyzed by Image J (NIH) from a minimum of 100 transfected cells and shown by box plots. Statistical significance analysis was performed with a two-tailed unpaired Student's t test *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (D) HIC retains Rev in the cytoplasm by inhibiting its nuclear import. COS7 cells were transfected with HA-Rev, and/or pFLAG-HIC and incubated with or without 20 nM Leptomycin B (LMB) for 3 hours. Upper panel: quantitative analysis of Rev subcellular localisation. Lower panel: quantitative analysis of Rev nuclear signal.