Abstract
Paragangliomas (extra-adrenal phaeochromocytomas) are tumours arising from extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue. The authors describe a case of a 54-year-old woman presenting with shortness of breath and chest pain. CT pulmonary angiogram demonstrated a mediastinal mass. Further history taking revealed spontaneous attacks of headaches and palpitations. Subsequent imaging and biochemical testing confirmed the presence of a rare posterior mediastinal paraganglioma.
The patient was prepared for surgery. A left thoracolaparotomy was performed and the mass was excised in its entirety. Postoperatively, 24-h urine collections showed normal normetanephrine and metanephrine levels. Since then, yearly catecholamine levels remain within the normal range.
Background
Tumours from extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue are referred to as extra-adrenal phaeochromocytomas or paragangliomas. We report an unusual case of a biochemically active paraganglioma in the posterior mediastinum of a 54-year-old woman, while highlighting the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges in such patients.
Case presentation
A 54-year-old woman presented with left lower chest pain and sudden onset breathlessness. She had no relevant past medical history and was not on any medication. Observations: pulse 94 bpm, blood pressure 108/62 mm Hg, O2 saturation 95% on air, respiratory rate 21/min and temperature 37°C. Her ECG was normal and a 12-h troponin level was negative.
Investigations
CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) excluded a pulmonary embolus but demonstrated a posterior mediastinal mass. Further history taking revealed spontaneous intermittent attacks of headaches and palpitations. CT imaging demonstrated a mass occupying the left retrocrural space (figure 1A and C) with no evidence of distant spread. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) confirmed the CT findings. A ioflupane-metaiodobenzylguanide (123I-MIBG) scan (figure 1B and D) was performed revealing peripheral enhancement of this cystic mass. Biochemical studies showed elevated levels of urine normetanephrine (30.2 µmol/24 h; normal range 0.4–3.4 µmol/24 h) and urine metanephrine (33.6 µmol/24 h; normal range 0.3–1.7 µmol/24 h) confirming the diagnosis of a functional paraganglioma.
Figure 1.
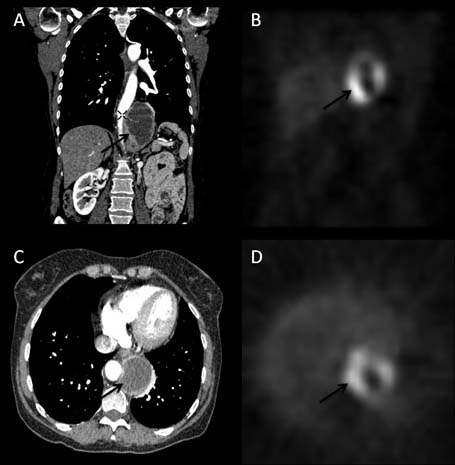
Coronal (A) and axial (C) CT images demonstrating a 65×65×95 mm partly solid partly cystic mass situated in the posterior mediastinum. The mass is predominantly occupying the left retrocrural space extending along the vertebral bodies of T10–L1 abutting the oesophagus, aorta and diaphragm. 123I-MIBG-SPECT (ioflupane-metaiodobenzylguanidine-single photon emission CT) images at a position that correlates with the mass demonstrated on CT (B) and (D). The peripheral isotope uptake correlates to the solid elements of the tumour, whereas the central lack of uptake correlates to the cystic elements.
Treatment
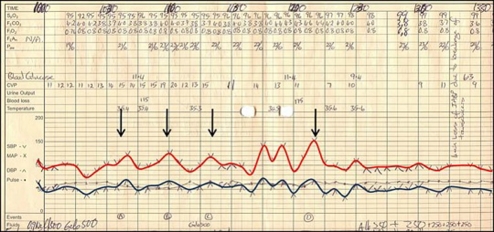
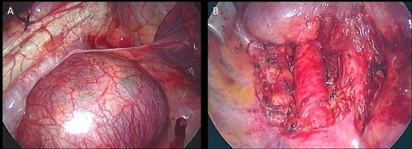
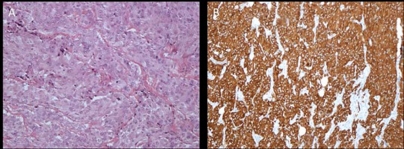
Over a 2-week period the patient was prepared for surgery initially with α-adrenoceptor blockade (phenoxybenzamine 30 mg once daily). One week later β-adrenoceptor blockade was also introduced (propanolol 160 mg once daily). A left thoracolaparotomy was performed with transitory increases in the patient's blood pressure reported during tumour mobilisation (figure 2). The mass (65×65×95 mm) was excised in its entirety (figure 3) and histology (figure 4) confirmed a paraganglioma.
Figure 2.
Anaesthetic record sheet demonstrating transitory changes in the patient's systolic (red line) and diastolic (blue line) blood pressure when the tumour was mobilised (arrows). Following tumour resection (final arrow), blood pressure stabilises dramatically.
Figure 3.
Intraoperative photograph taken through a left thoracolaparotomy before (A) and after (B) resection of the paraganglioma.
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemistry (×10 magnification) showing strong staining of the tumour cells with both H&E (A) and chromogranin (B). Sections reveal a tumour composed of a uniform population of cells with copious quantities of oeosinophilic cytoplasm and variably both oval and spindle shaped consistent with the diagnosis of a paraganglioma.
Outcome and follow-up
Adrenoceptor blockade was stopped postoperatively. Persisting hypotension (80/40 mm Hg) required aggressive fluid resuscitation. Twenty-four-hour urine collection on postoperative day 10 showed normal normetanephrine (3.4 µmol/24 h) and metanephrine levels (1.5 µmol/24 h). Yearly catecholamine levels remain within normal range.
Discussion
Approximately 15–20% of phaeochromocytomas arise from extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue. Paragangliomas of the mediastinum represent less than 0.3% of mediastinal tumours and less than 2% of all paragangliomas.1
Clinical presentation of a paraganglioma can vary greatly. If the classic triad (headaches, palpitations and sweating) is present in the context of hypertension, the specificity is reported to be more than 90%.2 Hypertension is often paroxysmal in nature and blood pressure may be completely normal.3
All patients with a suspected paraganglioma should undergo biochemical testing. Measurements of plasma and urinary fractionated metanephrines seem to be the most sensitive investigations for diagnosis and are the most suitable for reliable exclusion of such tumours.4 Characterisation of a mass detected by CT or MRI as a paraganglioma can be achieved by 123I-MIBG scanning with a specificity between 95% and 100%.5
Surgical removal of paragangliomas is the treatment of choice. The aim of medical pretreatment is to prevent catecholamine-induced complications. Several regimens using α-adrenoceptor blockade exist; phenoxybenzamine is often preferred because it blocks α-adrenoceptors non-competitively. This type of blockade may offer advantages over competitive blockade with drugs such as doxazosin, which may be displaced by excessive catecholamine increase during surgery. However, doxazosin is sometimes preferred due to a theoretical increased risk of postoperative hypotension due to extended, non-competitive, α-adrenergic blockade with phenoxybenzamine.6 β-blockade should never be started before α-blockade since the loss of β-adrenoceptor mediated vasodilatation leaves α-adrenoceptor stimulation unopposed, which could result in a hypertensive crisis.
The long-term prognosis of a single solitary paraganglioma is excellent with such tumours usually treated successfully with modest surgical risk.7 Genetic testing should be considered in all patients with paragangliomas; up to 25% of these tumours are hereditary.8 Our patient tested negative for all mutations. When this is the case, only biochemical testing for monitoring possible recurrence is needed. Paragangliomas show high recurrence rates and for this reason such patients should be followed up indefinitely.9
Paragangliomas pose several challenges for the unaware practitioner. Their often non-specific symptoms, extra-adrenal nature and rarity may lead to significant diagnostic delay and inappropriate, high-risk investigations. For the effective diagnosis and management of paragangliomas a multidisciplinary team of specialists is key in order to avoid common and often dangerous pitfalls.
Learning points.
-
▶
The non-specific symptoms, extra-adrenal nature and rarity of paragangliomas may lead to significant diagnostic delay and inappropriate, high-risk investigations (eg, biopsy).
-
▶
For the effective diagnosis and management of paragangliomas a multidisciplinary team of specialists is essential.
-
▶
Patients with paragangliomas require careful preoperative planning, genetic testing and life-long follow-up.
-
▶
The possibility of a functional paraganglioma should always be considered when investigating mediastinal masses.
Footnotes
Competing interests None.
Patient consent Obtained.
References
- 1.Ayadi-Kaddour A, Braham E, Ismail O, et al. Posterior mediastinal paragangliomas: a report of three patients with peculiar tumours. Respirology 2009;14:459–61 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Plouin PF, Degoulet P, Tugaye A, et al. Screening for phaeochromocytoma in which hypertensive patients? A semiology study of 2585 patients, including 11 with phaeochromocytoma (authors transl). Nouv Press Med 1981;10:869–72 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mantero F, Terzolo M, Arnaldi G, et al. A survey on adrenal incidentaloma in Italy. Study Group on Adrenal Tumors of the Italian Society of Endocrinology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:637–44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eisenhofer G, Lenders JW, Linehan WM, et al. Plasma normetanephrine and metanephrine for detecting pheochromocytoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1872–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pacak K, Linehan WM, Eisenhofer G, et al. Recent advances in genetics, diagnosis, localization, and treatment of pheochromocytoma. Ann Intern Med 2001;134:315–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Prys-Roberts C. Phaeochromocytoma–recent progress in its management. Br J Anaesth 2000;85:44–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brown ML, Zayas GE, Abel MD, et al. Mediastinal paragangliomas: the mayo clinic experience. Ann Thorac Surg 2008;86:946–51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Neumann HP, Bausch B, McWhinney SR, et al. Germ-line mutations in nonsyndromic pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1459–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lenders JW, Eisenhofer G, Mannelli M, et al. Phaeochromocytoma. Lancet 2005;366:665–75 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]