Abstract
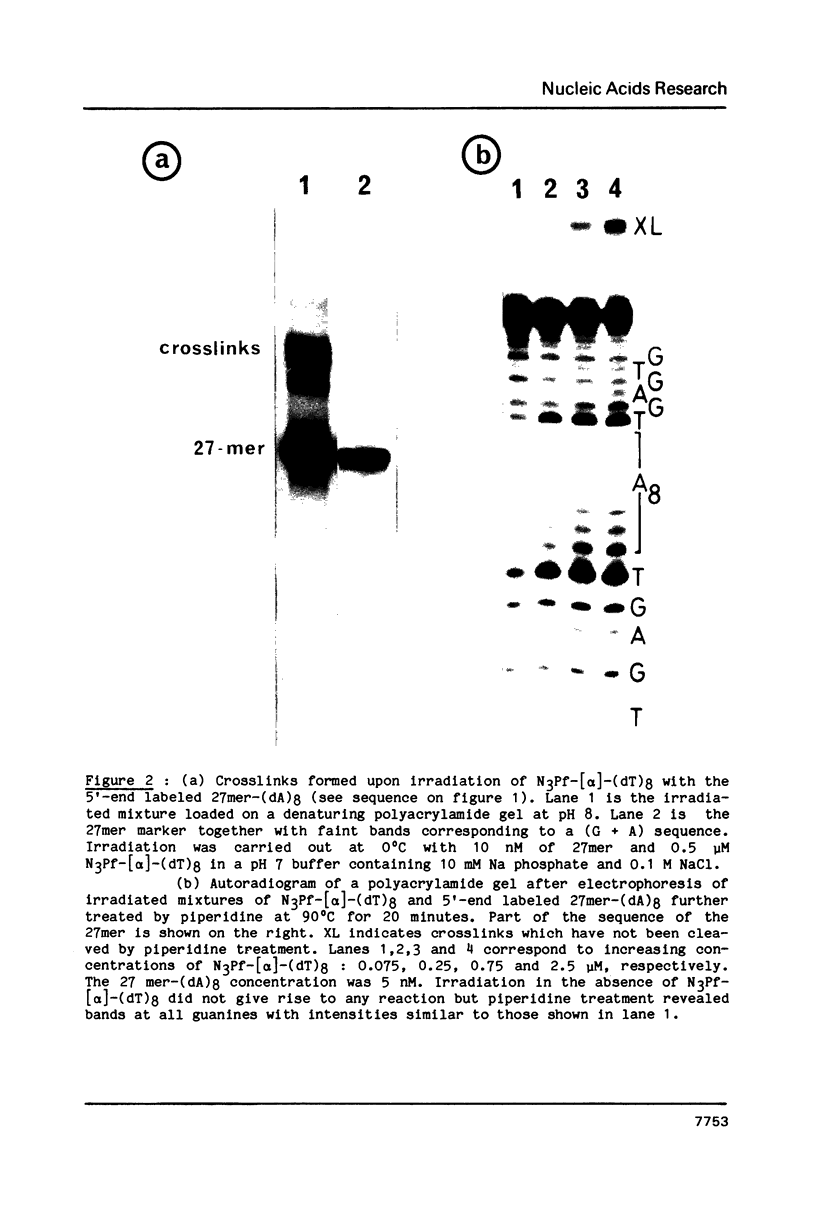
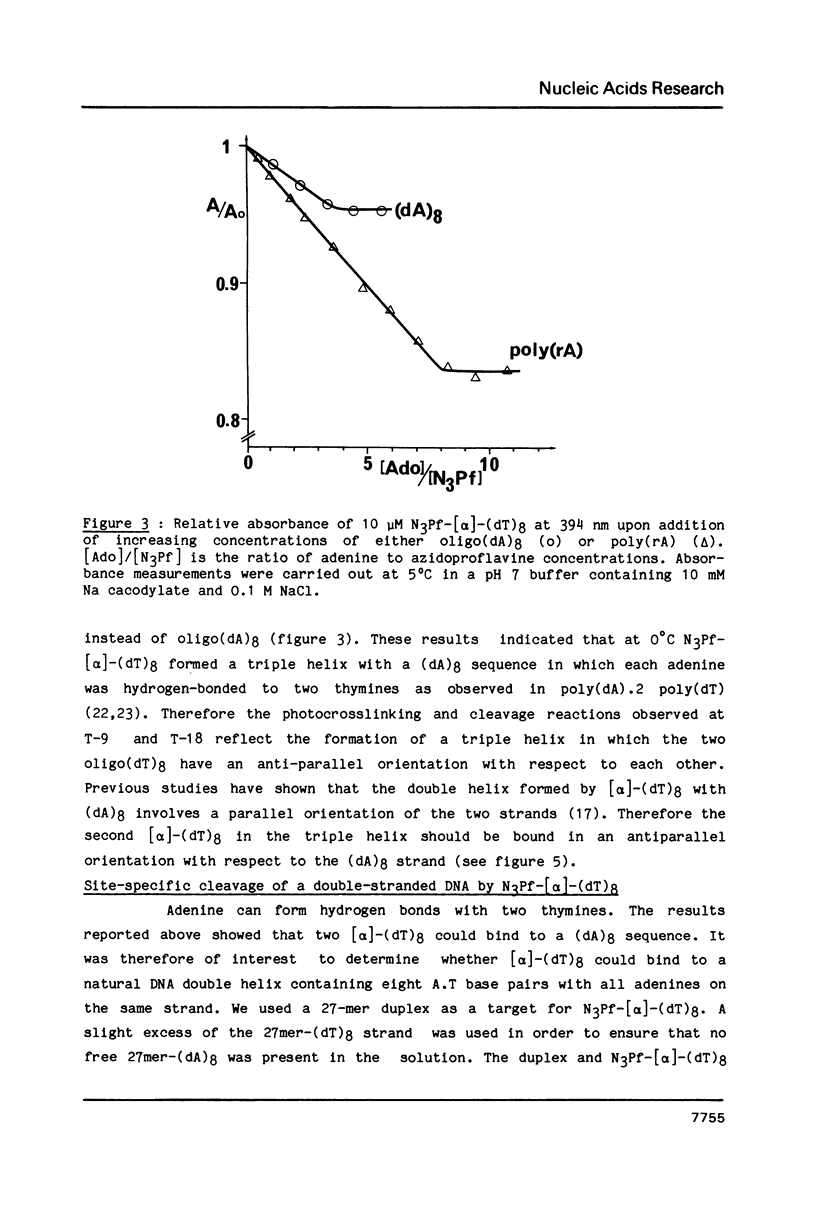
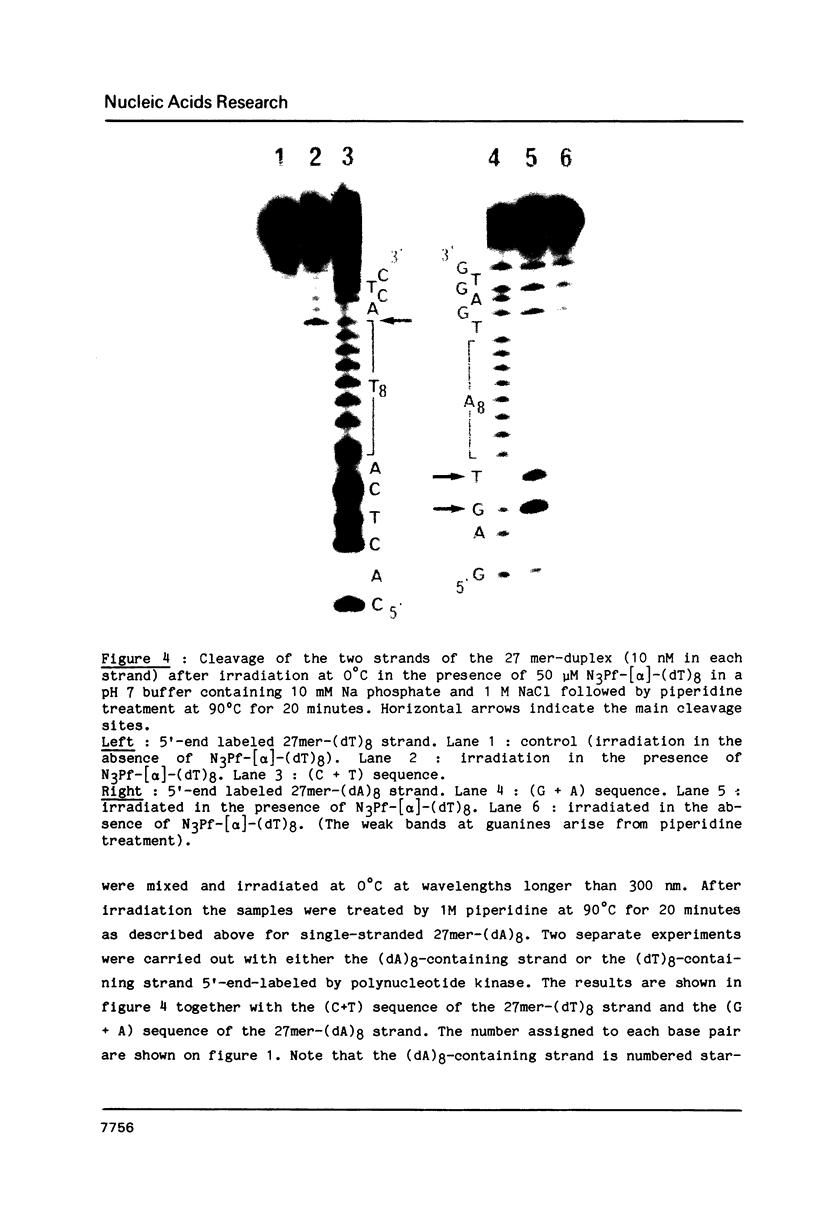
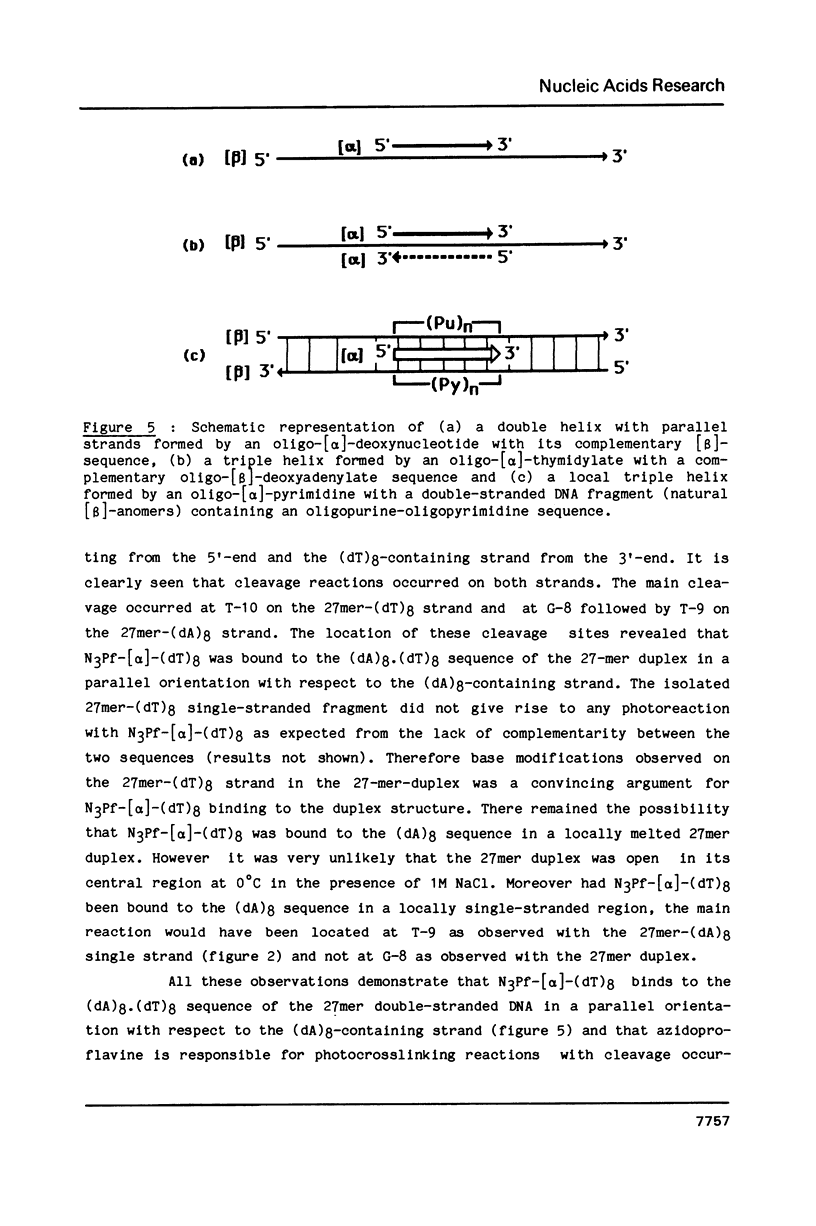
A 3-azidoproflavine derivative was covalently linked to the 5'-end of an octathymidylate synthesized with the [alpha]-anomers of the nucleoside. Two target nucleic acids were used for this substituted oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate: a 27-mer single-stranded DNA fragment containing an octadeoxyadenylate sequence and a 27-mer duplex containing eight contiguous A.T base pairs with all adenines on the same strand. Upon visible light irradiation the octa-[alpha]-thymidylate was photocrosslinked to the single-stranded 27-mer. Chain breaks were induced at the crosslinked sites upon piperidine treatment. From the location of the cleavage sites on the 27-mer sequence it was concluded that a triple helix was formed by the azidoproflavine-substituted oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate with its complementary oligodeoxyadenylate sequence. When the 27-mer duplex was used as a substrate cleavage sites were observed on both strands after piperidine treatment of the irradiated sample. They were located at well defined positions which indicated that the octathymidylate was bound to the (dA)8.(dT)8 sequence in parallel orientation with respect to the (dA)8-containing strand. Specific binding of the [alpha]-octathymidylate involved local triple strand formation with the duplex (dA)8.(dT)8 sequence. This result shows that it is possible to synthesize sequence-specific molecules which specifically bind oligopurine-oligopyrimidine sequences in double-stranded DNA via recognition of the major groove hydrogen bonding sites of the purines.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asseline U., Delarue M., Lancelot G., Toulmé F., Thuong N. T., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Nucleic acid-binding molecules with high affinity and base sequence specificity: intercalating agents covalently linked to oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3297–3301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asseline U., Nguyen T. T., Hélène C. Nouvelles substances à forte affinité spécifique pour des séquences d'acides nucléiques: oligodésoxynucléotides liés de façon covalente à un agent intercalant. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1983;297(7):369–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asseline U., Toulme F., Thuong N. T., Delarue M., Montenay-Garestier T., Hélène C. Oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating dyes as base sequence-specific ligands. Influence of dye attachment site. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):795–800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Efstratiadis A. Sequence-dependent S1 nuclease hypersensitivity of a heteronomous DNA duplex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14771–14780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Pines O., Inouye M. The role of antisense RNA in gene regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:569–597. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna M. M., Meares C. F. Synthesis of a cleavable dinucleotide photoaffinity probe of ribonucleic acid polymerase: application to trinucleotide labeling of an Escherichia coli transcription complex. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3546–3551. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland G. R., Robinson P. P. The number and size of axons at the apex of the cat's canine tooth. Anat Rec. 1983 Feb;205(2):215–222. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092050212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Lancelot G. Interactions between functional groups in protein-nucleic acid associations. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;39(1):1–68. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison T., Takasugi M., Toulmé J. J., Asseline U., Lancelot G., Maurizot J. C., Toulmé F., Thuong N. T. Oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents: a new class of gene regulatory substances. Biochimie. 1985 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):777–783. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knorre D. G., Vlassov V. V. Complementary-addressed (sequence-specific) modification of nucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:291–320. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelot G., Asseline U., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Proton and phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance studies of an oligothymidylate covalently linked to an acridine derivative and of its binding to complementary sequences. Biochemistry. 1985 May 7;24(10):2521–2529. doi: 10.1021/bi00331a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelot G., Thuong N. T. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of complex formation between the oligonucleotide d(TATC) covalently linked to an acridine derivative and its complementary sequence d(GATA). Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5357–5363. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Johnson D. A., Morgan A. R. Complexes formed by (pyrimidine)n . (purine)n DNAs on lowering the pH are three-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3073–3091. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan F., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Thenet S., Bertrand J. R., Paoletti J., Malvy C., Paoletti C. alpha-DNA II. Synthesis of unnatural alpha-anomeric oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing the four usual bases and study of their substrate activities for nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3421–3437. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Chassignol M., Takasugi M., Le Doan T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Double helices with parallel strands are formed by nuclease-resistant oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides and oligo-[alpha]-deoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent with complementary oligo-[beta]-deoxynucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):939–942. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Maling B. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):359–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Reddy M. P., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Antiviral effect of an oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate) complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2787–2791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séquin U. Nucleosides and nucleotides. Part 7. Four dithymidine monophosphates with different anomeric configurations, their synthesis and behaviour towards phosphodiesterases. Helv Chim Acta. 1974;57(1):68–81. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19740570108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuong N. T., Asseline U., Roig V., Takasugi M., Hélène C. Oligo(alpha-deoxynucleotide)s covalently linked to intercalating agents: differential binding to ribo- and deoxyribopolynucleotides and stability towards nuclease digestion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5129–5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Wähnert U. Nonintercalating DNA-binding ligands: specificity of the interaction and their use as tools in biophysical, biochemical and biological investigations of the genetic material. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;47(1):31–112. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]