Abstract
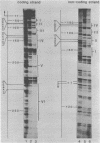
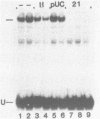
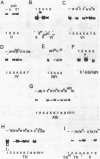
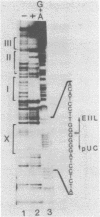
Multiple cellular transcription factors have been shown to interact with the upstream region of the adenovirus-2 EIIa-late promoter. One of these factors recognises each of the three CCAAT motifs present in the EIIL promoter at positions -72, -135 and -229, as well as the CCAAT elements in the rat albumin and herpes virus thymidine kinase promoters. A mutation known to reduce thymidine kinase promoter activity in vivo and in vitro abolishes binding of the factor, termed CCAAT recognition factor (CRF), which appears to be distinct from previously identified CCAAT factors. In addition, another protein, termed upstream factor II (USFII), shares binding sites at position -110 in the EIIL promoter and in the c-fos enhancer adjacent to the serum regulatable element. The recognition site for USFII is also found in the c-fos promoter and in the adenovirus early region EIV and EIIa-early promoters. An Sp1 recognition site has also been identified at position -41, and the binding sites for Sp1, USFII and CRF are all required for efficient EIIa-late promoter function. Finally, an additional factor recognising the consensus GGGGGGNT has been detected.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G., SivaRaman L., Murthy S., Domer P., Thimmappaya B. In vivo identification of multiple promoter domains of adenovirus EIIA-late promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2045–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. A CCAAT box confers cell-type-specific regulation on the Xenopus hsp70 gene in oocytes. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90703-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeuf H., Zajchowski D. A., Tamura T., Hauss C., Kédinger C. Specific cellular proteins bind to critical promoter sequences of the adenovirus early EIIa promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):509–527. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet L. J., Babiss L. E., Young C. S., Mills D. R. Mutations in the adenovirus major late promoter: effects on viability and transcription during infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1091–1100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R. A., Osheroff W. P., Rossini M. Two functions encoded by adenovirus early region 1A are responsible for the activation and repression of the DNA-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):707–713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard J. M., Herbomel P., Ott M. O., Mottura-Rollier A., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Determinants of rat albumin promoter tissue specificity analyzed by an improved transient expression system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R., Brady J. N., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Binding of the Sp1 transcription factor by the human Harvey ras1 proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1410–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3012774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Sp1 binds to promoter sequences and activates herpes simplex virus 'immediate-early' gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):179–182. doi: 10.1038/317179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Chambon P. Sequence-specific activation of transcription by adenovirus EIa products is observed in HeLa cells but not in 293 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):201–208. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Subramanian S., Thimmappaya B. Identification of a factor in HeLa cells specific for an upstream transcriptional control sequence of an EIA-inducible adenovirus promoter and its relative abundance in infected and uninfected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5914–5918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]