Abstract
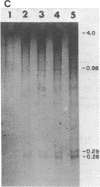
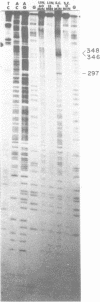
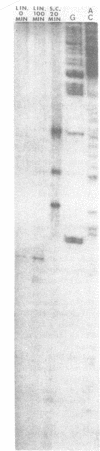
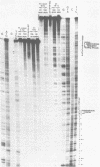
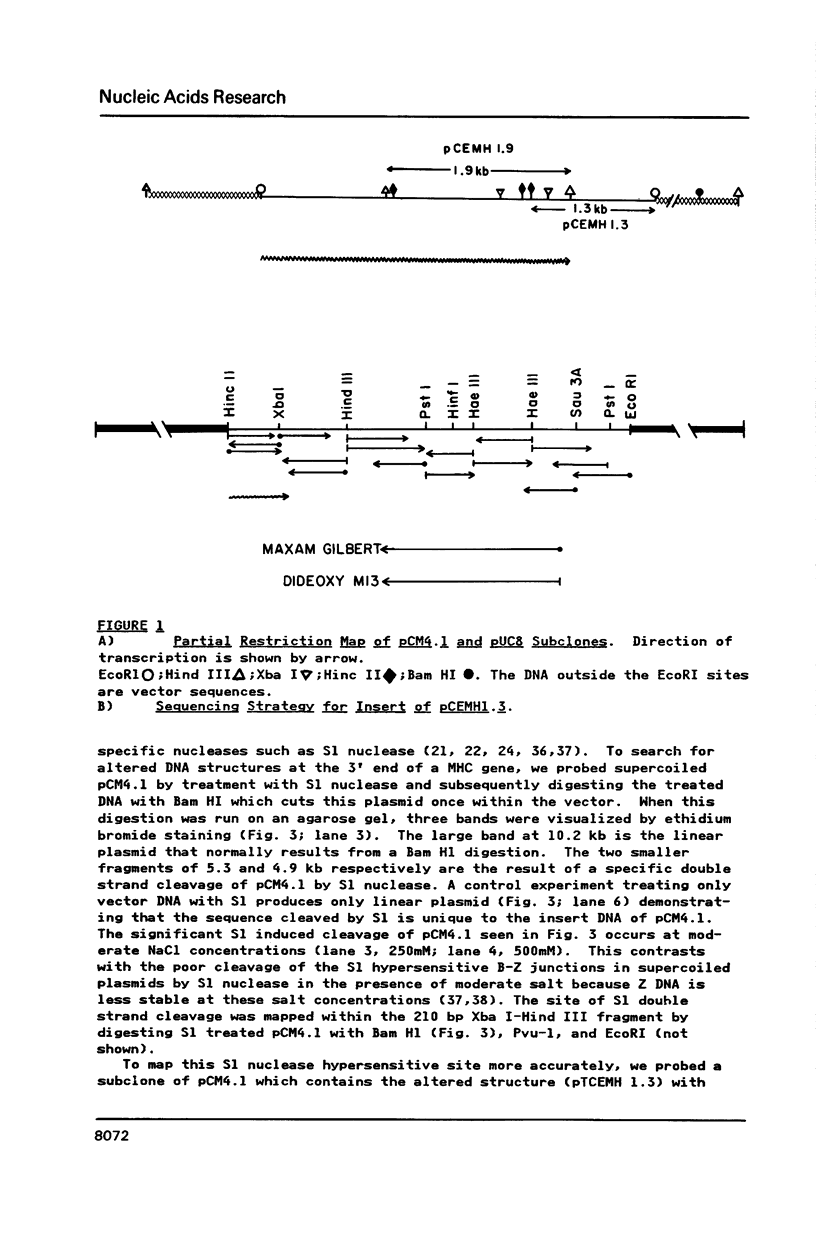
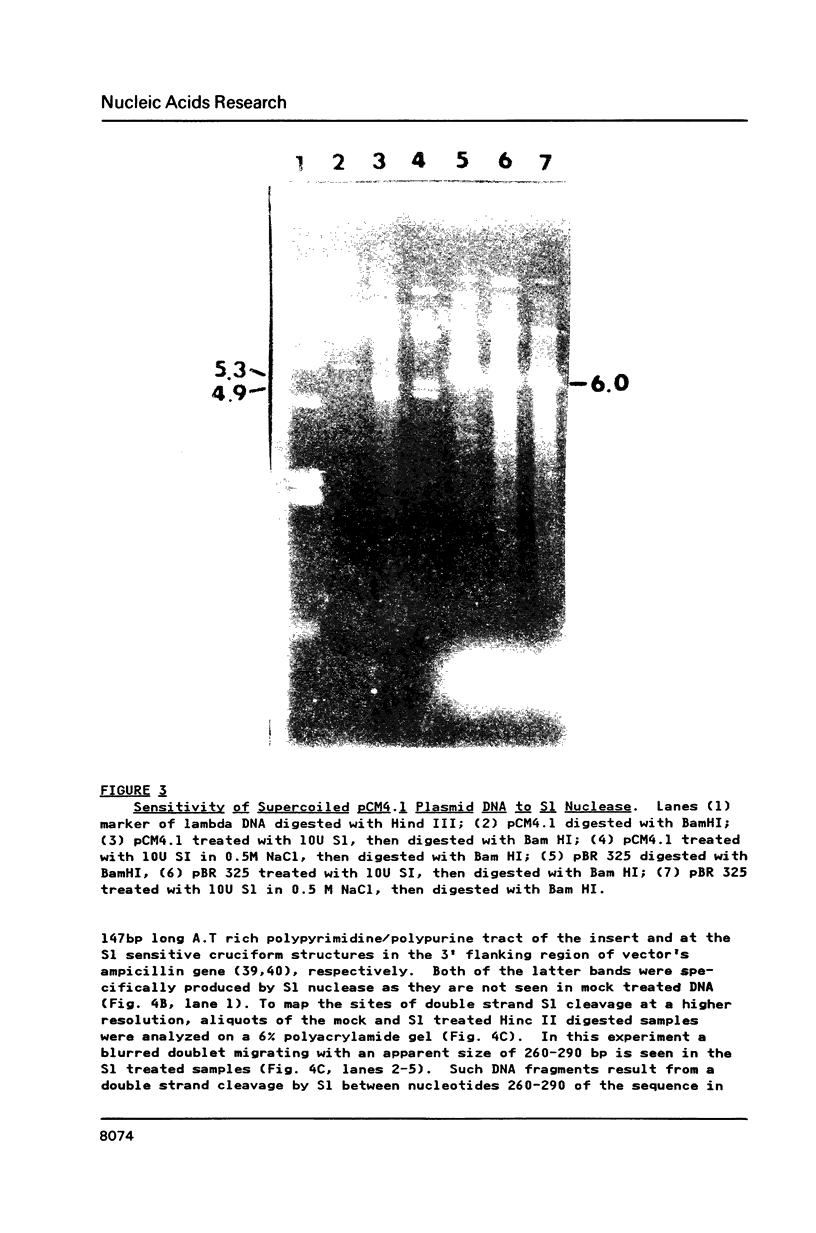
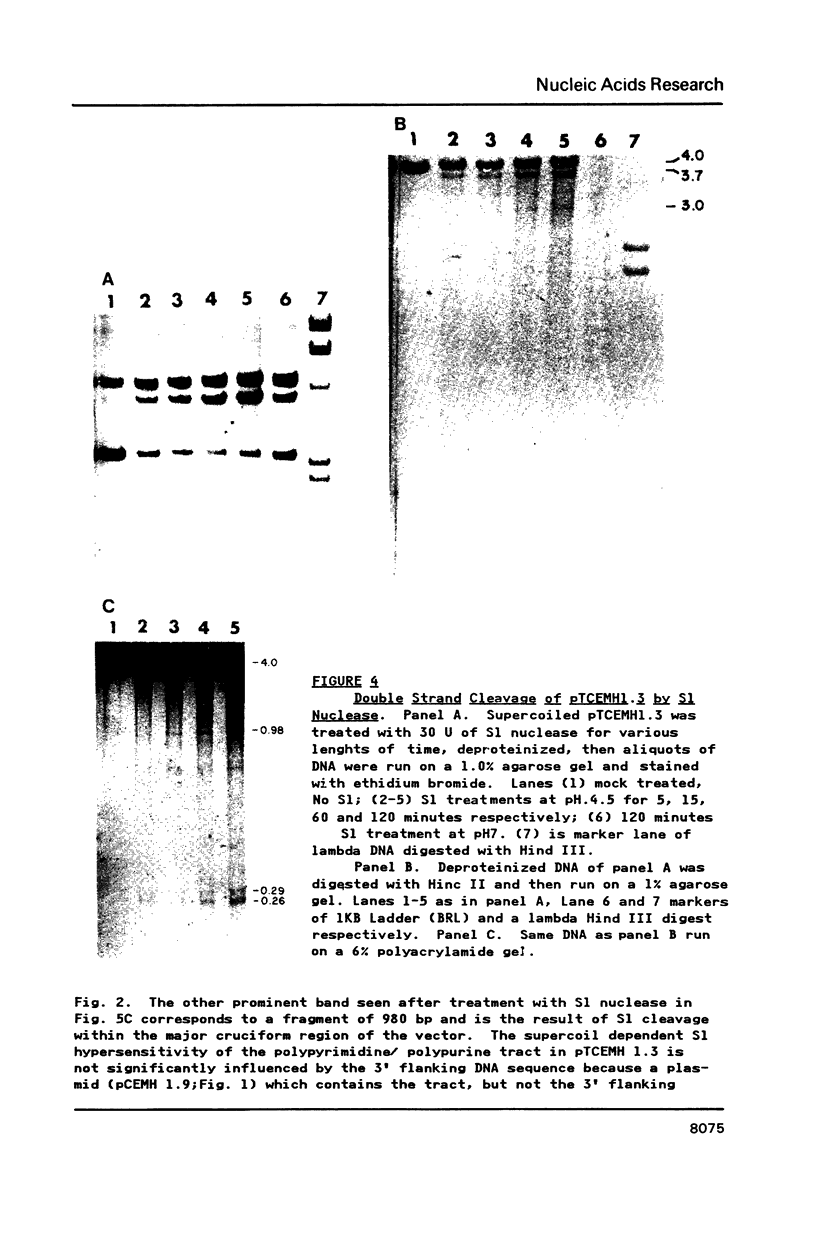
A long (147 base pairs), natural A.T rich polypyrimidine/polypurine tract has been found 55 base pairs downstream of a chicken embryonic myosin heavy chain (MHC) gene. Analysis at the nucleotide level of nicks induced by S1 and Neurospora crassa nucleases indicate that this long interrupted polypyrimidine/polypurine tract exists in an alternate DNA structure in vitro at pH 4.5 and pH 7.5 in both supercoiled and linear plasmid DNA. The polypyrimidine/polypurine tract induces this alternate structure upon at least 200 base pairs of its 5' flanking DNA, and thus extends into the 3' coding and non-coding regions of the neighboring MHC gene. The different nicking patterns induced by the nucleases S1 and N. crassa on each strand of this alternate structure suggests that the polypyrimidine/polypurine tract may form heteronomous DNA. When this long polypyrimidine/polypurine tract is present in a supercoiled plasmid at low pH, a new and as yet undefined S1 hypersensitive DNA alteration was detected near the center of this tract.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C. Heteronomous DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4141–4155. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Kaye J. S., Pratt-Kaye S., Chambon P. Hormonally induced alterations of chromatin structure in the polyadenylation and transcription termination regions of the chicken ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):567–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler-Browne G. S., Whalen R. G. Myosin isozyme transitions occurring during the postnatal development of the rat soleus muscle. Dev Biol. 1984 Apr;102(2):324–334. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Efstratiadis A. Possible structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine S1-hypersensitive sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8059–8072. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Temple G. F., Poon R., Neumann K. H., Kan Y. W. The nucleotide sequences of the untranslated 5' regions of human alpha- and beta-globin mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5145–5149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe D., Cabrer B., Bacolla A., Targovnik H., Pohl V., Vassart G. An unusually long poly(purine)-poly(pyrimidine) sequence is located upstream from the human thyroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5127–5144. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Efstratiadis A. Sequence-dependent S1 nuclease hypersensitivity of a heteronomous DNA duplex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14771–14780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Schon E., Gora-Maslak G., Patterson J., Efstratiadis A. S1-hypersensitive sites in eukaryotic promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8043–8058. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. Alternative sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites characterize the various functional states of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):163–165. doi: 10.1038/311163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. The organisation of chromatin loops: characterization of a scaffold attachment site. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Dixon J. E. Z-DNA in the rat somatostatin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8145–8156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Human U1 RNA genes contain an unusually sensitive nuclease S1 cleavage site within the conserved 3' flanking region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7288–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Lund E., Westin G., Pettersson U., Dahlberg J. E. Nuclease S1-sensitive sites in multigene families: human U2 small nuclear RNA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1839–1845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. All members of the MHC multigene family respond to thyroid hormone in a highly tissue-specific manner. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.3945800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang D. S., Wells R. D. B-Z DNA junctions contain few, if any, nonpaired bases at physiological superhelical densities. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7783–7790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavinsky C. J., Umeda P. K., Sinha A. M., Elzinga M., Tong S. W., Zak R., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Cloned mRNA sequences for two types of embryonic myosin heavy chains from chick skeletal muscle. I. DNA and derived amino acid sequence of light meromyosin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5196–5205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Kohwi Y. Poly(dG)-poly(dC) sequences, under torsional stress, induce an altered DNA conformation upon neighboring DNA sequences. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Larson J. E., Hart P. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA in restriction fragments and a recombinant plasmid. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):672–677. doi: 10.1038/290672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linxweller W., Hörz W. Reconstitution experiments show that sequence-specific histone-DNA interactions are the basis for nucleosome phasing on mouse satellite DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):281–290. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyamichev V. I., Mirkin S. M., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Structures of homopurine-homopyrimidine tract in superhelical DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):667–669. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Nguyen H. T., Destree A. T., Summers E., Nadal-Ginard B. A novel mechanism of alternative RNA splicing for the developmentally regulated generation of troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):409–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90496-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas R. H., Wright C. A., Cockerill P. N., Wyke J. A., Goodwin G. H. The nuclease sensitivity of active genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):753–772. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Energetics of B-to-Z transition in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Wydro R. M., Strehler-Page M. A., Strehler E. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of cDNA and genomic sequences corresponding to an embryonic myosin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15856–15862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Freyer G. A., Chisholm D., Gilliam T. C. Isolation of multiple genomic sequences coding for chicken myosin heavy chain protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Horan T., Gulick J., Kropp K. The chicken myosin heavy chain family. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6606–6612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Daubas P., Akimenko M. A., Cohen A., Garner I., Guenet J. L., Buckingham M. A single locus in the mouse encodes both myosin light chains 1 and 3, a second locus corresponds to a related pseudogene. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. N., Hogan M. An equilibrium between distorted and undistorted DNA in the adult chicken beta A-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8194–8202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weydert A., Daubas P., Caravatti M., Minty A., Bugaisky G., Cohen A., Robert B., Buckingham M. Sequential accumulation of mRNAs encoding different myosin heavy chain isoforms during skeletal muscle development in vivo detected with a recombinant plasmid identified as coding for an adult fast myosin heavy chain from mouse skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13867–13874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weydert A., Daubas P., Lazaridis I., Barton P., Garner I., Leader D. P., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Simon D., Guénet J. L. Genes for skeletal muscle myosin heavy chains are clustered and are not located on the same mouse chromosome as a cardiac myosin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7183–7187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Sell S. M., Butler-Browne G. S., Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Pinset-Härstöm I. Three myosin heavy-chain isozymes appear sequentially in rat muscle development. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):805–809. doi: 10.1038/292805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiid I. J., Boyd C. D., Bester A. J., Van Helden P. D. Evidence for transcriptional regulation of the myosin heavy chain gene during myogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2717–2729. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Clusters of CpG dinucleotides implicated by nuclease hypersensitivity as control elements of housekeeping genes. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):467–469. doi: 10.1038/314467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Gubits R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of sarcomeric myosin heavy chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):670–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezza D. J., Heywood S. M. The localization of a tcRNA102 gene near the 3' OH terminus of a fast myosin heavy chain gene. A comparison between normal and dystrophic chickens. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7455–7460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]