Abstract
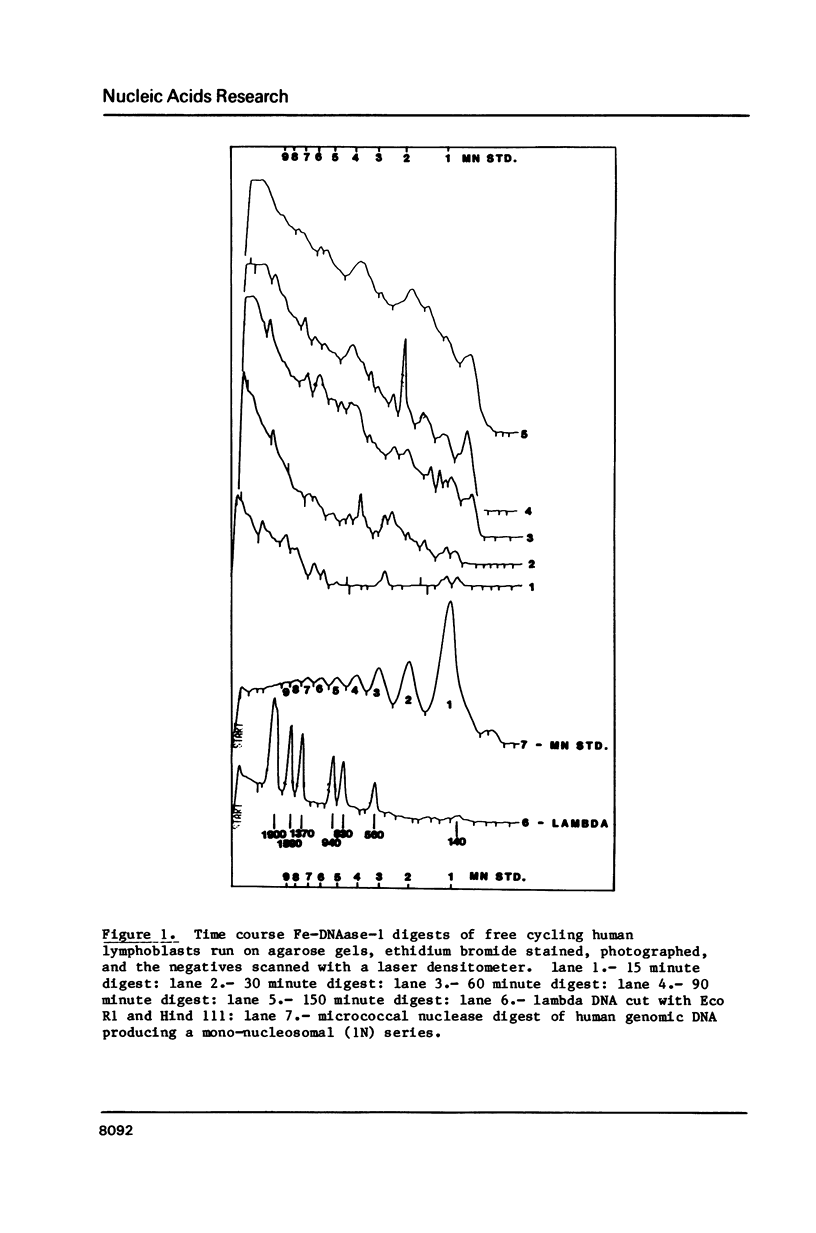
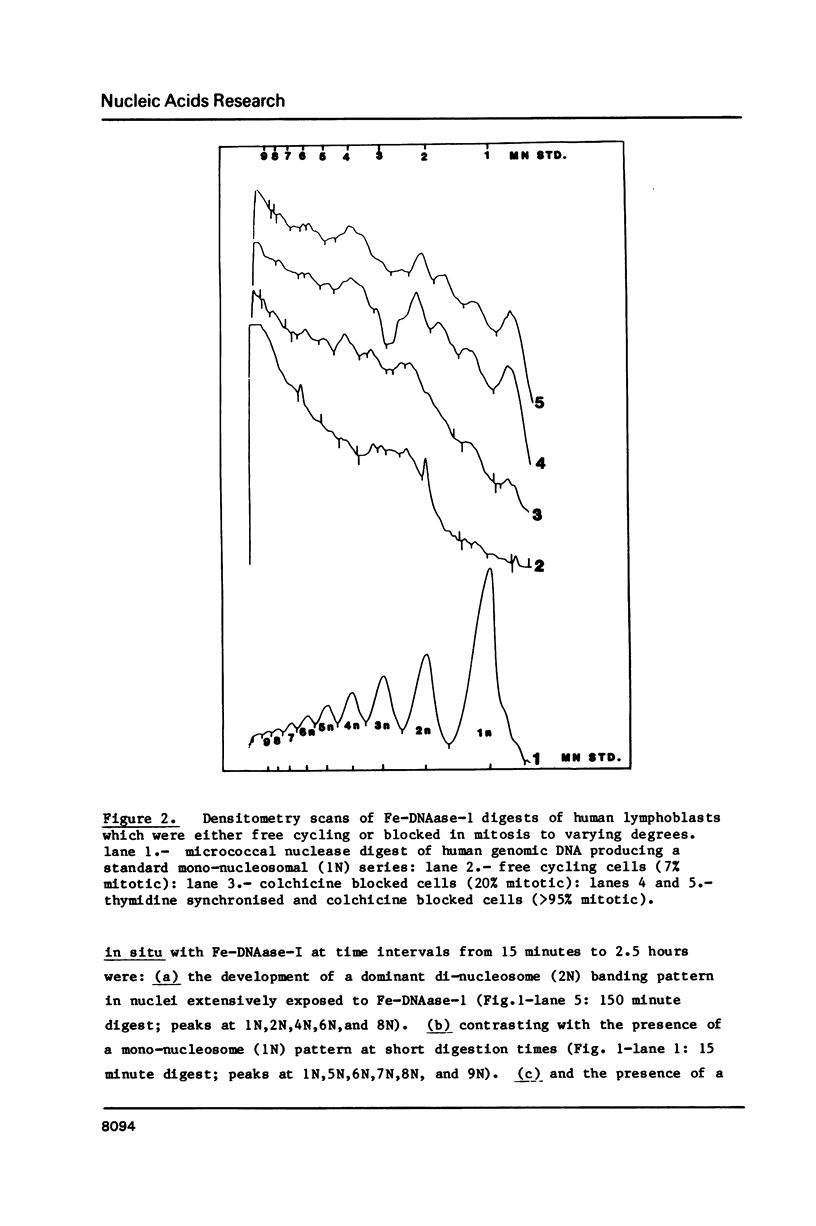
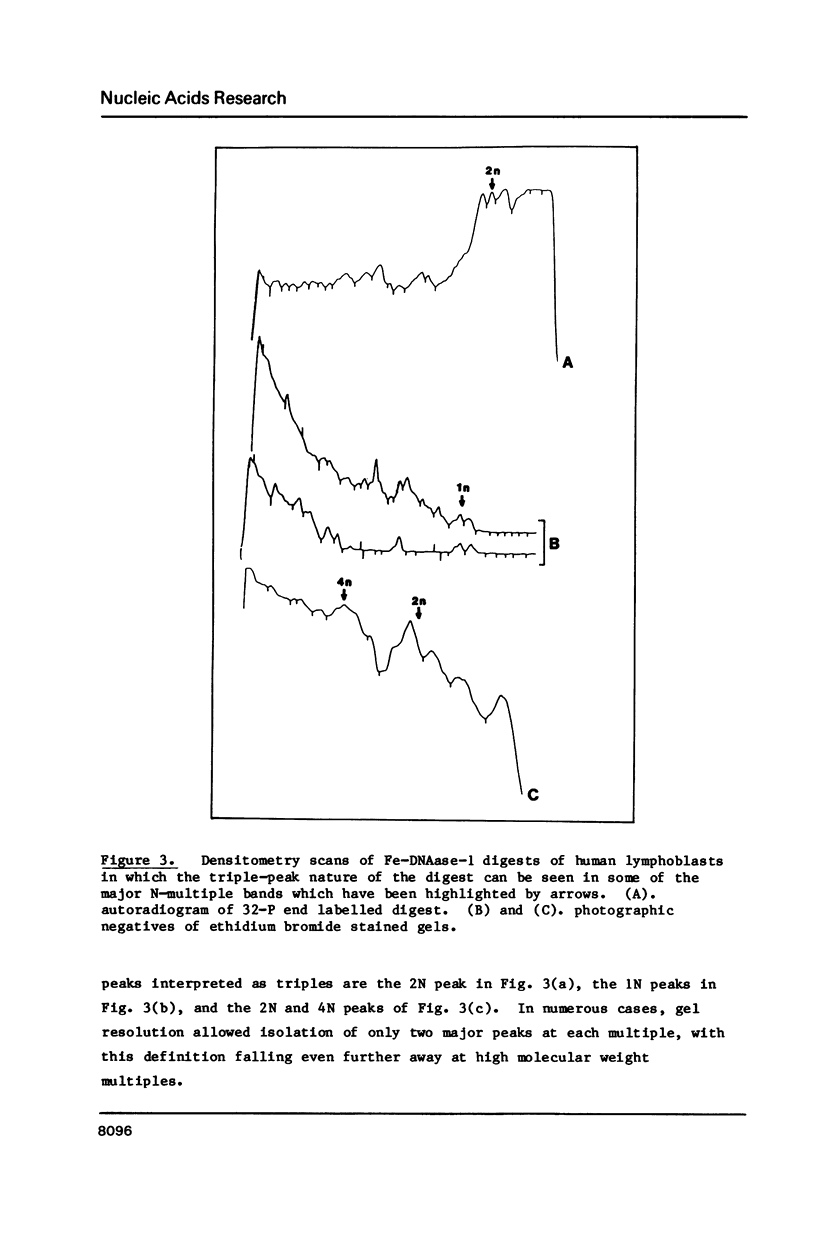
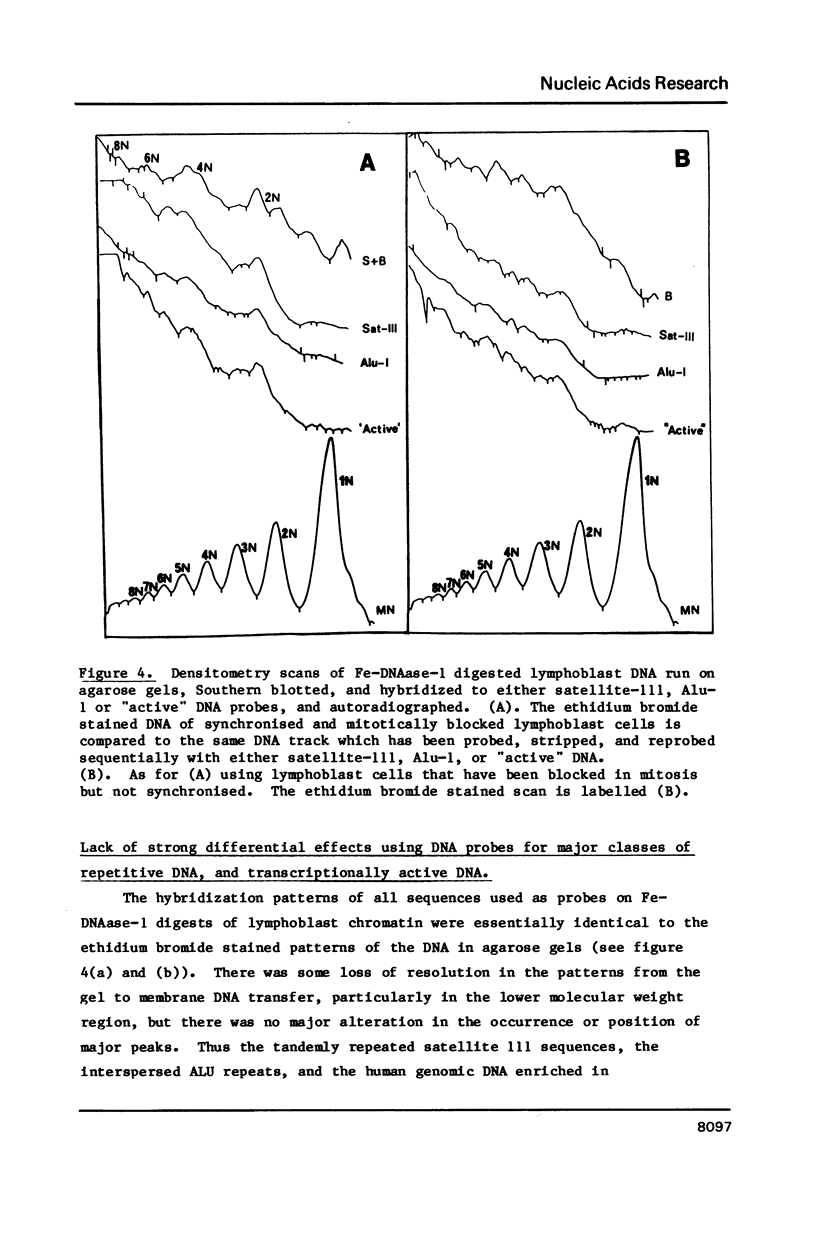
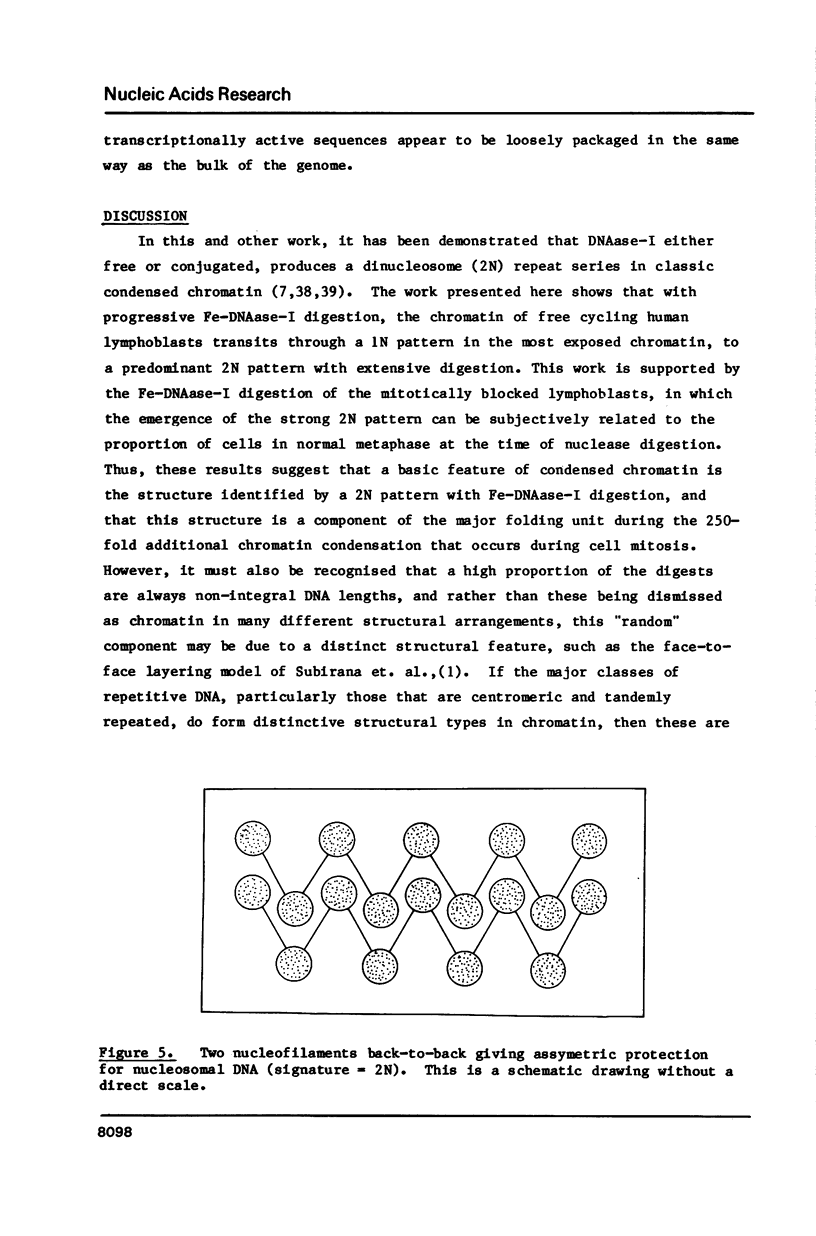
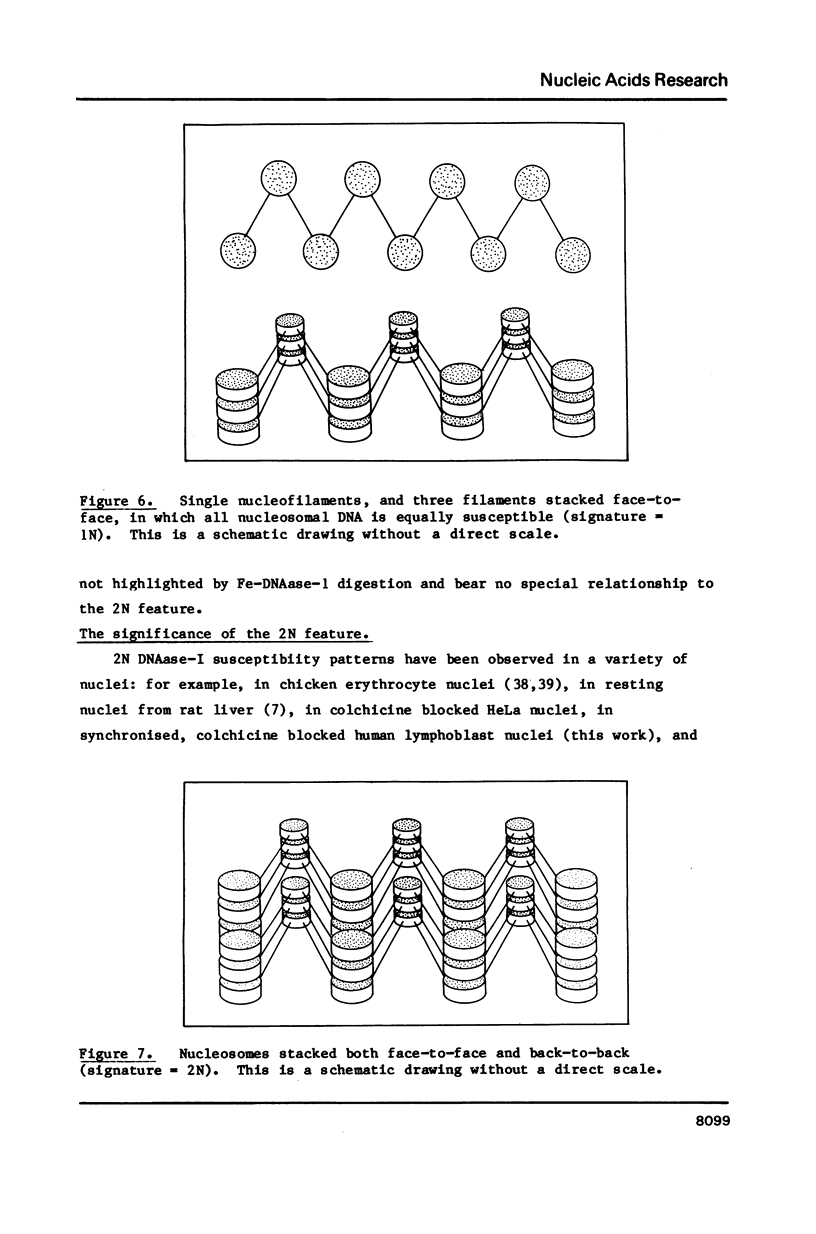
Four separate features could be distinguished in Fe-DNAase-1 digestions of human lymphoblast nuclei: a di-nucleosomal (2N) repeat, a mono-nucleosomal (1N) repeat, a component of "random" DNA, and triple splitting of major peaks. The random component is major, is unlikely to be completely artifactual, and is what would be expected from the face to face layering model of Subirana et. al., (1). The 2N pattern appeared to be associated with compact, metaphase-type chromatin, whereas the 1N pattern was associated with more exposed chromatin. These two modes are explained in terms of orderly back-to-back folding of zig-zag nucleofilaments, and face-to-face folding respectively. Hybridization studies indicated that the centromeric classes of repetitive DNA had the same digestion spectra as the major interspersed classes of repetitive DNA, and DNA enriched in transcriptionally active sequences. It is suggested that current coil models are all inadequate explanations of higher order chromatin packing.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolph K. W., Kreisman L. R., Kuehn R. L. Assembly of chromatin fibers into metaphase chromosomes analyzed by transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):221–231. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83636-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arceci R. J., Gross P. R. Sea urchin sperm chromatin structure as probed by pancreatic DNase I: evidence for a noval cutting periodicity. Dev Biol. 1980 Nov;80(1):210–224. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azorín F., Pérez-Grau L., Subirana J. A. Supranucleosomal organization of chromatin. Electron microscopic visualization of long polynucleosomal chains. Chromosoma. 1982;85(2):251–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00294969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A. A back-to-back zig-zag model for higher order chromatin structure. Cytobios. 1985;43(172-173):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Skinner J. D. Avian erythrocyte chromatin degradation: the progressive exposure of the dinucleosomal repeat by bovine-pancreatic-DNAase-I-armed probes and free DNAase-I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):665–673. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Skinner J. D. Chromatin superstructure: the next level of structure above the nucleosome has an alternating character. A two-nucleosome based series is generated by probes armed with DNAase-I acting on isolated nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Skinner J. D., Marshall A. Analysis of the penetrable space within the nucleus. J Cell Sci. 1978 Jun;31:1–11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.31.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Skinner J. D. Probing the free space within rat and chicken chromatin with active and passive probes. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:85–96. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J. A defined structure of the 30 nm chromatin fibre which accommodates different nucleosomal repeat lengths. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2599–2604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J. The folding of chromatin. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;15(1):57–91. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Noll M. Nucleosome arcs and helices. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):280–286. doi: 10.1126/science.694532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Klug A. Solenoidal model for superstructure in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greulich K. O., Wachtel E., Ausio J., Seger D., Eisenberg H. Transition of chromatin from the "10 nm" lower order structure, to the "30 nm" higher order structure as followed by small angle X-ray scattering. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):709–721. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90353-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R. E. Optical model studies of the salt-induced 10-30-nm fiber transition in chromatin. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):2011–2021. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssier C., Lasters I., Muyldermans S., Wyns L. The structural organization of dinucleosomes and oligonucleosomes. Electric dichroism and birefringence study. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5763–5784. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachatrian A. T., Pospelov V. A., Svetlikova S. B., Vorob'ev V. I. Nucleodisome - a new repeat unit of chromatin revealed in nuclei of pigeon erythrocytes by DNase I digestion. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 1;128(1):90–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Rhodes D., Smith J., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. A low resolution structure for the histone core of the nucleosome. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):509–516. doi: 10.1038/287509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Leffak M. Assembly of active chromatin. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2055–2060. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasters I., Wyns L., Muyldermans S., Baldwin J. P., Poland G. A., Nave C. Scatter analysis of discrete-sized chromatin fragments favours a cylindrical organization. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):283–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindigkeit R., Böttger M., von Mickwitz C. U., Fenske H., Karawajew L., Karawajew K. New evidence that the basic eukaryotic chromatin fiber consists of two 100 A fibrils arranged side-by-side. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(2):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka Y., Nielsen P. E., Nordén B. J. On the structure of active chromatin. A flow linear dichroism study of chromatin fractionated by nuclease digestion. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 24;169(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G., Rau D. C. Higher order structure of chromatin: orientation of nucleosomes within the 30 nm chromatin solenoid is independent of species and spacer length. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):831–841. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Rau D. C., Charney E., Felsenfeld G. Orientation of the nucleosome within the higher order structure of chromatin. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muyldermans S., Lasters I., Hamers R., Wyns L. Assembly of oligonucleosomes into a limit series of multimeric higher-order chromatin structures. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Aug 1;150(3):441–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Core particle, fiber, and transcriptionally active chromatin structure. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:117–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pospelov V. A., Svetlikova S. B. Higher order chromatin structure determines double-nucleosome periodicity of DNA fragmentation. Mol Biol Rep. 1982 Mar 31;8(2):117–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00778514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Nehls P., Hozier J. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the chromosome fiber. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1879–1883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Mitra S., Crothers D. M. Higher order structure of chromatin: evidence from photochemically detected linear dichroism. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3441–3447. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Lieberman M. W. Nucleosome arrangement in alpha-satellite chromatin of African green monkey cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6493–6510. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staynov D. Z., Dunn S., Baldwin J. P., Crane-Robinson C. Nuclease digestion patterns as a criterion for nucleosome orientation in the higher order structure of chromatin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 4;157(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80567-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subirana J. A., Muñoz-Guerra S., Aymamí J., Radermacher M., Frank J. The layered organization of nucleosomes in 30 nm chromatin fibers. Chromosoma. 1985;91(5):377–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00291012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subirana J. A., Muñoz-Guerra S., Radermacher M., Frank J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of chromatin fibers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):705–714. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. R., Sikorska M. Modulation of the sensitivity of chromatin to exogenous nucleases: implications for the apparent increased sensitivity of transcriptionally active genes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3839–3845. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. R., Sikorska M., Whitfield J. F. Chromatin structure. Nuclease digestion profiles reflect intermediate stages in the folding of the 30-nm fiber rather than the existence of subunit beads. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7044–7051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom J., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. Higher-order structure of long repeat chromatin. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3189–3194. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom J., Klug A. Structure of the 300A chromatin filament: X-ray diffraction from oriented samples. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. P., Athey B. D., Muglia L. J., Schappe R. S., Gough A. H., Langmore J. P. Chromatin fibers are left-handed double helices with diameter and mass per unit length that depend on linker length. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):233–248. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83637-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L., Frado L. L., Rattner J. B. The higher-order structure of chromatin: evidence for a helical ribbon arrangement. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):42–52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Strogatz S., Riley D. Structure of chromatin and the linking number of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentgraf H., Franke W. W. Differences of supranucleosomal organization in different kinds of chromatin: cell type-specific globular subunits containing different numbers of nucleosomes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):272–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



