Abstract
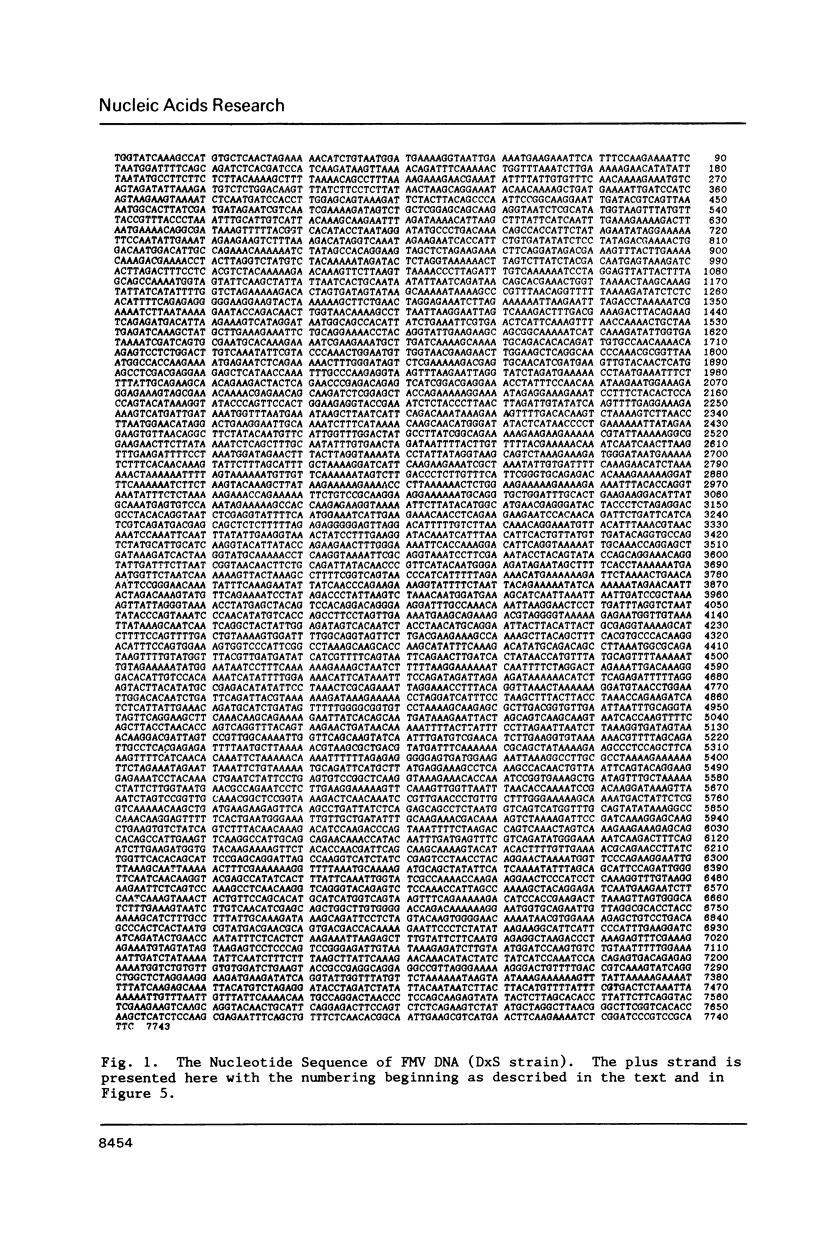
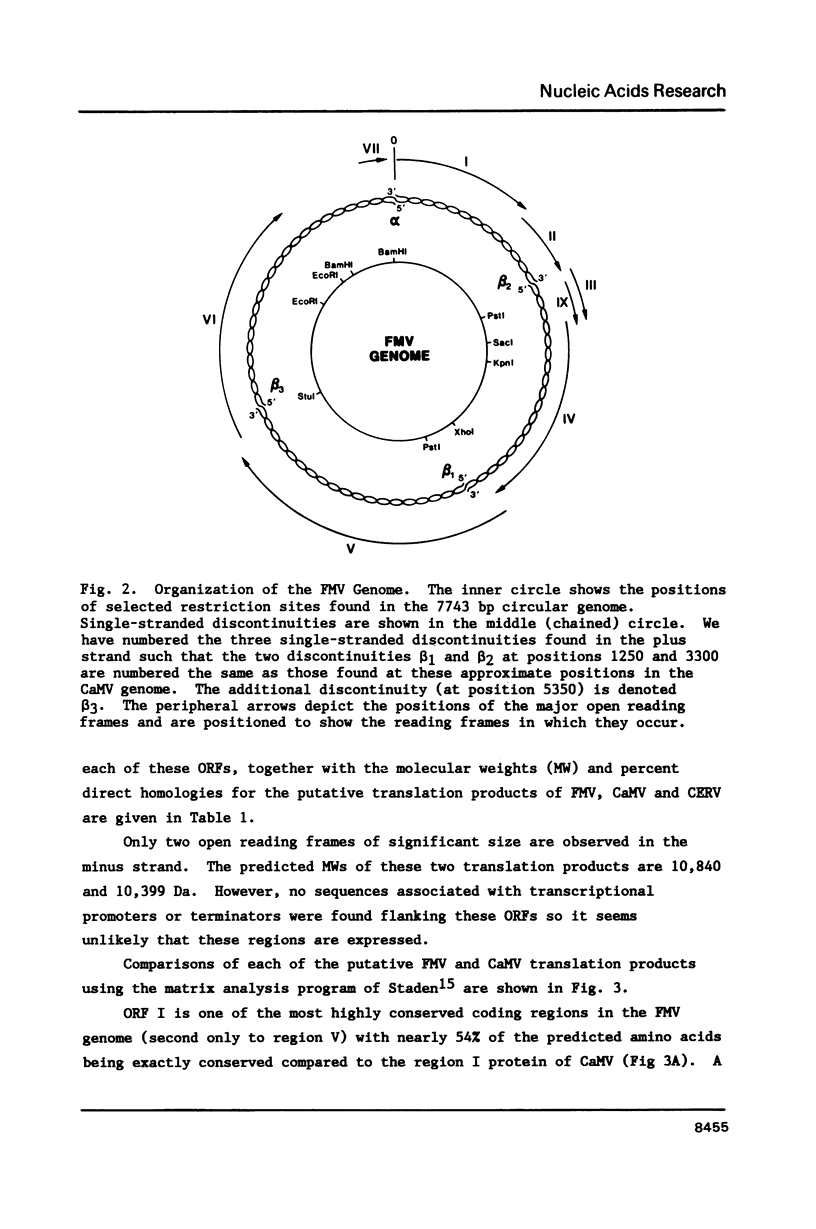
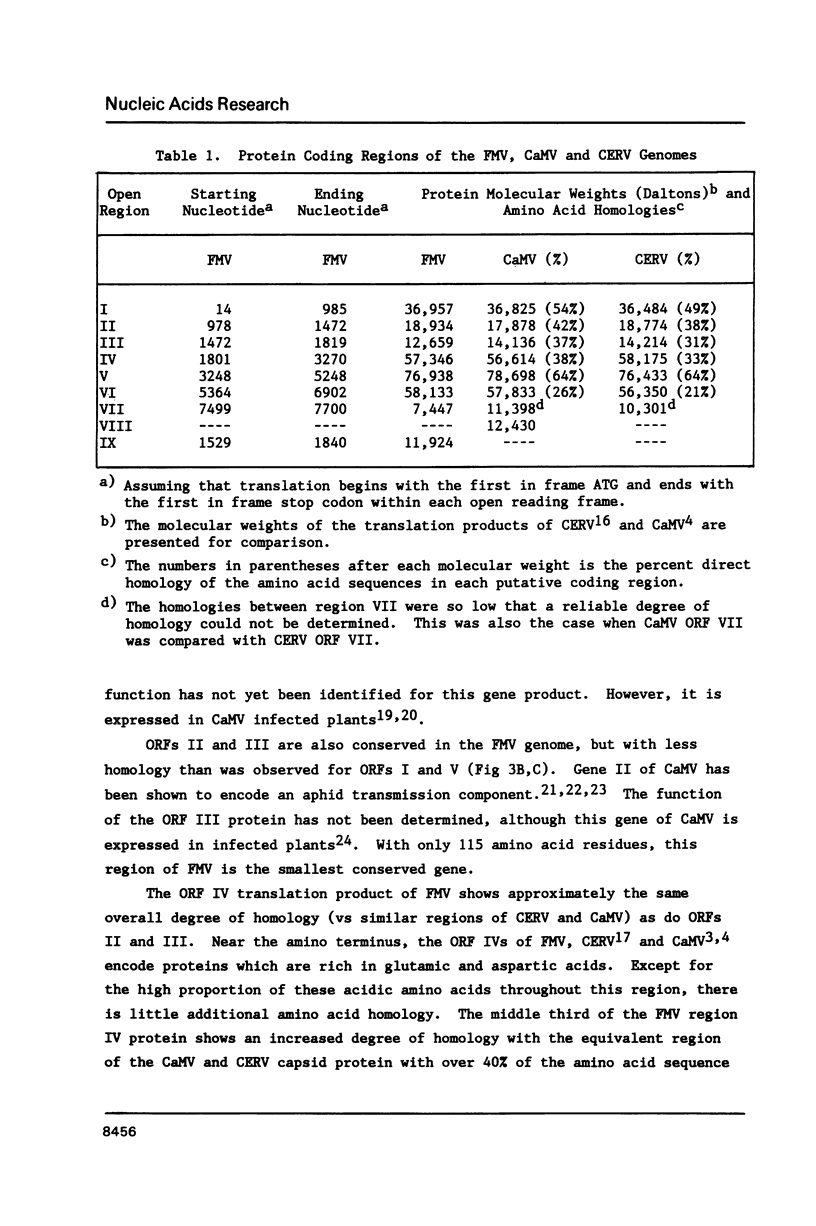
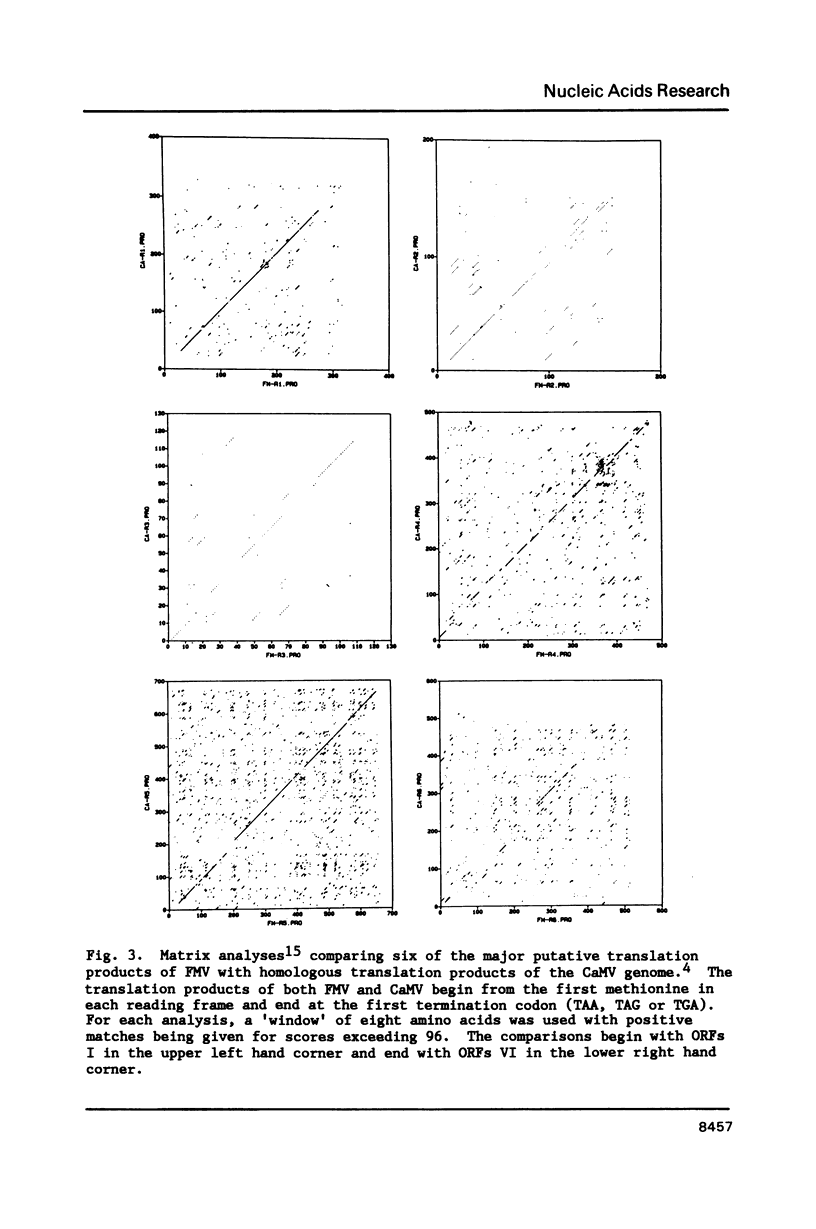
The nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of figwort mosaic virus (FMV) was determined using the dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. The double-stranded DNA genome (7743 base pairs) contained eight open reading frames (ORFs), seven of which corresponded approximately in size and location to the ORFs found in the genome of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) and carnation etched ring virus (CERV). ORFs I and V of FMV demonstrated the highest degrees of nucleotide and amino acid sequence homology with the equivalent coding regions of CaMV and CERV. Regions II, III and IV showed somewhat less homology with the analogous regions of CaMV and CERV, and ORF VI showed homology with the corresponding gene of CaMV and CERV in only a short segment near the middle of the putative gene product. A 16 nucleotide sequence, complementary to the 3' terminus of methionine initiator tRNA (tRNAimet) and presumed to be the primer binding site for initiation of reverse transcription to produce minus strand DNA, was found in the FMV genome near the discontinuity in the minus strand. Sequences near the three interruptions in the plus strand of FMV DNA bear strong resemblance to similarly located sequences of 3 other caulimoviruses and are inferred to be initiation sites for second strand DNA synthesis. Additional conserved sequences in the small and large intergenic regions are pointed out including a highly conserved 35 bp sequence that occurs in the latter region.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balàzs E., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K. Nucleotide sequence of DNA from an altered-virulence isolate D/H of the cauliflower mosaic virus. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaday J., Guillemaut P., Weil J. H. The nucleotide sequences of the initiator transfer RNAs from bean cytoplasm and chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):999–1008. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N. Amino acid sequence homology in gag region of reverse transcribing elements and the coat protein gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):623–633. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N., Lomonossoff G. P., Hull R. Characterisation of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA sequences which encode major polyadenylated transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6735–6747. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubert S., Shepherd R. J., Gardner R. C. Insertional mutagenesis of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Hohn T. Initiation of translation of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome from a polycistronic mRNA: evidence from deletion mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2731–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck A., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. C., Howarth A. J., Hahn P., Brown-Luedi M., Shepherd R. J., Messing J. The complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of cauliflower mosaic virus by M13mp7 shotgun sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2871–2888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Ghosh K., Simsek M., RajBhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequence of wheat germ cytoplasmic initiator methionine transfer ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3241–3247. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Dudley R. K., Jonard G., Balàzs E., Richards K. E. Transcription of Cauliflower mosaic virus DNA: detection of promoter sequences, and characterization of transcripts. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilley H., Richards K. E., Jonard G. Observations concerning the discontinuous DNAs of cauliflower mosaic virus. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):277–282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison B. D., Finch J. T., Gibbs A. J., Hollings M., Shepherd R. J., Valenta V., Wetter C. Sixteen groups of plant viruses. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):356–363. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Richards K., Geneviève-Lebeurier Cauliflower mosaic virus on its way to becoming a useful plant vector. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;96:194–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H., Hull R. Replication of cauliflower mosaic virus and transcription of its genome in turnip leaf protoplasts. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):468–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H., Walker L. L., Dudley R. K. Cloned Cauliflower Mosaic Virus DNA Infects Turnips (Brassica rapa). Science. 1980 Jun 13;208(4449):1265–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4449.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Covey S. N., Stanley J., Davies J. W. The polarity of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):669–677. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Sadler J., Longstaff M. The sequence of carnation etched ring virus DNA: comparison with cauliflower mosaic virus and retroviruses. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3083–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeurier G., Hirth L., Hohn T., Hohn B. Infectivities of native and cloned DNA of cauliflower mosaic virus. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Subramani S., Berg P. Effect of upstream reading frames on translation efficiency in simian virus 40 recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2704–2711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer P., Hohn T. Involvement of reverse transcription in the replication of cauliflower mosaic virus: a detailed model and test of some aspects. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):781–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant A. L., Covey S. N., Grierson D. Detection of a subgenomic mRNA for gene V, the putative reverse transcriptase gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8305–8321. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoelz J., Shepherd R. J., Daubert S. Region VI of cauliflower mosaic virus encodes a host range determinant. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2632–2637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd R. J., Wakeman R. J., Romanko R. R. DNA in cauliflower mosaic virus. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):150–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Kikuno R., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Kugimiya W., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Close structural resemblance between putative polymerase of a Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6 and pol gene product of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1267–1272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A. TFIIIA and homologous genes. The 'finger' proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4385–4391. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolston C. J., Covey S. N., Penswick J. R., Davies J. W. Aphid transmission and a polypeptide are specified by a defined region of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome. Gene. 1983 Jul;23(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong C., Lebeurier G., Hirth L. Detection in vivo of a new gene product (gene III) of cauliflower mosaic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6608–6612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. J., Daubert S. D., Shepherd R. J. Gene I products of cauliflower mosaic virus detected in extracts of infected tissue. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):444–446. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



