Abstract
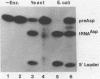
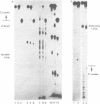
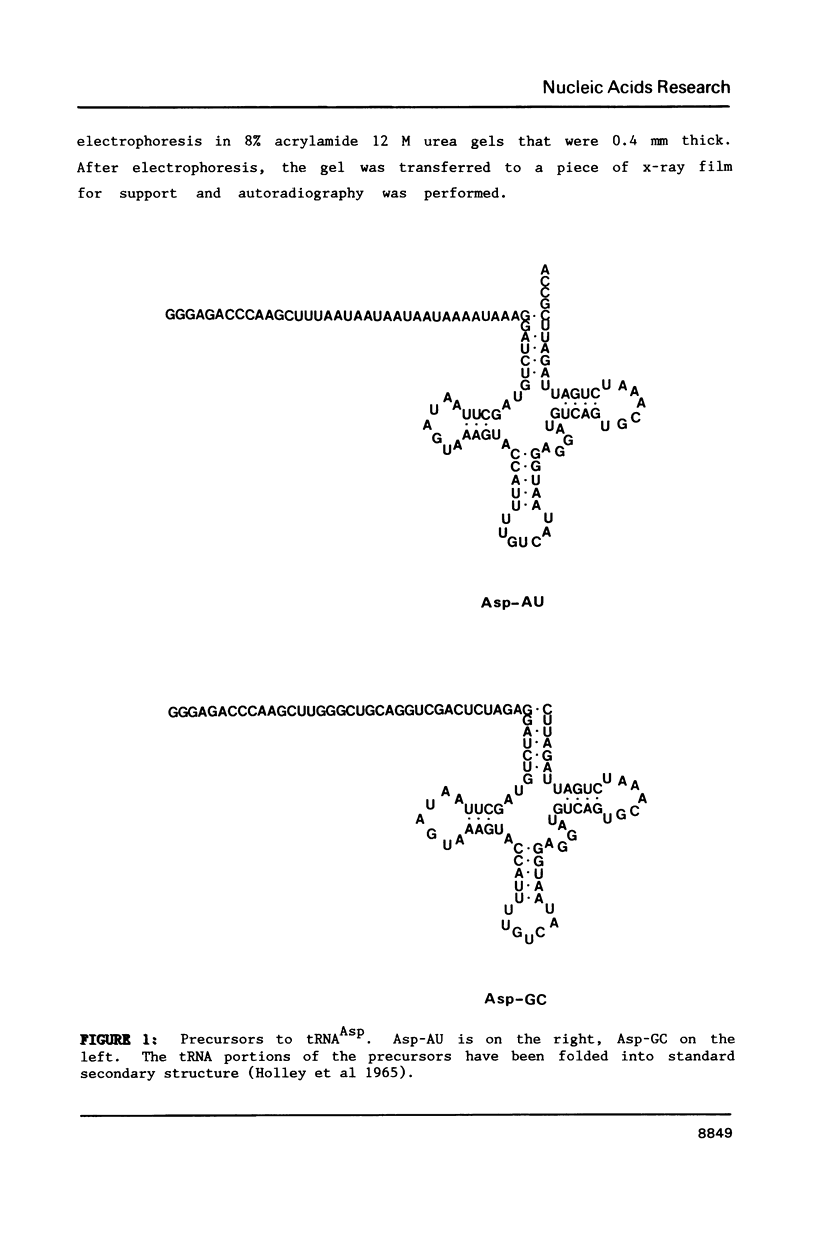
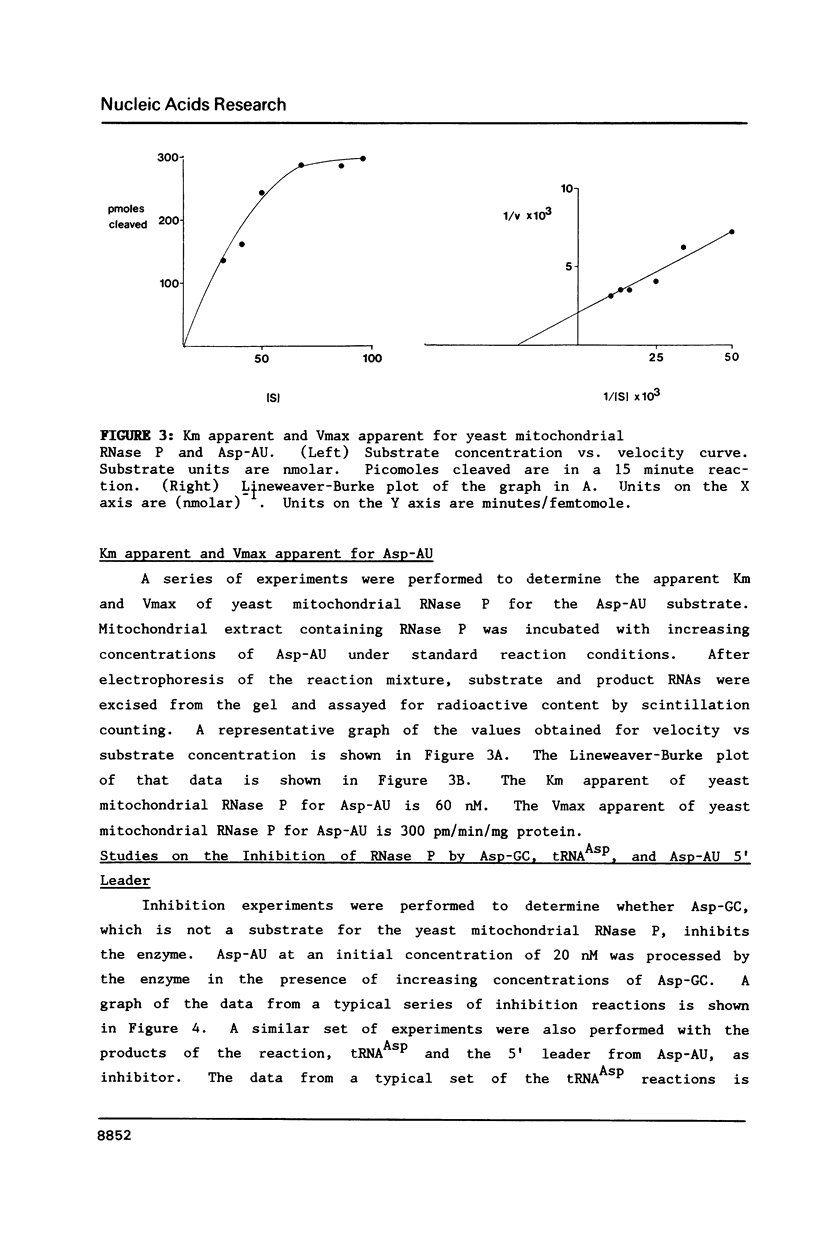
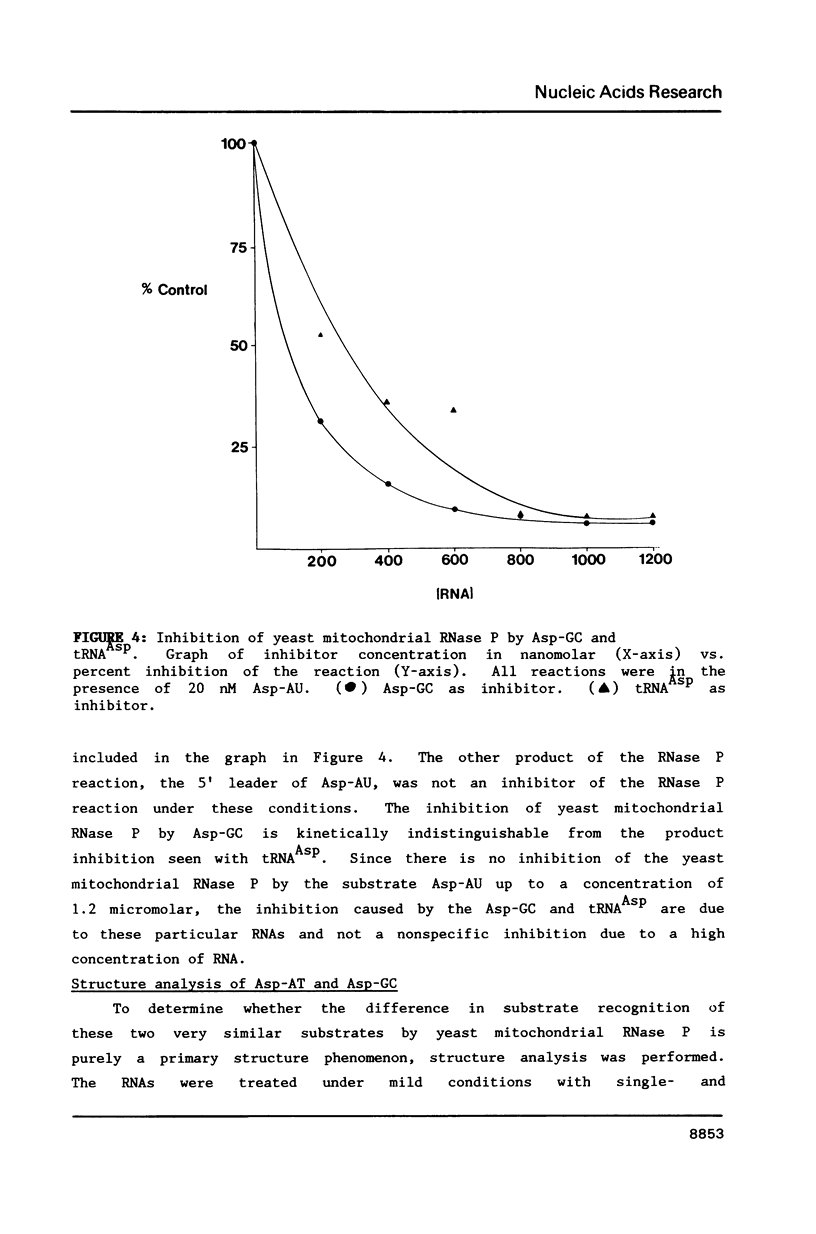
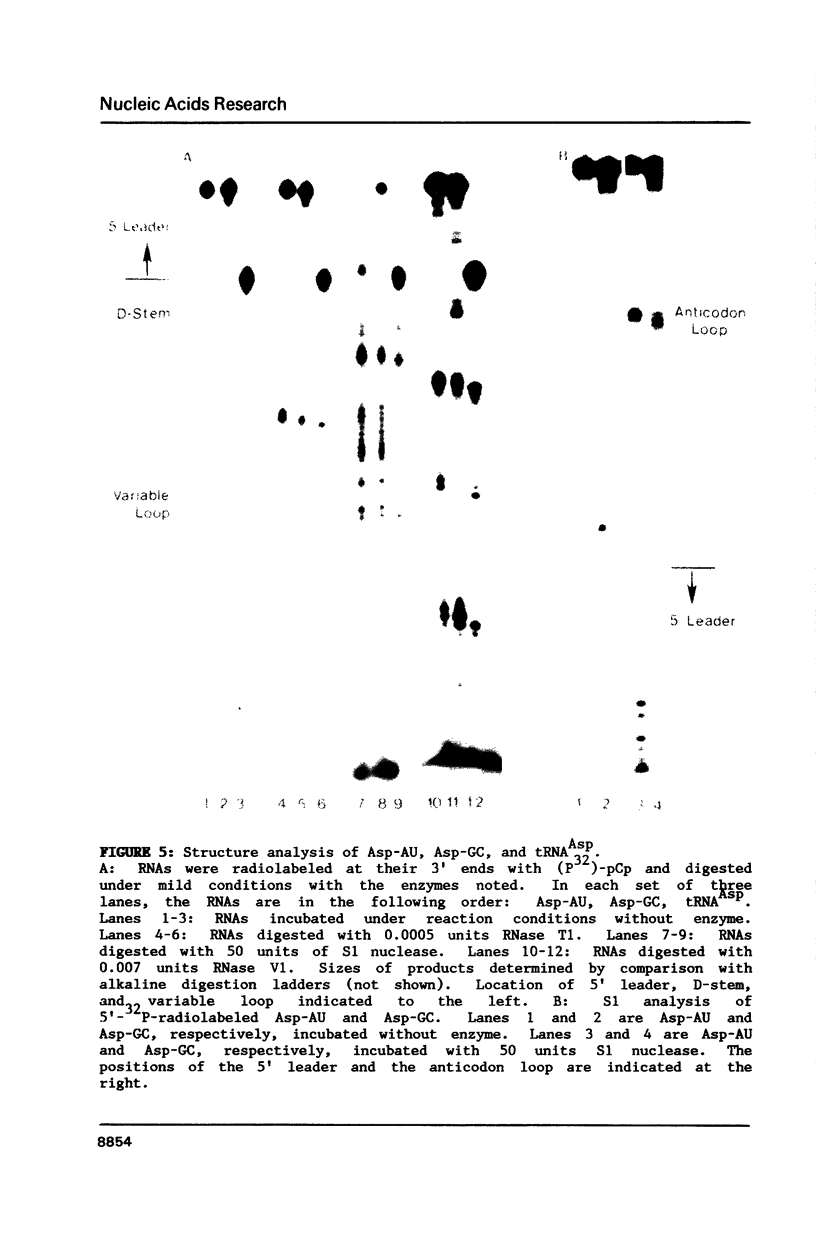
A mitochondrial specific RNase P is required to process 5' leaders from mitochondrial tRNA precursors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Experiments with a pair of mitochondrial pretRNAs(Asp) having leaders of different base composition suggest that this enzyme is unexpectedly sensitive to leader sequence or structure. Asp-AU (75% AU leader) is cleaved by the mitochondrial RNase P while Asp-GC (39% AU) is not. Both are substrates for E. coli RNase P. Partial nuclease digestions show that the tRNA portions of the two precursors differ in tertiary structure, while their 5' leaders differ in secondary structure. It is unusual for an RNaseP to have substrate specificity requirements which preclude processing of a pretRNA known to be a suitable substrate for an RNaseP from another species.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaboshi E., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Veal heart ribonuclease P has an essential RNA component. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):831–837. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Ornberg R., Koster J. G., Tobian J. A., Zasloff M. Eukaryotic pre-tRNA 5' processing nuclease: copurification with a complex cylindrical particle. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Pace N. R. RNase P of Bacillus subtilis has a RNA component. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7507–7509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. M1 RNA with large terminal deletions retains its catalytic activity. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLEY R. W., APGAR J., EVERETT G. A., MADISON J. T., MARQUISEE M., MERRILL S. H., PENSWICK J. R., ZAMIR A. STRUCTURE OF A RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1462–1465. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth M. J., Martin N. C. RNase P activity in the mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on both mitochondrion and nucleus-encoded components. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1058–1064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline L., Nishikawa S., Söll D. Partial purification of RNase P from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5058–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole R., Baer M. F., Stark B. C., Altman S. E. coli RNAase P has a required RNA component. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):881–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence N. P., Altman S. Site-directed mutagenesis of M1 RNA, the RNA subunit of Escherichia coli ribonuclease P. The effects of an addition and small deletions on catalytic function. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh T. L., Pace N. R. Ribonuclease P catalysis differs from ribosomal RNA self-splicing. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):79–81. doi: 10.1126/science.4012313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. C., Underbrink-Lyon K. A mitochondrial locus is necessary for the synthesis of mitochondrial tRNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4743–4747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoccia E., Baldi M. I., Pande G., Ogden R., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Mutation in the a block of the yeast tRNAleu3 gene that allows transcription but abolishes splicing and 5'-end maturation. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90497-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Martin N. C. Characterization of the yeast mitochondrial locus necessary for tRNA biosynthesis: DNA sequence analysis and identification of a new transcript. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):911–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90548-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Kurjan J., Hall B. D., De Robertis E. M. Genetic analysis of the processing of a spliced tRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):263–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson D., Willis I., Hottinger H., Bell J., Kumar A., Leupold U., Söll D. Mutations preventing expression of sup3 tRNASer nonsense suppressors of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):808–815. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly R. M., RajBhandary U. L. A single mutation in loop IV of Escherichia coli SuIII tRNA blocks processing at both 5'- and 3'-ends of the precursor tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2928–2935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi H., Shimura Y. Mutations affecting two distinct functions of the RNA component of RNase P. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3673–3679. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. Mutations in Box B of the promoter of a eucaryotic tRNAPro gene affect rate of transcription, processing, and stability of the transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis I., Frendewey D., Nichols M., Hottinger-Werlen A., Schaack J., Söll D. A single base change in the intron of a serine tRNA affects the rate of RNase P cleavage in vitro and suppressor activity in vivo in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5878–5885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis I., Nichols M., Chisholm V., Söll D., Heyer W. D., Szankasi P., Amstutz H., Munz P., Kohli J. Functional complementation between mutations in a yeast suppressor tRNA gene reveals potential for evolution of tRNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]