Abstract
During these last years, a powerful methodology has been developed to study the secondary and tertiary structure of RNA molecules either free or engaged in complex with proteins. This method allows to test the reactivity of every nucleotide towards chemical or enzymatic probes. The detection of the modified nucleotides and RNase cleavages can be conducted by two different paths which are oriented both by the length of the studied RNA and by the nature of the probes used. The first one uses end-labeled RNA molecule and allows to detect only scissions in the RNA chain. The second approach is based on primer extension by reverse transcriptase and detects stops of transcription at modified or cleaved nucleotides. The synthesized cDNA fragments are then sized by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide:urea gels. In this paper, the various structure probes used so far are described, and their utilization is discussed.
Full text
PDF




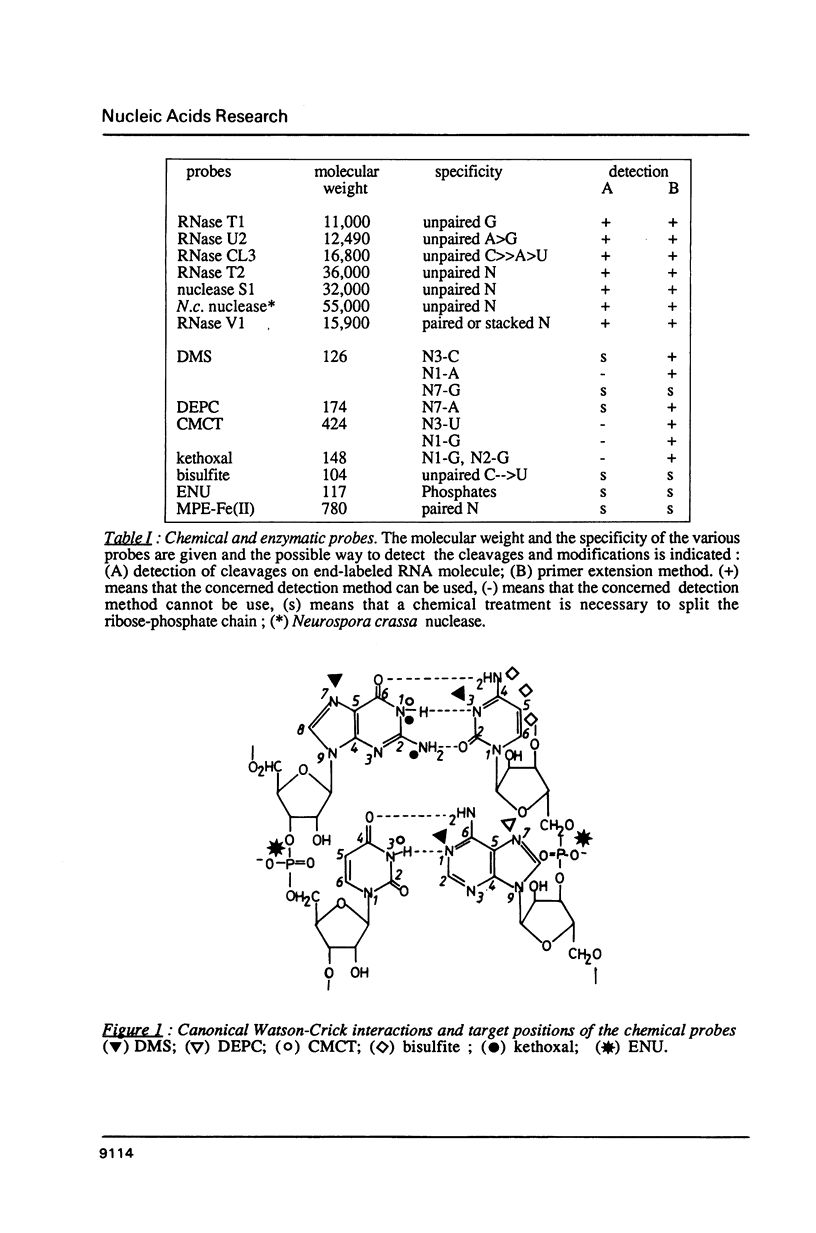

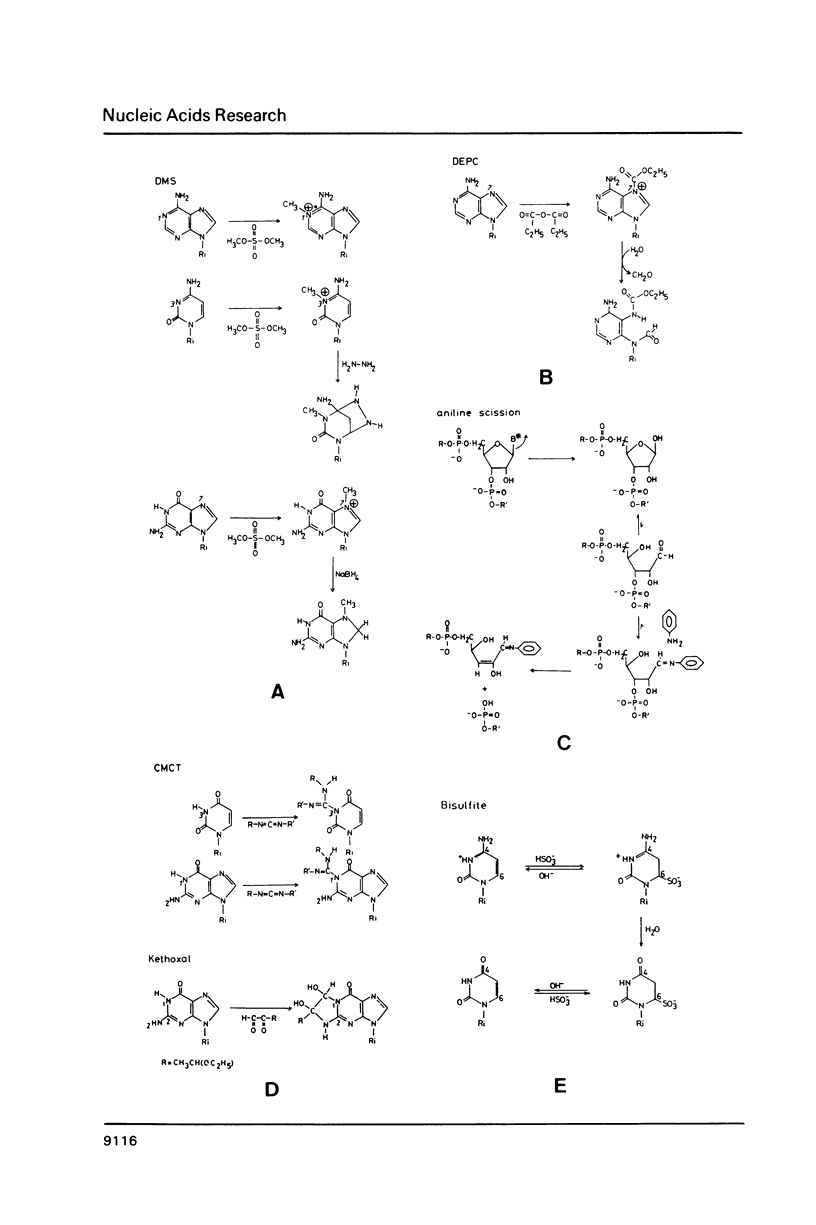
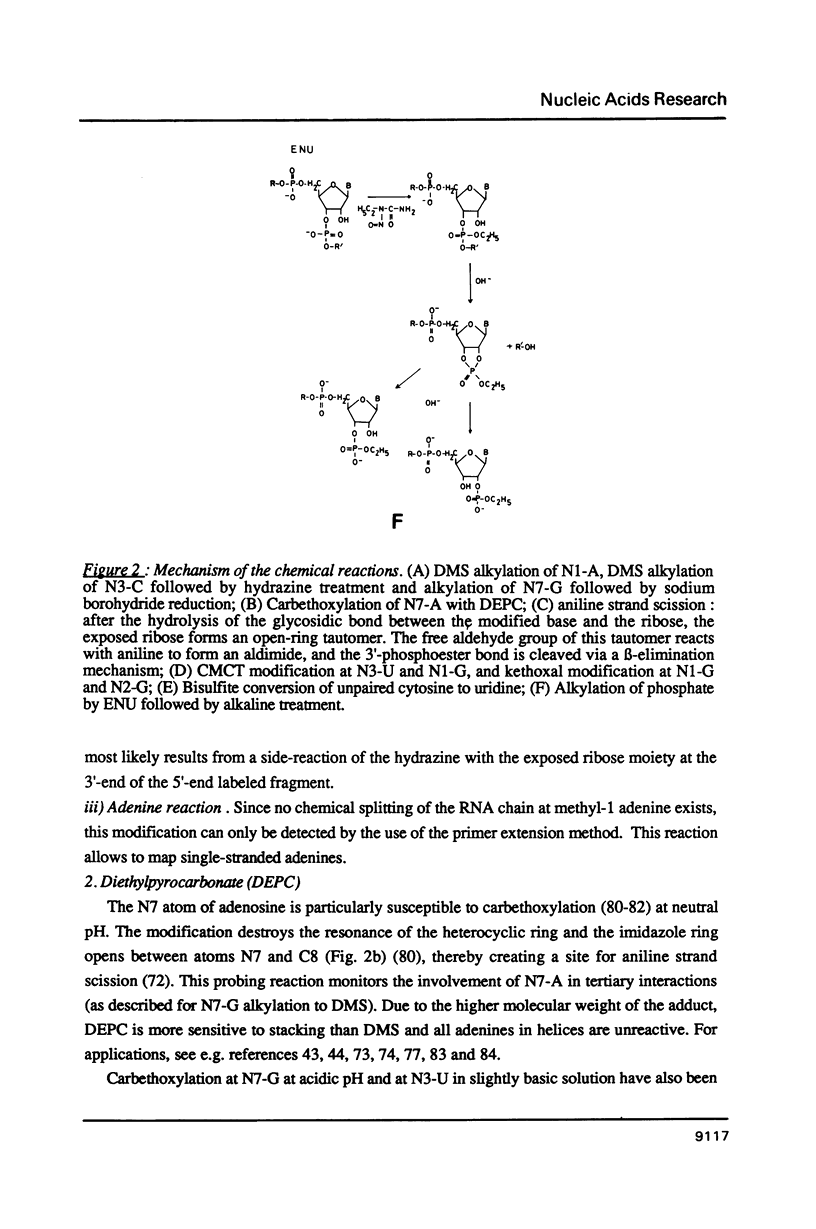








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando T. A nuclease specific for heat-denatured DNA in isolated from a product of Aspergillus oryzae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Weber L. D., Rich A. Comparison of transfer ribonucleic acid structures using cobra venom and S1 endonucleases. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4700–4706. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKES P., LAWLEY P. D. EFFECTS OF ALKYLATING AGENTS ON T2 AND T4 BACTERIOPHAGES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:138–144. doi: 10.1042/bj0890138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., Hieter P. A., Levy C. C. Identification of a cytidine-specific ribonuclease from chicken liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2160–2163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolyreva L. G., Butorin A. S., Vasilenko S. K. Izuchenie raspredeleniia po molekuliarnym vesam produktov gidroliza poliuridilovoi kisloty ribonukleazoi iz iada kobry. Preparativnoe poluchenie polinukleotidov s zadannym molekuliarnym vesom. Biokhimiia. 1978 Sep;43(9):1659–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Gallinaro H., Lazar E., Jacob M. The conformation of chicken, rat and human U1A RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):841–858. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Maly P., Zwieb C. The structure of ribosomal RNA and its organization relative to ribosomal protein. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes P., Lawley P. D. The reaction of mono- and di-functional alkylating agents with nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1042/bj0800496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butorin A. S., Remy P., Ebel J. P., Vassilenko S. K. Comparison of the hydrolysis patterns of several tRNAs by cobra venom ribonuclease in different steps of the aminoacylation reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(3):587–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA splicing: three themes with variations. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: implications for evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:3–22. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., Van de Sande J. H., Church R. B. End group labelling of RNA and double stranded DNA by phosphate exchange catalyzed by bacteriophage T4 induced polynucleotide kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):962–969. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90734-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Brown R. S., Sproat B. S., Garrett R. A. Xenopus transcription factor IIIA binds primarily at junctions between double helical stems and internal loops in oocyte 5S RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):453–460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04775.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas P., Ebel J. P., Giegé R., Moras D., Thierry J. C., Westhof E. Crystal structure of yeast tRNAAsp: atomic coordinates. Biochimie. 1985 Jun;67(6):597–606. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas P., Moras D., Florentz C., Giegé R., Verlaan P., Van Belkum A., Pleij C. W. 3-D graphics modelling of the tRNA-like 3'-end of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA: structural and functional implications. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Apr;4(5):707–728. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg L., Fedorcsak I., Solymosy F. Diethyl pyrocarbonate in nucleic acid research. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;16:189–262. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60758-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favorova O. O., Fasiolo F., Keith G., Vassilenko S. K., Ebel J. P. Partial digestion of tRNA--aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complexes with cobra venom ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1006–1011. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florentz C., Briand J. P., Romby P., Hirth L., Ebel J. P., Glegé R. The tRNA-like structure of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA: structural organization of the last 159 nucleotides from the 3' OH terminus. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furois-Corbin S., Pullman A. A theoretical study of the effect of structural variations on the biochemical reactivity of yeast tRNAPhe and yeast tRNAAsp. Biophys Chem. 1985 Jun;22(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(85)80020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret M., Labouesse B., Litvak S., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Giegé R. Tertiary structure of animal tRNATrp in solution and interaction of tRNATrp with tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret M., Romby P., Giegé R., Litvak S. Interactions between avian myeloblastosis reverse transcriptase and tRNATrp. Mapping of complexed tRNA with chemicals and nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2259–2271. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett R. A., Olesen S. O. Structure of eukaryotic 5S ribonucleic acid: a study of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5S ribonucleic acid with ribonucleases. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4823–4830. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giege R., Moras D., Thierry J. C. Yeast transfer RNAasp: a new high-resolution x-ray diffracting crystal form of a transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep;115(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayatsu H. Bisulfite modification of nucleic acids and their constituents. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;16:75–124. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60756-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Saenger W. Specific protein-nucleic acid recognition in ribonuclease T1-2'-guanylic acid complex: an X-ray study. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):27–31. doi: 10.1038/299027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook S. R., Sussman J. L., Warrant R. W., Church G. M., Kim S. H. RNA-ligant interactions. (I) Magnesium binding sites in yeast tRNAPhe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2811–2820. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Klug A. Crystallographic refinement of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA at 2-5A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 25;108(4):619–649. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Klug A. A crystallographic study of metal-binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 15;111(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. E., Reed D. J. Reaction of DNA with alkylating agents. Quantitation of alkylation by ethylnitrosourea of oxygen and nitrogen sites on poly[dA-dT] including phosphotriester formation. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5098–5107. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Draper D. E. Secondary structure of a 345-base RNA fragment covering the S8/S15 protein binding domain of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5052–5061. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., White S. A., Draper D. E. Detection of high-affinity intercalator sites in a ribosomal RNA fragment by the affinity cleavage intercalator methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II). Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5062–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Ando Y., Shiba T. Unusual priming mechanism of RNA-directed DNA synthesis in copia retrovirus-like particles of Drosophila. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):824–826. doi: 10.1038/323824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuśmierek J. T., Singer B. Sites of alkylation of poly(U) by agents of varying carcinogenicity and stability of products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):420–431. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINN S., LEHMAN I. R. AN ENDONUCLEASE FROM NEUROSPORA CRASSA SPECIFIC FOR POLYNUCLEOTIDES LACKING AN ORDERED STRUCTURE. II. STUDIES OF ENZYME SPECIFICITY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1294–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Pullman A. A new theoretical index of biochemical reactivity combining steric and electrostatic factors. An application to yeast tRNAPhe. Biophys Chem. 1984 Mar;19(2):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(84)85017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lempereur L., Nicoloso M., Riehl N., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Bachellerie J. P. Conformation of yeast 18S rRNA. Direct chemical probing of the 5' domain in ribosomal subunits and in deproteinized RNA by reverse transcriptase mapping of dimethyl sulfate-accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8339–8357. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard N. J., McDonald J. J., Henderson R. E., Reichmann M. E. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Adenosine. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3335–3342. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy C. C., Karpetsky T. P. The purification and properties of chicken liver RNase: An enzyme which is useful in distinguishing between cytidylic and uridylic acid residues. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2153–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Kumar A. Mapping tRNA structure in solution using double-strand-specific ribonuclease V1 from cobra venom. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5125–5140. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber B., Giegé R., Ebel J. P., Berthet C., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Crystallization of a tRNA . aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex. Characterization and first crystallographic data. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8429–8435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman H. B., Draper D. E. On the recognition of helical RNA by cobra venom V1 nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5396–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J., Nazar R. N. Evolutionary changes in the higher order structure of the ribosomal 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):161–179. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall J., Nazar R. N. Tertiary structure of the eukaryotic ribosomal 5 S RNA. Accessibility of phosphodiester bonds to ethylnitrosourea modification. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5256–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
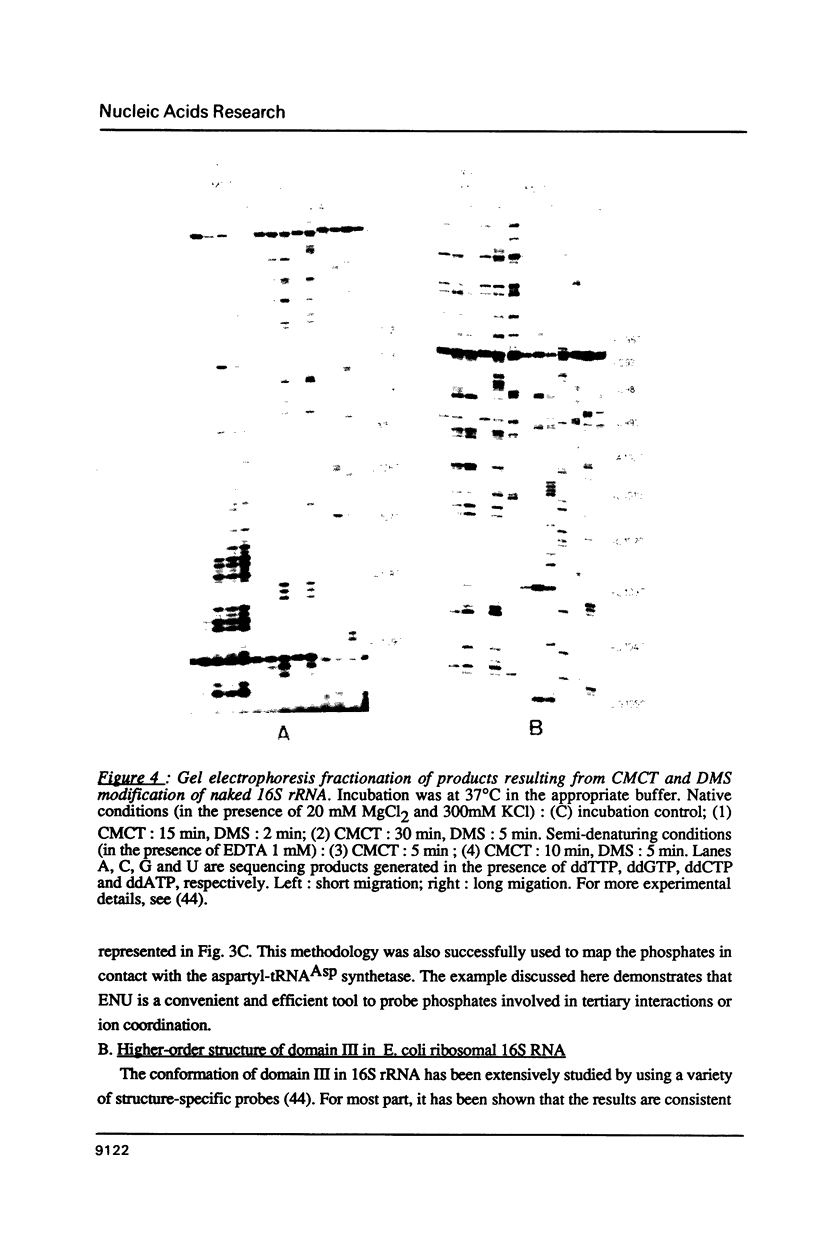
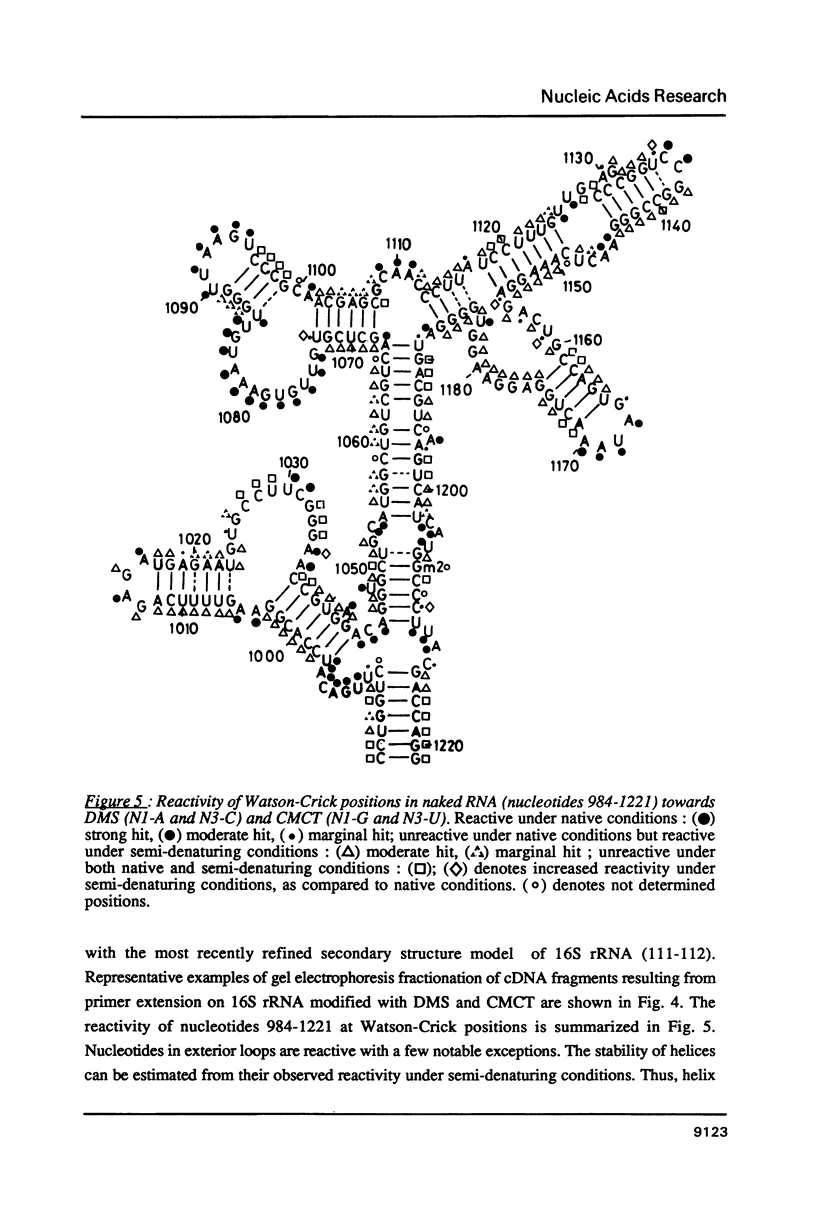
- Moazed D., Stern S., Noller H. F. Rapid chemical probing of conformation in 16 S ribosomal RNA and 30 S ribosomal subunits using primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):399–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor R., Ho N. W., Gilham P. T. Selective chemical modifications of uridine and pseudouridine in polynucleotides and their effect on the specificities of ribonuclease and phosphodiesterases. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Sep 20;87(18):4209–4210. doi: 10.1021/ja01096a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R., Tinoco I., Jr, Jacobson A. B. Secondary structure model for the complete simian virus 50 late precursor mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):351–363. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. A "bulged" double helix in a RNA-protein contact site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7331–7335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Digweed M., Bartsch M., Erdmann V. A. Comparative structural analysis of cytoplasmic and chloroplastic 5S rRNA from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):591–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Digweed M., Erdmann V. A. RNA structural dynamics: pre-melting and melting transitions in E. coli 5S rRNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Dec;3(3):495–514. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Three-dimensional structural model of eubacterial 5S RNA that has functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu H. L., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Improved methods for structure probing in large RNAs: a rapid 'heterologous' sequencing approach is coupled to the direct mapping of nuclease accessible sites. Application to the 5' terminal domain of eukaryotic 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5903–5920. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Teeter M. M., Rich A. Structural analysis of spermine and magnesium ion binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley G. J., Wang A. H., Seeman N. C., Suddath F. L., Rich A., Sussman J. L., Kim S. H. Hydrogen bonding in yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4866–4870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin E. Z., Mustard M., Fraser M. J. Specific inhibition by ATP and other properites of an endonuclease of Neurospora crassa. Can J Biochem. 1968 Oct;46(10):1285–1291. doi: 10.1139/o68-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rether B., Bonnet J., Ebel J. P. Studies on tRNA nucleotidyltransferase from baker's yeast. 1. Purification of the enzyme. Protection against thermal inactivation and inhibition by several substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld K., Van Poelgeest R., Pleij C. W., Van Boom J. H., Bosch L. The tRNA-like structure at the 3' terminus of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Differences and similarities with canonical tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1929–1946. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J. Characterization of the RNA binding properties of transcription factor IIIA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5369–5387. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
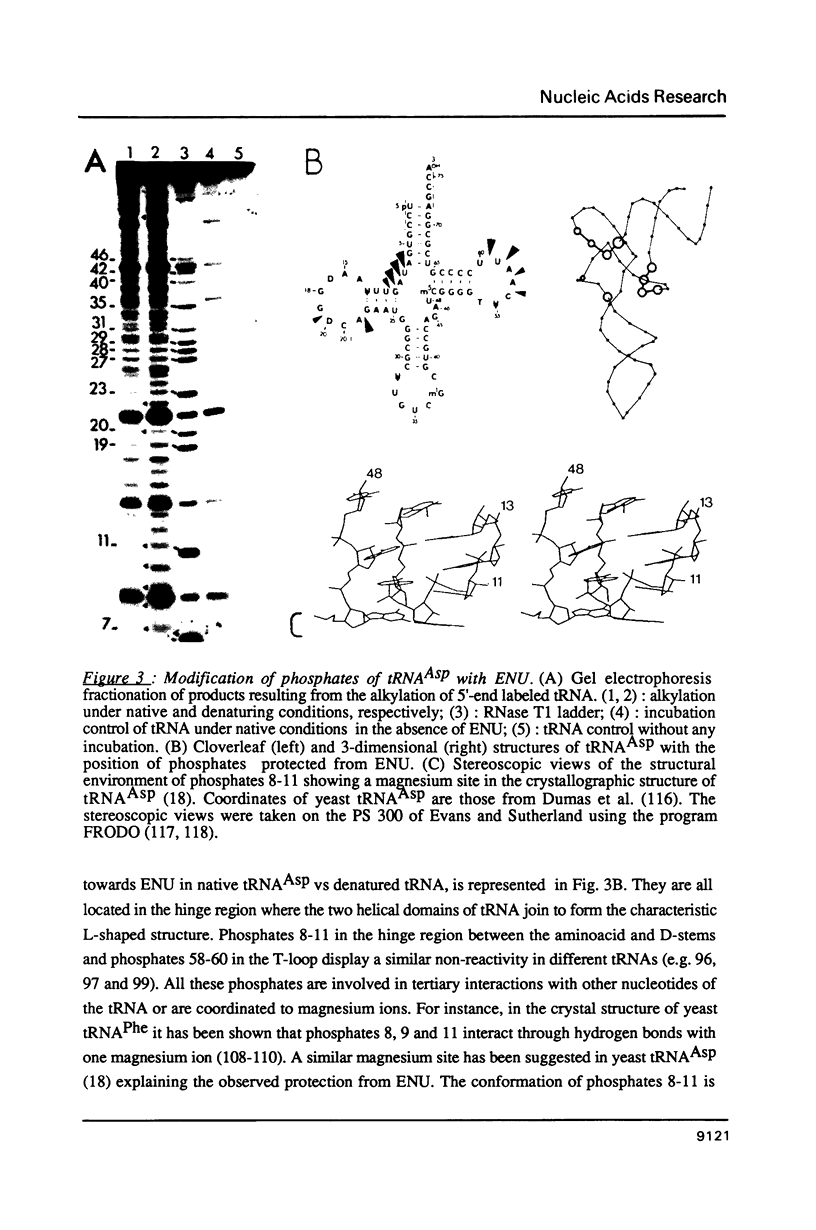
- Romby P., Moras D., Bergdoll M., Dumas P., Vlassov V. V., Westhof E., Ebel J. P., Giegé R. Yeast tRNAAsp tertiary structure in solution and areas of interaction of the tRNA with aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. A comparative study of the yeast phenylalanine system by phosphate alkylation experiments with ethylnitrosourea. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):455–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romby P., Moras D., Dumas P., Ebel J. P., Giegé R. Comparison of the tertiary structure of yeast tRNA(Asp) and tRNA(Phe) in solution. Chemical modification study of the bases. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romby P., Westhof E., Moras D., Giegé R., Houssier C., Grosjean H. Studies on anticodon-anticodon interactions: hemi-protonation of cytosines induces self-pairing through the GCC anticodon of E. coli tRNA-Gly. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Oct;4(2):193–203. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Krupp G., Gough S., Berry-Lowe S., Kannangara C. G., Söll D. The RNA required in the first step of chlorophyll biosynthesis is a chloroplast glutamate tRNA. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):281–284. doi: 10.1038/322281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Cohen B. I., Shiuey S. J., Maurer H. On the reaction of guanine with glyoxal, pyruvaldehyde, and kethoxal, and the structure of the acylguanines. A new synthesis of N2-alkylguanines. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):238–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Hachmann J. The reaction of guanine derivatives with 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2799–2807. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa M., Padmanabhan R. Inhibition of a nuclease contaminant in the commercial preparations of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90756-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. All oxygens in nucleic acids react with carcinogenic ethylating agents. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):333–339. doi: 10.1038/264333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Wilson R. C., Noller H. F. Localization of the binding site for protein S4 on 16 S ribosomal RNA by chemical and enzymatic probing and primer extension. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. L., Holbrook S. R., Warrant R. W., Church G. M., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. I. Crystallographic refinement. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):607–630. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSinger B., Fraenkel-Conrat H. The specificity of different classes of ethylating agents toward various sites in RNA. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):772–782. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troutt A., Savin T. J., Curtiss W. C., Celentano J., Vournakis J. N. Secondary structure of Bombyx mori and Dictyostelium discoideum 5S rRNA from S1 nuclease and cobra venom ribonuclease susceptibility, and computer assisted analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):653–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Arima T., Egami F. Specificity of RNase U2. J Biochem. 1970 Jan;67(1):91–102. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Stolk B. J., Noller H. F. Chemical probing of conformation in large RNA molecules. Analysis of 16 S ribosomal RNA using diethylpyrocarbonate. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):151–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary C. P., Vournakis J. N. RNA structure analysis using T2 ribonuclease: detection of pH and metal ion induced conformational changes in yeast tRNAPhe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6763–6778. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary C. P., Vournakis J. N. RNA structure analysis using methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II): a base-pair-specific RNA structure probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6978–6982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko S. K., Ryte V. C. [Isolation of highly purified ribonuclease from cobra (Naja oxiana) venom]. Biokhimiia. 1975 May-Jun;40(3):578–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincze A., Henderson R. E., McDonald J. J., Leonard N. J. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Bases and nucleosides derived from guanine, cytosine, and uracil. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Apr 18;95(8):2677–2682. doi: 10.1021/ja00789a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassov V. V., Giegé R., Ebel J. P. Tertiary structure of tRNAs in solution monitored by phosphodiester modification with ethylnitrosourea. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassov V. V., Kern D., Romby P., Giegé R., Ebel J. P. Interaction of tRNAPhe and tRNAVal with aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. A chemical modification study. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):537–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington R. C. Ribonuclease T1 catalyzed degradation of transfer RNA: an unusual alteration induced by urea. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 14;353(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Dumas P., Moras D. Crystallographic refinement of yeast aspartic acid transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):119–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermeyer W., Zachau H. G. Tertiary structure interactions of 7-methylguanosine in yeast tRNA Phe as studied by borohydride reduction. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):306–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Clayton D. A. DNA primase of human mitochondria is associated with structural RNA that is essential for enzymatic activity. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90556-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo N. H., Roe B. A., Rich A. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli initiator tRNAfMet. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):346–351. doi: 10.1038/286346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Wurst R., Vournakis J., Rich A. Conformational changes of yeast tRNAPhe and E. coli tRNA2Glu as indicated by different nuclease digestion patterns. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9608–9616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Klug A. A model for the tertiary structure of mammalian mitochondrial transfer RNAs lacking the entire 'dihydrouridine' loop and stem. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1309–1321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]