Abstract
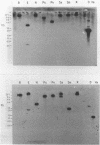
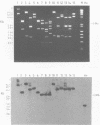
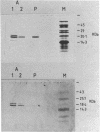
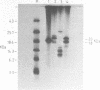
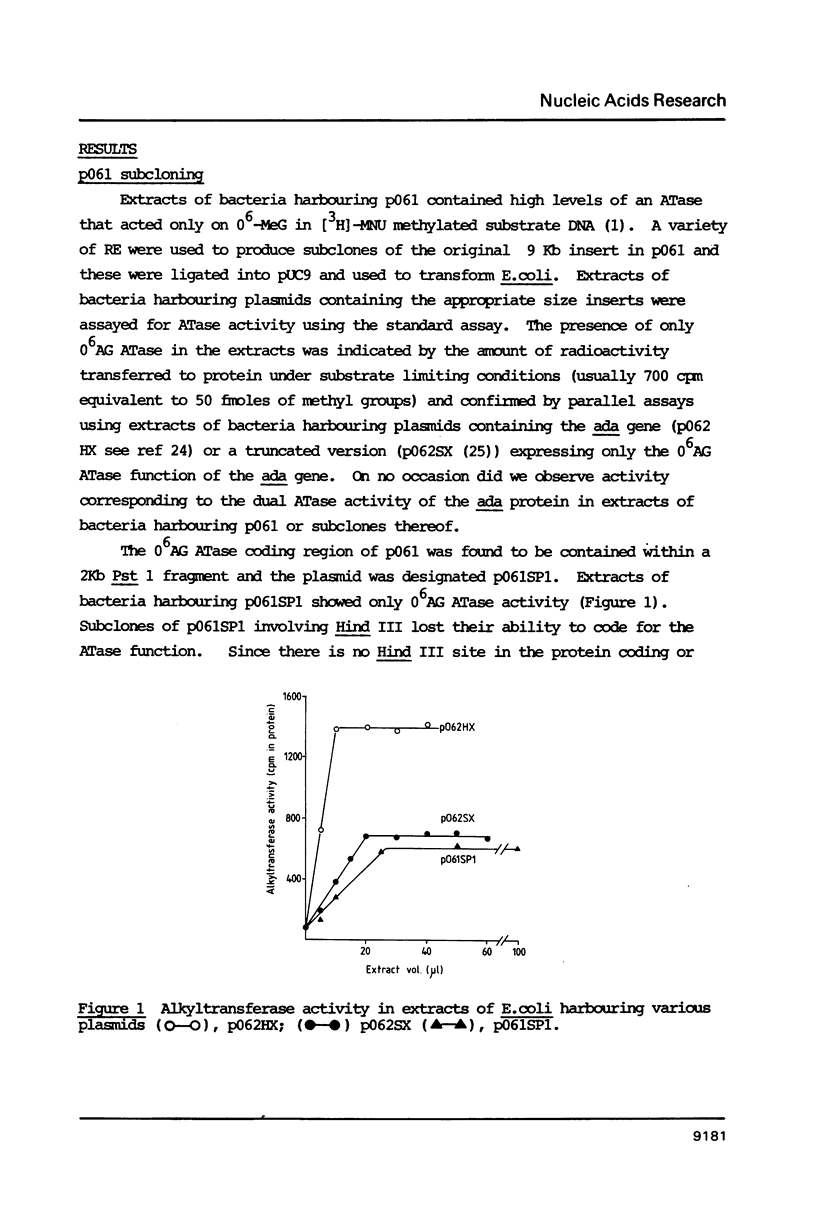
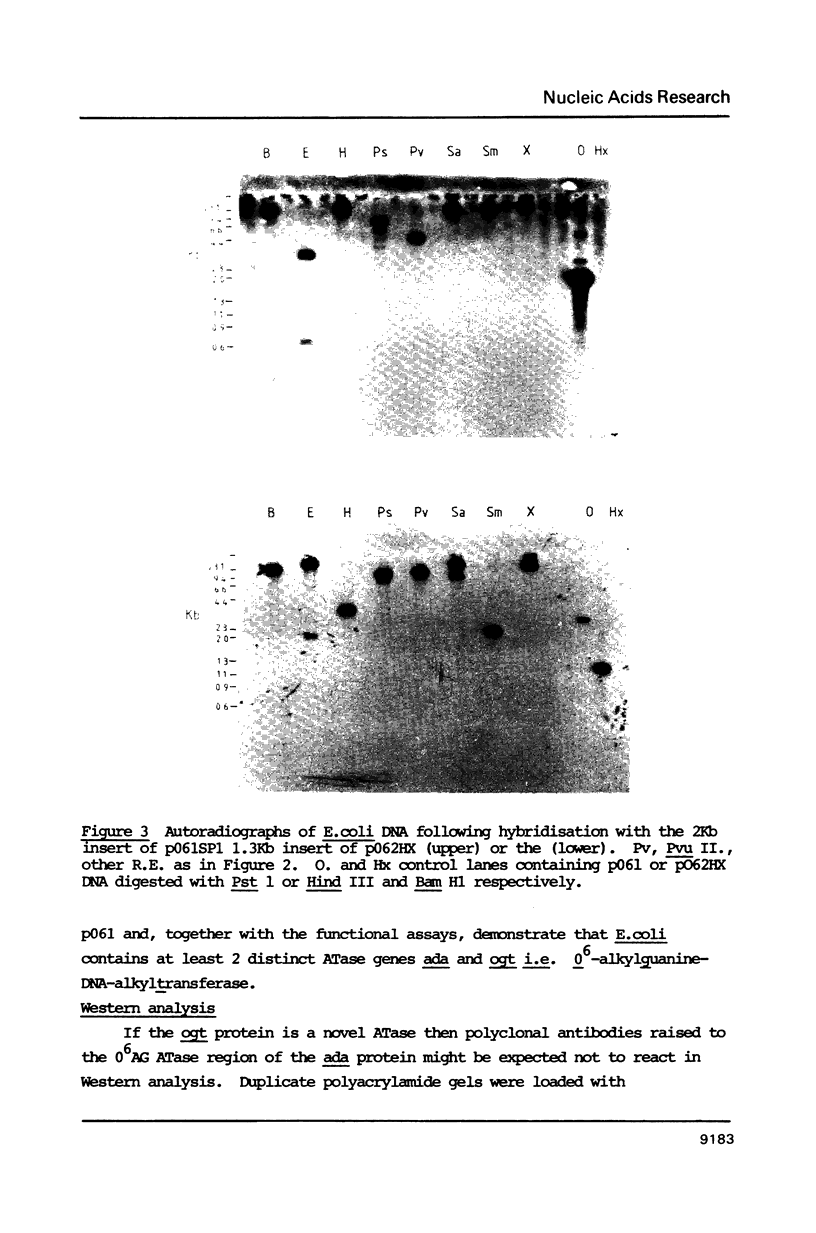
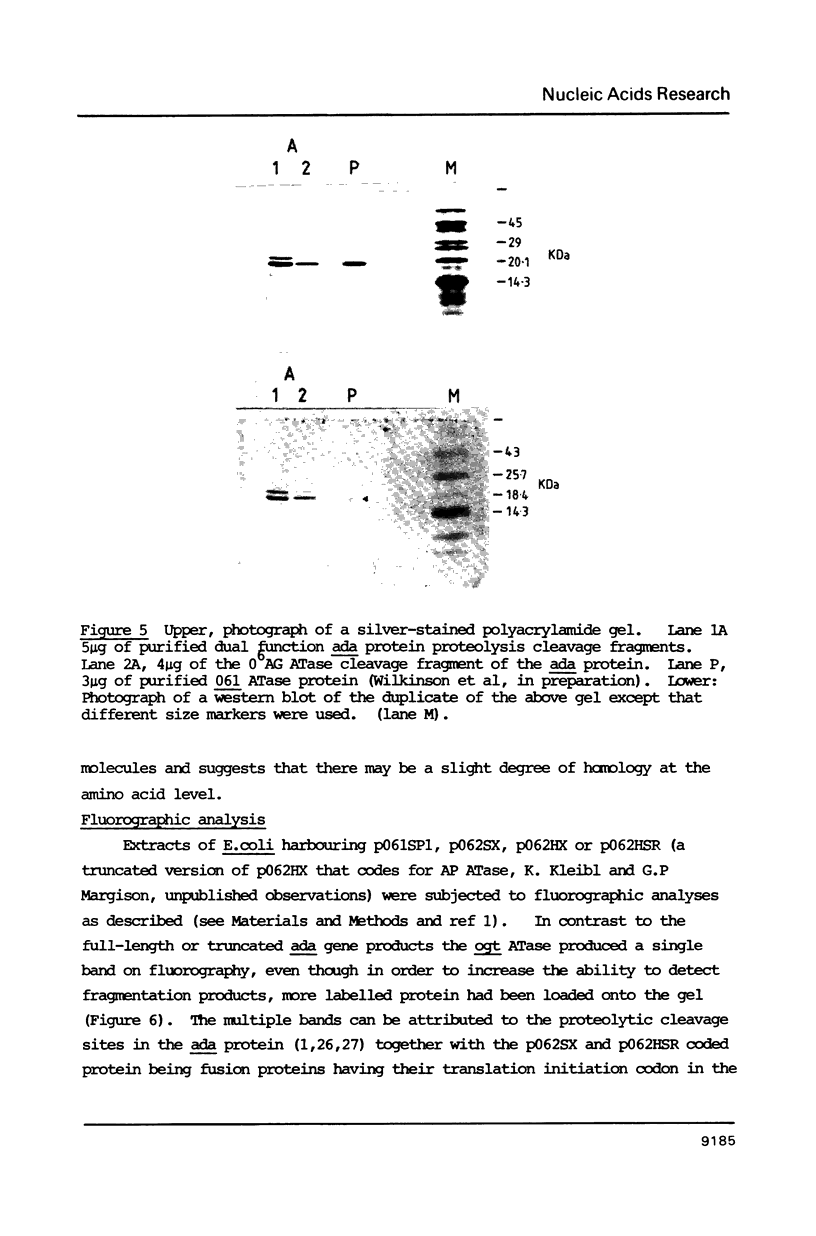
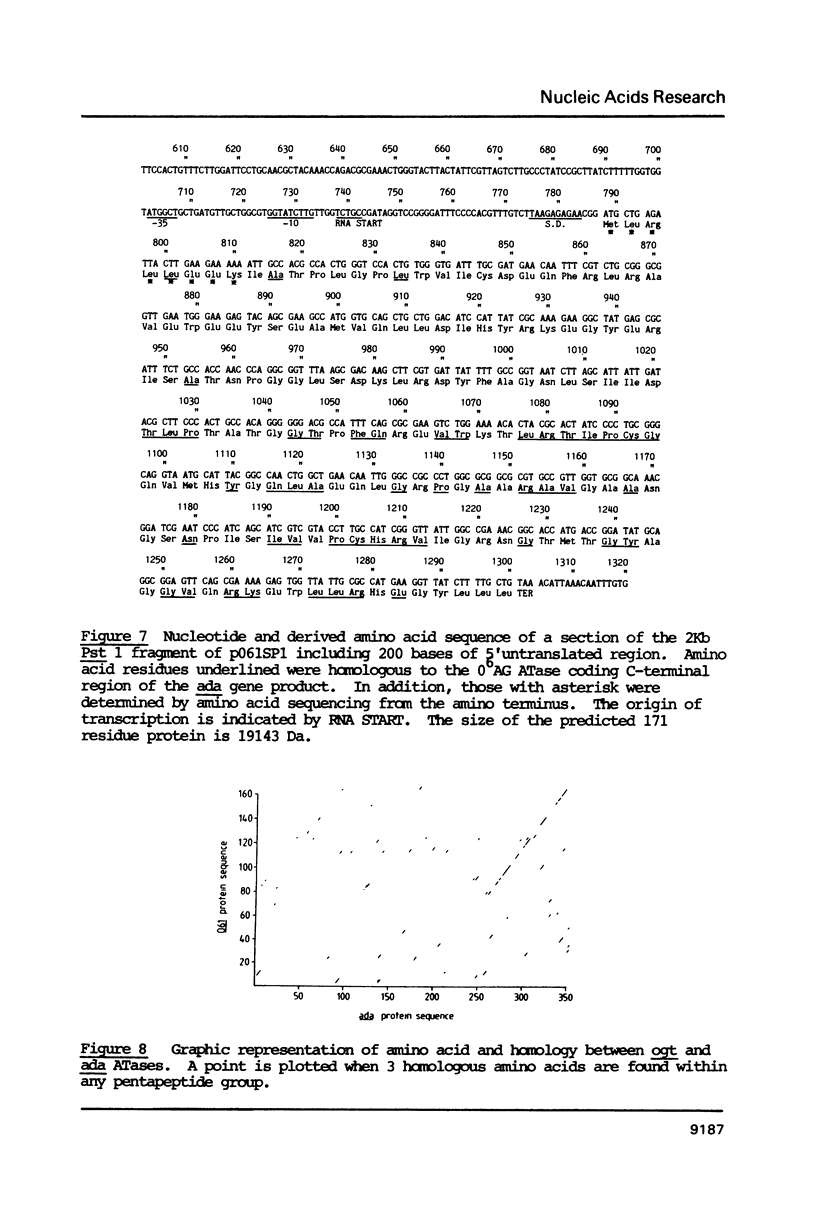
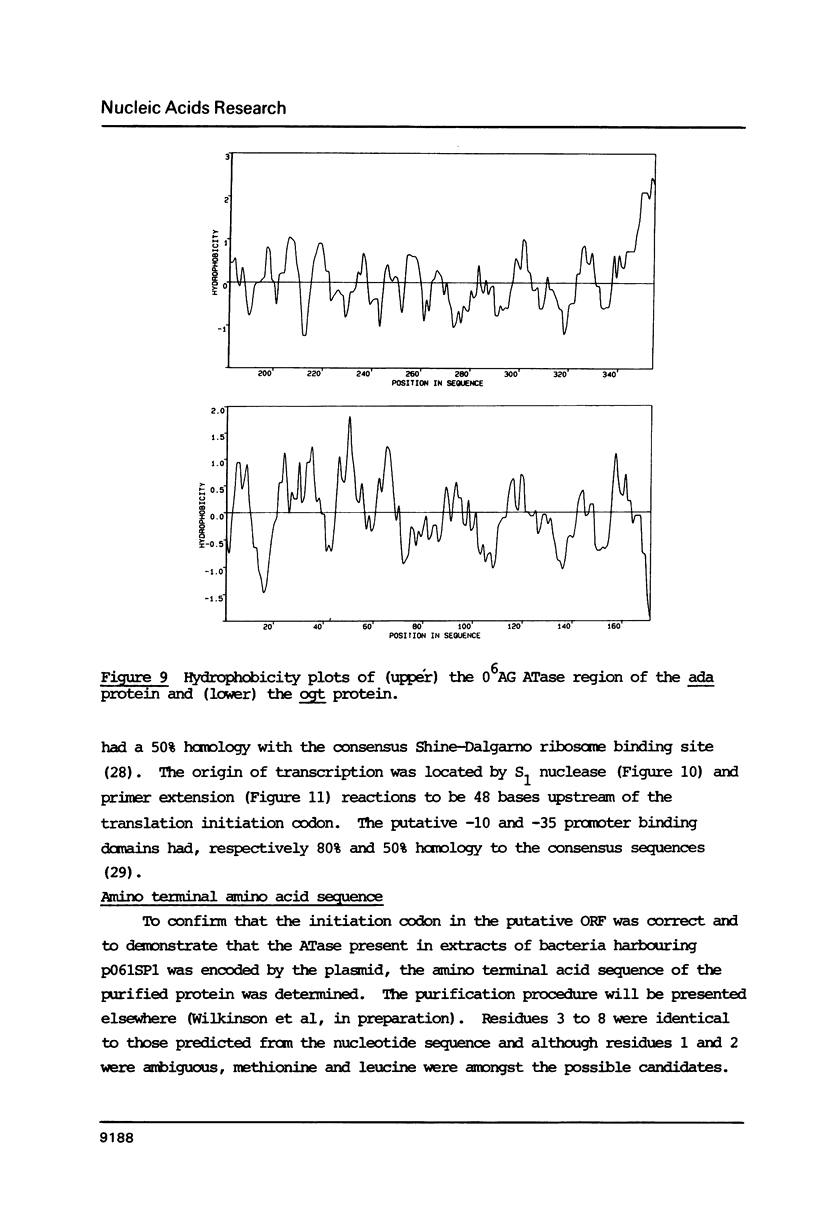
The plasmid pO61 that was isolated from an E. coli genomic DNA library and codes for O6-alkylguanine (O6AG) DNA alkyltransferase (ATase) activity (1) has been further characterised. Subclones of the 9 Kb insert of pO61 showed that the ATase activity was encoded in a 2Kb Pst1 fragment but a partial restriction endonuclease map of this was different to that of the E. coli ada gene that codes for O6-AG and alkylphosphotriester dual ATase protein. Fluorographic analyses confirmed that the molecular weight of the pO61-encoded ATase was 19KDa i.e. similar to that of the O6AG ATase function that is cleaved from the 39KDa ada protein but rabbit polyclonal antibodies to the latter reacted only very weakly with the pO61-encoded protein. A different set of hybridisation signals was produced when E. coli DNA, which had been digested with a variety of restriction endonucleases was probed with 2Kb Pst 1 fragment or the ada gene. These results provided evidence for the existence of a second ATase gene in E. coli. The 2Kb Pst-1 fragment of pO61 was therefore sequenced and an open reading frame (ORF) that would give rise to a 19KDa protein was identified. The derived amino acid sequence of this showed a 93 residue region with 49% homology with the O6AG ATase region of the ada protein and had a pentamer and a heptamer of identical sequence separated by 34 amino acids in both proteins. The pentamer included the alkyl accepting cysteine residue of the ada O6AG ATase. The hydrophobic domains were similarly distributed in both proteins. Shine-Dalgarno, -10 and -35 sequences were identified and the origin of transcription was located by primer extension and S1 nuclease mapping. The amino-terminal amino acid sequence of the protein was as predicted from the ORF.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Margison G. P. Expression in mammalian cells of a truncated Escherichia coli gene coding for O6-alkylguanine alkyltransferase reduces the toxic effects of alkylating agents. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Dec;7(12):2081–2084. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.12.2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Margison G. P. Expression of the E. coli O6-methylguanine-methylphosphotriester methyltransferase gene in mammalian cells. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Jan;7(1):185–188. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.1.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B. Mutant Escherichia coli Ada proteins simultaneously defective in the repair of O6-methylguanine and in gene activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5575–5589. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Sedgwick B., Robins P., Totty N., Waterfield M. D., Lindahl T. Active site and complete sequence of the suicidal methyltransferase that counters alkylation mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2688–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley P. D., Orr D. J. Specific excision of methylation products from DNA of Escherichia coli treated with N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Chem Biol Interact. 1970 Aug;2(2):154–157. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(70)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margison G. P., Cooper D. P., Brennand J. Cloning of the E. coli O6-methylguanine and methylphosphotriester methyltransferase gene using a functional DNA repair assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1939–1952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Karran P., Lindahl T. Inducible repair of O-alkylated DNA pyrimidines in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):545–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. Methyl phosphotriesters in alkylated DNA are repaired by the Ada regulatory protein of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2683–2698. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J. R., Ludlum D. B., Renard A., Verly W. G. Repair of O6-ethylguanine in DNA by a chromatin fraction from rat liver: transfer of the ethyl group to an acceptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6766–6770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micard D., Sobrier M. L., Couderc J. L., Dastugue B. Purification of RNA-free plasmid DNA using alkaline extraction followed by Ultrogel A2 column chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jul;148(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90636-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohoshi F., Munakata N. Multiple species of Bacillus subtilis DNA alkyltransferase involved in the adaptive response to simple alkylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):587–592. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.587-592.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor P. J., Capps M. J., Craig A. W. Comparative studies of the hepatocarcinogen N,N-dimethylnitrosamine in vivo: reaction sites in rat liver DNA and the significance of their relative stabilities. Br J Cancer. 1973 Feb;27(2):153–166. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffhill R., Margison G. P., O'Connor P. J. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by alkylating agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 17;823(2):111–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Cairns J. A new pathway for DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):281–283. doi: 10.1038/267281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B. Genetic mapping of ada and adc mutations affecting the adaptive response of Escherichia coli to alkylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):984–988. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.984-988.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Fukuda R. Structure of the gene for the stringent starvation protein of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1153–1163. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell P. A. A large database DNA sequence handling program with generalized searching specifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):115–125. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Kilpatrick M. W., McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. The intracellular signal for induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinfeld M., Drake A. F., Saunders J. K., Paterson M. C. Stereospecific removal of methyl phosphotriesters from DNA by an Escherichia coli ada+ extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7067–7077. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]