Abstract
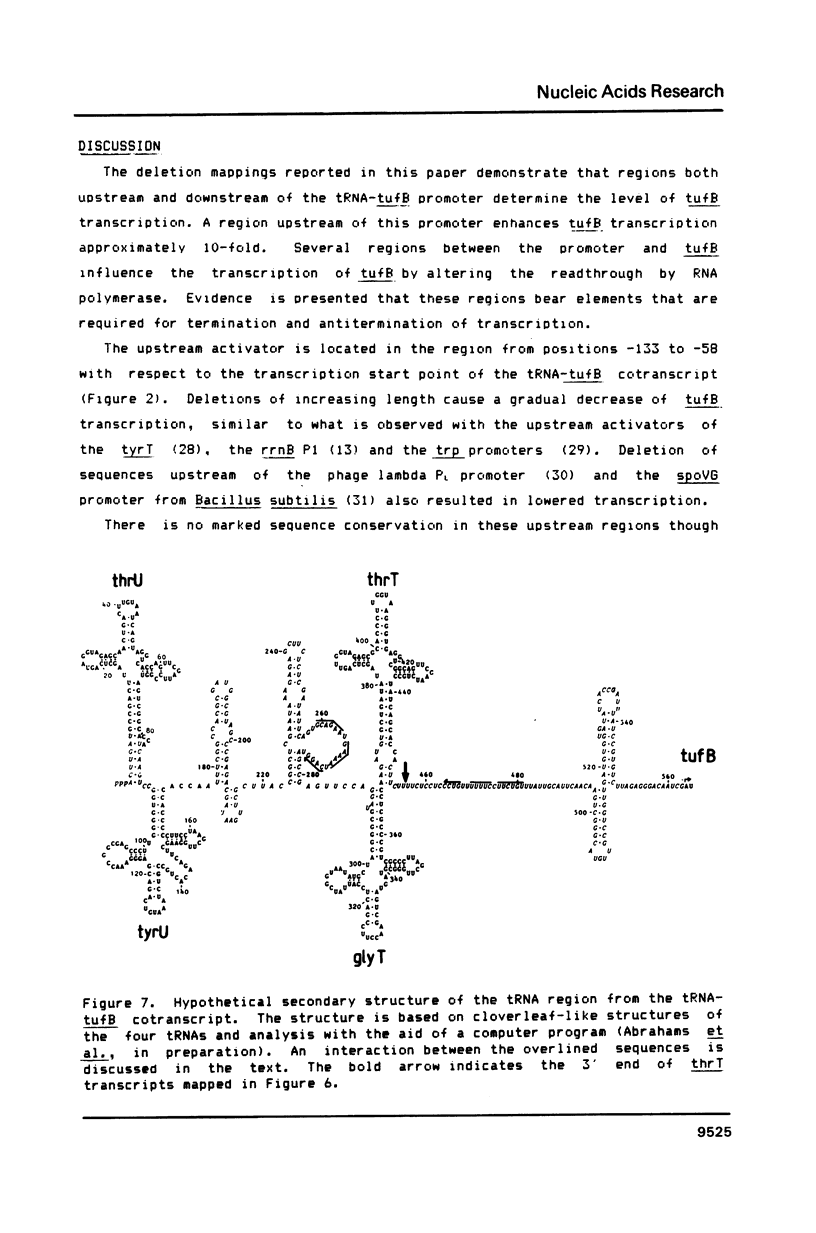
Signals setting the level of transcription of the tRNA-tufB operon have been studied by deletion mapping. TufB transcription was measured in vivo with plasmid-borne tRNA-tufB:galk operon fusions. Removal of the sequences from -133 to -58 with respect to the transcription start point, results in a 90% decrease of tufB transcription. This demonstrates the presence of a region, upstream of the tRNA-tufB promoter, that enhances the expression of the operon. DNA fragments bearing this upstream activator region do not display an abnormal electrophoretic mobility, as has been observed for the rrnB P1 upstream activator. Deletions starting in the first tRNA gene and directing towards tufB reveal at least two sites that influence tufB transcription. One signals transcription termination in the intergenic region between thrT and tufB. The other may be involved in antitermination. Possible mechanisms underlying antitermination and termination are considered in the light of the nucleotide sequence.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Hatfield G. W. Effects of promoter strengths and growth conditions on copy number of transcription-fusion vectors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7399–7403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Friesen J. D. The nucleotide sequence of tufB and four nearby tRNA structural genes of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossi L., Smith D. M. Conformational change in the DNA associated with an unusual promoter mutation in a tRNA operon of Salmonella. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Carbon J. The nucleotide sequence of a precursor to the glycine- and threonine-specific transfer ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5542–5555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. R., Georgopoulos C., Tilly K., Herskowitz I., Banuett F. Interactions of bacteriophage and host macromolecules in the growth of bacteriophage lambda. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):299–325. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.299-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Definition of a novel promoter for the major adenovirus-associated virus mRNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Wells R. D. The leftward promoter of bacteriophage lambda. Structure, biological activity, and influence by adjacent regions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):2003–2009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Boyce R. P., Theriot L. Three loci in Escherichia coli K-12 that control the excision of pyrimidine dimers and certain other mutagen products from DNA. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1119–1136. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L., Rossi J., Landy A. Dual function transcripts specifying tRNA and mRNA. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):422–427. doi: 10.1038/294422a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinks-Robertson S., Gourse R. L., Nomura M. Expression of rRNA and tRNA genes in Escherichia coli: evidence for feedback regulation by products of rRNA operons. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):865–876. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Genetically separable functional elements mediate the optimal expression and stringent regulation of a bacterial tRNA gene. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Roberts J. W., Wu R., Georges F., Narang S. A. A potential stem-loop structure and the sequence CAAUCAA in the transcript are insufficient to signal rho-dependent transcription termination at lambda tR1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1287–1299. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., An G., Friesen J. D., Fill N. P. Location of the tufB promoter of E. coli: cotranscription of tufB with four transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Squires C. L., Squires C. Antitermination of E. coli rRNA transcription is caused by a control region segment containing lambda nut-like sequences. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Archer R., Zengel J. M. Transcription of the S10 ribosomal protein operon is regulated by an attenuator in the leader. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:297–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Shibuya M., Kaziro Y. Construction and characterization of the two hybrid Co1E1 plasmids carrying Escherichia coli tufB gene. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Shibuya M., Kuchino Y., Kaziro Y. Transcription of the E. coli tufB gene: cotranscription with four tRNA genes and inhibition by guanosine-5'-diphosphate-3'-diphosphate. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):13–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00270131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Yokota T., Takebe Y., Nakamura M., Kaziro Y. A deletion mutant lacking three out of four transfer RNA genes upstream of the coding region of tufB. J Biochem. 1983 Apr;93(4):1101–1108. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima-Sugano J., Kaziro Y. Regulation of the expression of the tufB operon: DNA sequences directly involved in the stringent control. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1053–1058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03738.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima-Sugano J., Miyajima A., Kaziro Y. Selective inhibition of transcription of the E. coli tufB operon by guanosine-5'-diphosphate-3'-diphosphate. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(2):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00337802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. A. Antitermination mechanisms in rRNA operons of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.1-5.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Itoh S. Enhancement of transcriptional activity of the Escherichia coli trp promoter by upstream A + T-rich regions. Gene. 1986;44(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock R. A., Gourse R. L., Nomura M. Defective antitermination of rRNA transcription and derepression of rRNA and tRNA synthesis in the nusB5 mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5275–5279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Conserved features of coordinately regulated E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2605–2618. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Lamond A. I., Mace H. A., Berman M. L. RNA polymerase interactions with the upstream region of the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90229-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Lamond A. I., Weeks J. R. Alteration of the growth-rate-dependent regulation of Escherichia coli tyrT expression by promoter mutations. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider H. J., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. A relationship between DNA helix stability and recognition sites for RNA polymerase. Science. 1979 Aug 3;205(4405):508–511. doi: 10.1126/science.377494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. Transcription of ribosomal genes during a nutritional shift-up of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1095–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1095-1097.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Kastelein R. A., Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. tuf gene dosage effects on the intracellular concentration of EF-TuB. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Vijgenboom E., Talens A., Bosch L. The role of EF-Tu in the expression of tufA and tufB genes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):397–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




