Abstract
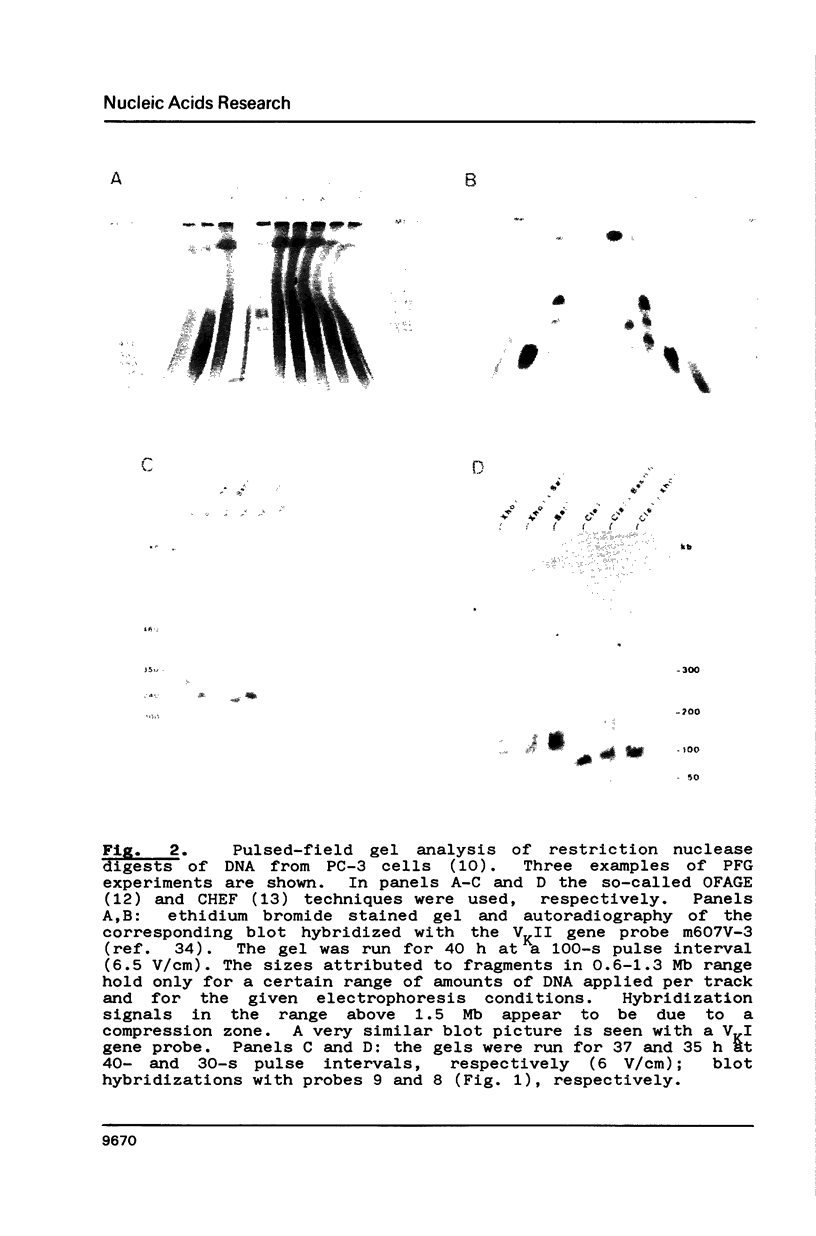
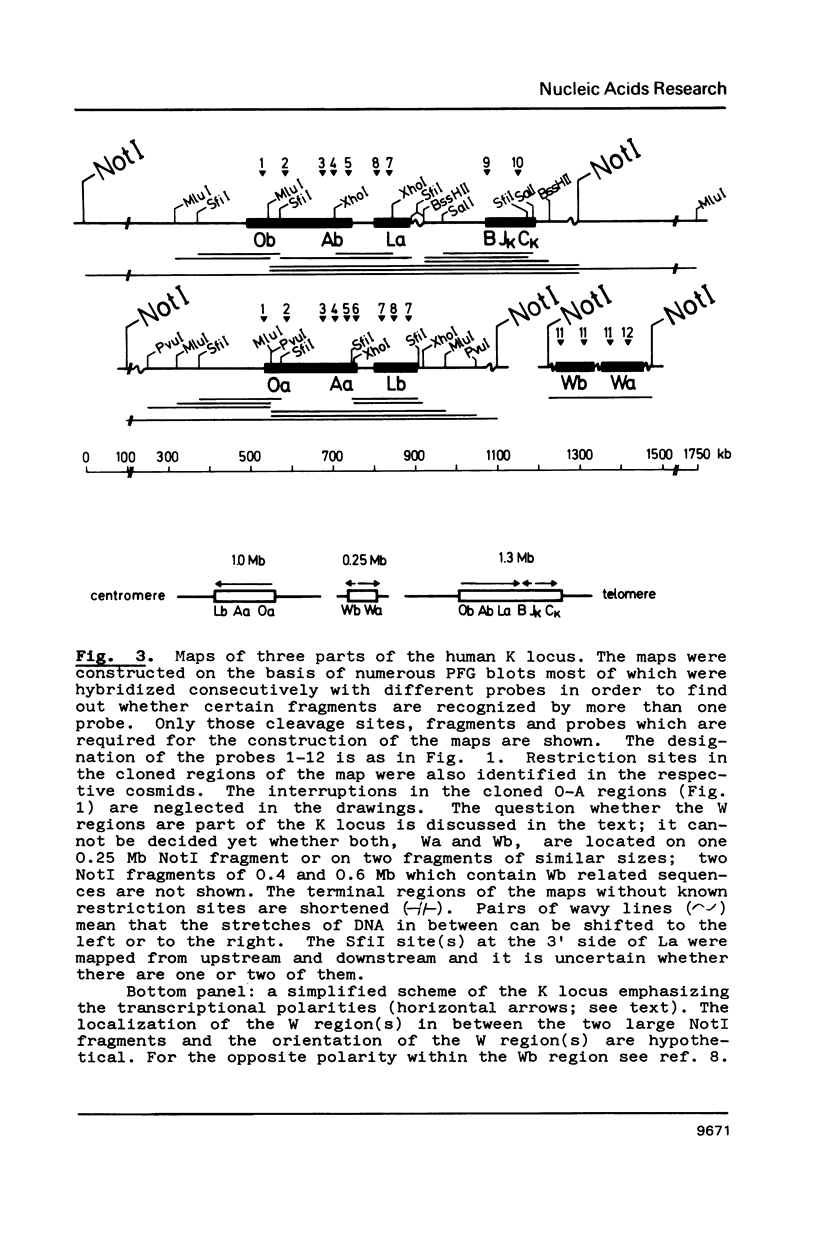
Genomic regions containing numerous cloned VK genes (abbreviations in ref. 2) were investigated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. 31 and 32 genes were linked within 1.0 and 1.3 Mb NotI fragments, respectively; the latter fragment includes also the JKCK gene segment. A 0.25 Mb NotI fragment comprises further 10 VK genes. Since the transcriptional polarities of the VK genes within the genomic regions are known the linking of the regions allows us now to answer unequivocally some longstanding questions concerning the mechanism of VK-JK rearrangement. The VK genes of the 1.3 Mb NotI fragment except for the two JK proximal ones (accompanying paper) are arranged in the same transcriptional polarity as JKCK and therefore must rearrange by a deletion mechanism. The VK genes of the 1.0 Mb NotI fragment which has not yet been linked to VKJK have identical polarity within the fragment. They should be arranged in opposite polarity to JKCK since reciprocal recombination products derived from them are known to exist; such recombination products must have been formed by inversion of oppositely oriented gene segments.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Evolution of immunoglobulin V genes: evidence indicating that recently duplicated human V kappa sequences have diverged by gene conversion. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deev S. M., Combriato G., Klobeck H. G., Zachau H. G. Reciprocal recombination products of VK-JK joining reactions in human lymphoid cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Finan J., Emanuel B., Lenoir G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Translocation of an immunoglobulin kappa locus to a region 3' of an unrearranged c-myc oncogene enhances c-myc transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7581–7585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feddersen R. M., Van Ness B. G. Double recombination of a single immunoglobulin kappa-chain allele: implications for the mechanism of rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4793–4797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Gellert M., Mizuuchi K. Extrachromosomal DNA substrates in pre-B cells undergo inversion or deletion at immunoglobulin V-(D)-J joining signals. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Habu S. Origin of immune diversity: genetic variation and selection. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:803–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höchtl J., Müller C. R., Zachau H. G. Recombined flanks of the variable and joining segments of immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaighn M. E., Narayan K. S., Ohnuki Y., Lechner J. F., Jones L. W. Establishment and characterization of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest Urol. 1979 Jul;17(1):16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Bornkamm G. W., Combriato G., Mocikat R., Pohlenz H. D., Zachau H. G. Subgroup IV of human immunoglobulin K light chains is encoded by a single germline gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6515–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Combriato G., Zachau H. G. Immunoglobulin genes of the kappa light chain type from two human lymphoid cell lines are closely related. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):6995–7006. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.6995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Combriato G., Zachau H. G. N segment insertion and region-directed somatic hypermutation in a kappa gene of a t(2;8) chromosomal translocation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4877–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Solomon A., Zachau H. G. Contribution of human V kappa II germ-line genes to light-chain diversity. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):73–76. doi: 10.1038/309073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Gifford A., Baltimore D. Joining of V kappa to J kappa gene segments in a retroviral vector introduced into lymphoid cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):425–428. doi: 10.1038/308425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lötscher E., Grzeschik K. H., Bauer H. G., Pohlenz H. D., Straubinger B., Zachau H. G. Dispersed human immunoglobulin kappa light-chain genes. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):456–458. doi: 10.1038/320456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., McCoy C., Blanc D., Trucy J., Devaux C., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Fitch F., Hood L., Malissen B. Direct evidence for chromosomal inversion during T-cell receptor beta-gene rearrangements. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):28–33. doi: 10.1038/319028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh P., Mills F., Gould H. Detection of a unique human V kappa IV germline gene by a cloned cDNA probe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6531–6544. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Smola H., Pohlenz H. D., Straubinger B., Gerl R., Zachau H. G. A large section of the gene locus encoding human immunoglobulin variable regions of the kappa type is duplicated. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlenz H. D., Straubinger B., Thiebe R., Pech M., Zimmer F. J., Zachau H. G. The human V kappa locus. Characterization of extended immunoglobulin gene regions by cosmid cloning. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Kekish O., Batter D., Grenier J., Balazs I., Henderson E., Zegers B. J. Aberrant recombination events in B cell lines derived from a kappa-deficient human. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3495–3514. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Altenburger W., Zachau H. G. A rearranged DNA sequence possibly related to the translocation of immunoglobulin gene segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1709–1720. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Vollmer A. C., Erikson J., Isobe M., Croce C., Parnes J. R. Gene for the human T cell differentiation antigen Leu-2/T8 is closely linked to the kappa light chain locus on chromosome 2. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):429–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Weigert M. DNA between variable and joining gene segments of immunoglobulin kappa light chain is frequently retained in cells that rearrange the kappa locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]