Abstract
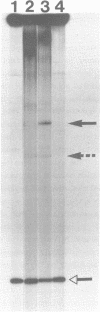
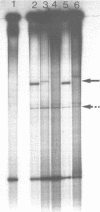
In Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae, the regulatory nodulation nodD gene has at least two functions. It constitutively represses its own transcription and in the presence of inducer flavonoid molecules, it activates the expression of two other nod gene transcriptional units, nodABCIJ and nodFE. Upstream of nodA and nodF is a conserved sequence, the nod box, which has been implicated in nodD-mediated transcriptional activation of these genes. DNA fragments spanning the nod boxes that precede nodA and nodF were end-labelled and were exposed to cell-free extracts obtained from strains of Rhizobium. Using the gel retardation technique, it was shown that a complex between protein and these DNA fragments was formed, but only if the extract contained a functional nodD gene. Evidence that the protein that binds to the regulatory sequences is the nodD gene product came from the observation that a complex was formed between the nod box preceding nodA and protein from a cell-free extract isolated from Escherichia coli containing the cloned nodD gene. Extracts from Rhizobium strains containing mutant forms of nodD which were specifically affected in autoregulation or in flavonoid-dependent activation formed either no protein DNA complex or formed a complex with altered mobility compared to that obtained with extracts from wild-type strains.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Sharma S. B. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti RCR2011 genes involved in host specificity of nodulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7453–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Redmond J. W., Batley M., Rolfe B. G. Clovers secrete specific phenolic compounds which either stimulate or repress nod gene expression in Rhizobium trifolii. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1173–1179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Fisher R. F., Jacobs T. W., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti 1021 nodulation genes: nodD is read divergently from nodABC. DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):241–248. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. J., Downie J. A. The nodI gene product of Rhizobium leguminosarum is closely related to ATP-binding bacterial transport proteins; nucleotide sequence analysis of the nodI and nodJ genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Brierley H. L., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Transcription of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Identification of a nodD transcription initiation site in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6849–6855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Tu J. K., Long S. R. Conserved Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1432–1435. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1432-1435.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Horvath B., Kondorosi E., Putnoky P., Rodriguez-Quiñones F., Kondorosi A. At least two nodD genes are necessary for efficient nodulation of alfalfa by Rhizobium meliloti. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Bachem C. W., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):841–848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. W., Downie J. A., Johnston A. W. Cloning of the nodulation (nod) genes of Rhizobium phaseoli and their homology to R. leguminosarum nod DNA. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. L., Gielow W. O., Wallace R. G. Mechanism of araC autoregulation and the domains of two overlapping promoters, Pc and PBAD, in the L-arabinose regulatory region of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. DNA sequence of the Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation genes nodAB and C required for root hair curling. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9497–9508. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossen L., Shearman C. A., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The nodD gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum is autoregulatory and in the presence of plant exudate induces the nodA,B,C genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3369–3373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Watson J. M. DNA sequence of Rhizobium trifolii nodulation genes reveals a reiterated and potentially regulatory sequence preceding nodABC and nodFE. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2891–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F. Conserved nodulation genes from the non-legume symbiont Bradyrhizobium sp. (Parasponia). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2905–2919. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman C. A., Rossen L., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation gene nodF encodes a polypeptide similar to acyl-carrier protein and is regulated by nodD plus a factor in pea root exudate. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):647–652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Kondorosi E., Stepkowski T., Pósfai J., Kondorosi A. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9509–9524. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]