Interfacing carbon nanotubes with biomaterials (DNA, proteins, etc.) for the development of sensitive amplified detection methods is a major challenge at the nanotechnology frontier. Amplified DNA detection is particularly important and sensitive, robust, and economically feasible detection methods for the analysis of genetic disorders or the detection of pathogens and biowarfare agents could have a major impact on human health and safety.1 Current detection methods have utilized enzymes,2 nanoparticles,3 quantum dots,4 piezoelectric devices,5 electrochemical approaches6 and nano-scale force interactions7 to address this difficult problem. Alternative methods based on hybrid biomaterial-carbon nanotube (CNT) systems find growing interest in the developing research area of nanotube-based field-effect transistors due to their excellent operating characteristics.8,9 Within this area, recent research efforts have focused on the detection of biomaterials using proteins,10 aptamers,11 and DNA.12 CNT network field-effect transistor (CNTNFET) devices for detection of antibodies13 and DNA14–16 have been explored and offer sensitivity, selectivity, and rapid analysis times coupled with low power and cost benefits.
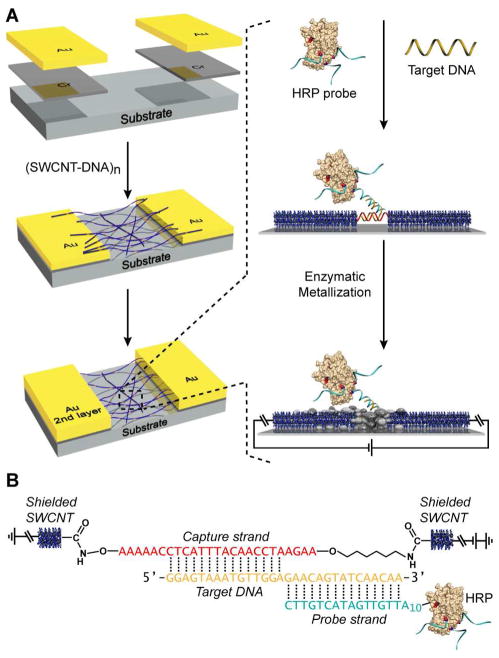
Here, we report a conductivity-based DNA detection method utilizing carbon nanotube-DNA network devices using oligonucleotide-functionalized enzymes (Figure 1). This method represents a straightforward approach to highly sensitive and selective detection of oligonucleotide analytes. Key to our sensor design is a new DNA linked-CNT nanowire material which we have recently reported, the synthesis of which relies on a new regioselective nanotube functionalization methodology.17,18 The sensing surface consists of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) bridging a gap between two single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT’s) via covalent attachment at their termini, leading to the formation of a network of ssDNA linked CNT wires fixed between two gold electrodes.19 In the presence of the ssDNA analyte, selective binding occurs at the ssDNA junction between contiguous nanotubes resulting in a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) assembly. The ssDNA analyte has adjacent recognition sequences that are complementary to the nanotube bridging capture strand at one end and to an oligonucleotide-functionalized enzyme (horseradish peroxidase, HRP) probe at the other end (Figure 1B).20,21 For HRP probe characterization see Figure S1. Thus, when the device is immersed in a solution consisting of the probe and analyte, the enzyme probe will hybridize with the analyte recognition domain and occupy the sensing gap between contiguous nanotubes. Exposure of the device to the appropriate reagents initiates enzymatic metallization, resulting in conductive connection between the interrupted nanotube wires upon analyte detection and provides significant signal amplification.22–24 The overall device assembly process and sensing strategy is outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Sensing strategy and device assembly. (A) Device assembly process and sensing scheme. (B) DNA-CNT nanowire and HRP probe hybridization for DNA junction visualization.
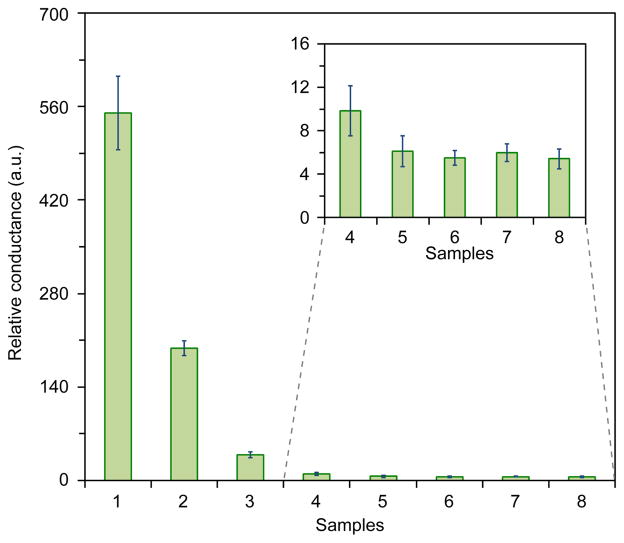
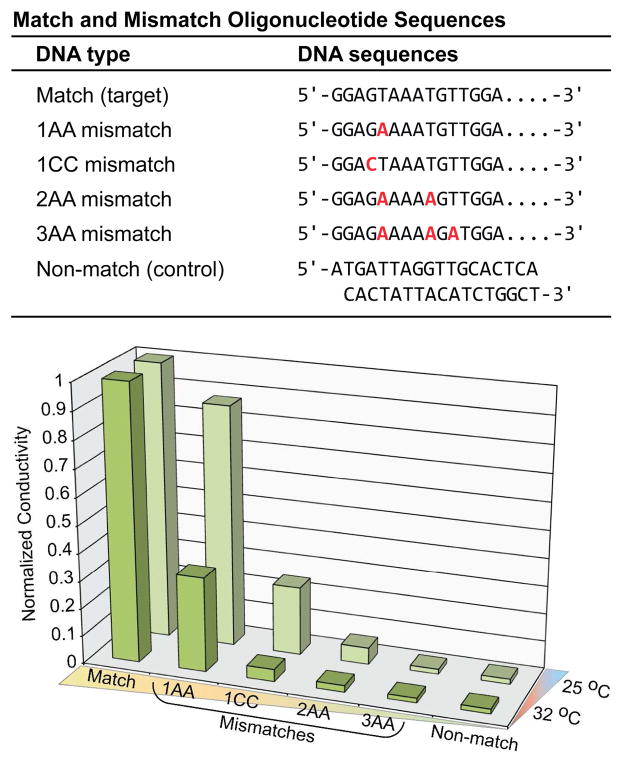
Studies to detect DNA, by means of simple conductivity measurements were performed using the scheme shown in Figure 1 and the details of the recognition domain are shown in Figure 1B. DNA detection studies with HRP probes were conducted using a range of DNA analyte concentrations from 1 nM to 1 fM. Conductance changes of the devices after silver deposition were measured at a fixed development time of 2 min and are shown in Figure 2. The The relative conductance value for detection of the DNA analyte at nanomolar concentrations was 550 (20 MΩ before silver development and 36.35 kΩ after silver development). The experiment was repeated with analyte concentrations ranging from 1 nM to 1 fM. The control experiment where complete mismatch DNA was used as a negative control did not lead to any significant silver deposition and resulted in a low conductivity change (Figure 2, sample 6). In addition, control experiments in the absence of analyte or DNA probe lead to negligible conductivity increases (Figure 2, samples 7,8). The relative conductance of the device was shown to decrease as a function of decreasing analyte concentration. The detection limit of DNA was found to be ~10 fM. Specificity studies were conducted beyond the full mismatch control (Figure 2, sample 6) to elucidate the impact of single, double, and triple base pair mismatches in the oligonucleotides analyte sequence. The match and mismatch sequences are shown in the table at the top of Figure 3 and the detection data is shown in the Figure 3 plot (bottom). As expected the sensitivity decreases as the number of mismatch base pairs increases. Additionally, there is a gain in sensitivity when the experiment is conducted at a slightly elevated temperature, due to an increase in oligonucleotide hybridization kinetics. For a single base pair mismatch (1AA mismatch) there is ~70% decrease in the response relative to the analyte containing the fully matched sequence at 32 °C (Figure 3). When the experiment is conducted at 25 °C mismatch detection sensitivity is significantly diminished relative to matched analyte with <20% decrease in response (Figure 3). Trends in the mismatch data parallel theoretical melting temperature data and a summary can be found in the supporting information figure S2. As a final test for device function in a complex biologically relevant environment we ran the assay with human serum samples, and the results are shown in Figure S3.
Figure 2.
Conductimetric response data from concentration dependent DNA-detection studies. DNA concentrations for samples 1–5, 1 nM, 10 pM, 1 pM, 10 fM, and 1 fM respectively. Control samples 6–8, 1 nM control DNA, no DNA, and no DNA/no probe respectively. All experiments were conducted with a silver development time of 2 min. Note: No significant difference was found between controls 5–8 in accordance with the t-test at the 95% confidence level, however a significant difference was found between sample 4 and the controls (inset). The error bars represent mean values ± s.d.
Figure 3.
Conductimetric response data for match versus mismatch oligonucleotides sequences. (Top) Table of match and mismatch sequences used for experiments. (Bottom) Normalized conductimetric response data for single, double, and triple mismatch oligonucleotides sequences compared to the match sequence.
Additionally, SEM characterization of the device junctions showed silver deposition as a result of DNA detection (Figure S2). In order to further characterize the sensing gap of the device before and after silver deposition, laser scanning Raman confocal microscopy was performed. Previous resonance Raman studies have demonstrated that SWCNTs filled with metallic silver lead to Fermi level alteration where silver behaves as an electron donor, which is consistent with an increase in electron carrier density.25–27
Utilizing laser scanning confocal Raman microscopy, we characterized our device junction before and after analyte (1 nM) detection in addition to characterization of the control device. A laser excitation wavelength of 784.4 nm (1.58 eV) was used and the results are shown in Figure S4. Silver modification of the nanotubes after analyte detection results in significant changes in the Raman spectra as shown in Figure S4. Changes in the radial breathing mode (RBM), D-band, G-band, and G′-band regions were observed. The RBM region showed 3 major peaks at 221, 230, and 238 cm−1, which decreased in intensity after silver deposition (Figure S4). Additionally, an RBM peak at ~272 cm−1 shows a significant increase in intensity upon silver deposition consistent with increased tube-tube interactions as previously assigned.25 The intensity of the D-band increases with significant broadening upon silver deposition and shows a slight ~1–2 cm−1 shift to lower frequency from 1296 cm−1, consistent with previous studies of SWCNTs on silver surfaces.28 Additionally, there is an increase in the D/G ratio upon silver deposition reflecting modification of the nanotube surface. The G+ (~1593 cm−1) and G− (~1564 cm−1) bands also show a slight decrease in frequency and the ratio of the G−/G+ band intensity increases from 0.15 for the device without silver deposition to 0.31 with silver deposition, which is consistent with an increase in the metallic state of the nanotubes. Characterization of device junctions after mismatch DNA control (1 nM) treatment and development using HRP catalyzed silver deposition showed similar results to untreated devices, indicating a lack of silver deposition in the absence of analyte or presence of mismatch control (see Figure S4).
The development of hybrid biocatalyzed-CNT network based detection methods offers a highly sensitive and specific platform for the fabrication of simple and effective conductimetric devices. Peroxidase enzymes provide a specific method for silver deposition at disrupted nanotube network connections, leading to amplified conductimetric detection of analytes. We have demonstrated in this study that this device design has the potential to be used for DNA detection at the femtomolar level and could provide a simple and cost effective method for the detection of infective agents such as Ebola virus. The potential for applications beyond DNA detection are considerable and we believe that the sensitivity can be further enhanced by regulating the assembly of the SWCNT network. Controlling the ratio between metallic to semiconducting nanotubes, the length of the nanotubes, the concentration of the assembly network, the nanotube species, and the device gap size between the two gold electrodes are topic for future optimization studies. In addition, the DNA molecular recognition domain connecting the nanotubes is flexible and easily amenable to modification such as length and sequence composition for alternative analytes. The potential for using different enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase, glucose oxidase or DNAzymes, which can also deposit gold and silver ions, provides many new avenues for the construction of hybrid biocatalytic-CNT devices. Additionally, this technology could have important implications for the mass production of new sensitive, robust, and economically feasible bio-diagnostic sensory devices.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by ARO W911NF-07-D-0004. D.M.C. is grateful for an NIH-NIGMS postdoctoral fellowship (1-F32-GM087028-01A1).
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Full experimental details and figures S1–S4. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Lockhart DJ, Winzeler EA. Nature. 2000;405:827–836. doi: 10.1038/35015701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saghatelian A, Guckian KM, Thayer DA, Ghadiri MR. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:344–345. doi: 10.1021/ja027885u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cao YC, Jin R, Mirkin CA. Science. 2002;297:1536–1540. doi: 10.1126/science.297.5586.1536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H. Nat Mater. 2005;4:435–446. doi: 10.1038/nmat1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Okahata Y, Matsunobu Y, Ijiro K, Mukae M, Murakami A, Makino K. J Am Chem Soc. 1992;114:8299–8300. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Drummond TG, Hill MG, Barton JK. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:1192–1199. doi: 10.1038/nbt873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fritz J, Baller MK, Lang HP, Rothuizen H, Vettiger P, Meyer E, Guntherodt H-J, Gerber Ch, Gimzewski JK. Science. 2000;288:316–318. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5464.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Avouris P, Chen Z, Perebeinos V. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:605–615. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Snow ES, Novak JP, Campbell PM, Park D. Appl Phys Lett. 2003;82:2145–2147. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Star A, Gabriel JCP, Bradley K, Gruner G. Nano Lett. 2003;3:459–463. [Google Scholar]
- 11.So HM, Won K, Kim YH, Kim BK, Ryu BH, Na PS, Kim H, Lee JO. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:11906–11907. doi: 10.1021/ja053094r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guo X, Gorodetsky AA, Hone J, Barton JK, Nuckolls C. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3:163–167. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li C, Curreli M, Lin H, Lei B, Ishikawa FN, Datar R, Cote RJ, Thompson ME, Zhou C. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:12484–12485. doi: 10.1021/ja053761g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dong X, Lau CM, Lohani A, Mhaisalkar SG, Kasim J, Shen Z, Ho X, Rogers JA, Li L. J Adv Mater. 2008;20:2389–2393. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gui EL, Li LJ, Zhang K, Xu Y, Dong X, Ho X, Lee PS, Kasim J, Shen ZX, Rogers JA, Mhaisalkar SG. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:14427–14432. doi: 10.1021/ja075176g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Star A, Tu E, Niemann J, Gabriel JC, Joiner CS, Valcke C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:921–926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504146103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weizmann Y, Chenoweth DM, Swager TM. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:14009–14011. doi: 10.1021/ja106352y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Weizmann Y, Lim J, Chenoweth DM, Swager TM. Nano Lett. 2010;10:2466–2469. doi: 10.1021/nl1008025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.The use of ssDNA linked CNTs provide flexible control of the recognition gap between contiguous nanotubes allowing for rapid sequence and length variations.
- 20.Peroxidase enzymes are capable of reducing silver ions to silver metal in the presence of an oxidant leading to the deposition and accumulation of silver metal in a highly localized manner.
- 21.Moller R, Powell RD, Hainfeld JF, Fritzsche W. Nano Lett. 2005;5:1475–1482. doi: 10.1021/nl050824k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Niemeyer CM, Ceyhan B. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2001;40:3685–3688. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20011001)40:19<3685::aid-anie3685>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Taton TA, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL. Science. 2000;289:1757–1760. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5485.1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Park SJ, Taton TA, Mirkin CA. Science. 2002;295:1503–1506. doi: 10.1126/science.1067003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Corio P, Santos AP, Santos PS, Temperini MLA, Brar VW, Pimenta MA, Dresselhaus MS. Chem Phys Lett. 2004;383:475–480. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Saito R, Jorio A. Phys Reports. 2005;409:47. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Hofmann M. Vibrational Spectroscopy. 2007;45:71–81. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu B, Zhang J, Wei Z, Cai S, Liu Z. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:5075–5078. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.