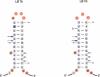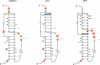Abstract
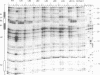
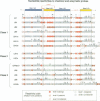
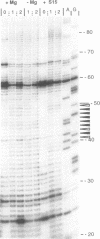
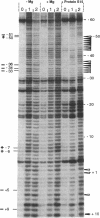
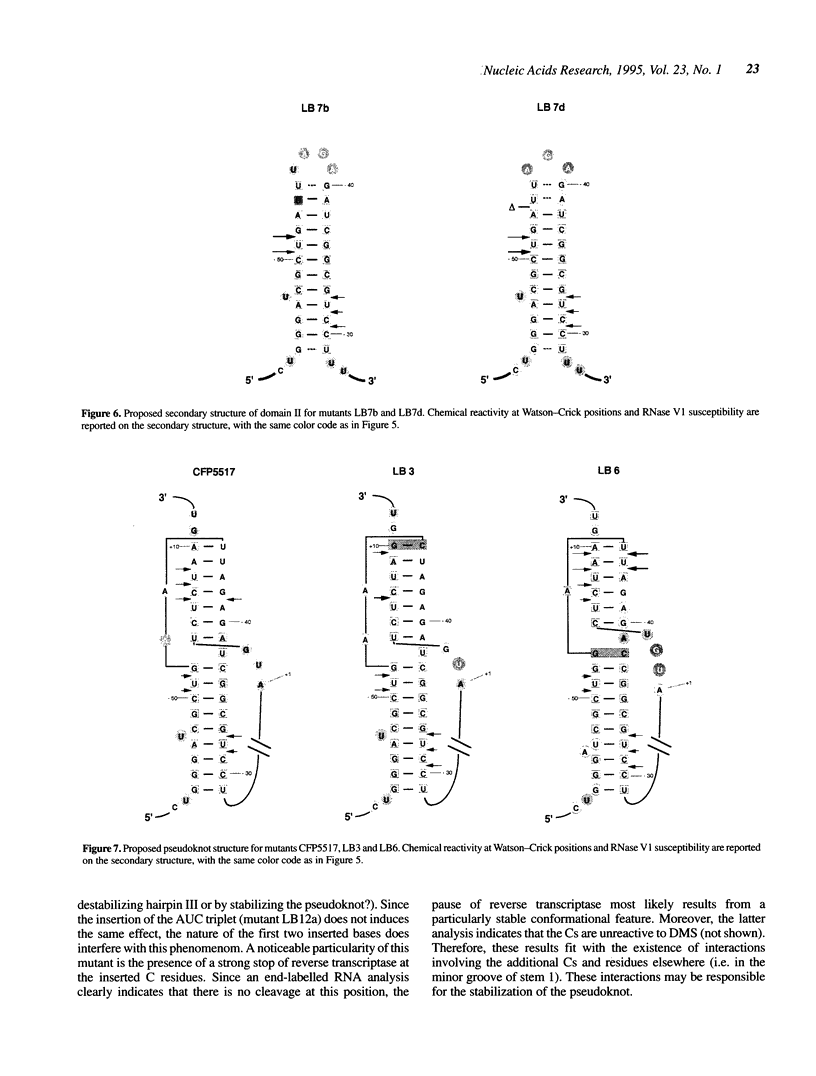
The ribosomal protein S15 controls its own translation by binding to a mRNA region overlapping the ribosome binding site. That region of the mRNA can fold in two mutually exclusive conformations that are in dynamic equilibrium: a structure with two hairpins and a pseudoknot. A mutational analysis provided evidence for the existence and requirement of the pseudoknot for translational control in vivo and S15 recognition in vitro. In this study, we used chemical probing to analyze the structural consequences of mutations and their effect on the stem-loop/pseudoknot equilibrium. Interactions between S15 and the pseudoknot structure were further investigated by footprinting experiments. These data, combined with computer modelling and the previously published data on S15 binding and in vivo control, provide important clues on pseudoknot formation and S15 recognition. An unexpected result is that the relevant control element, here the pseudoknot form, can exist in a variety of topologically equivalent structures recognizable and shapable by S15. S15 sits on the deep groove of the co-axial stack and makes contacts with both stems, shielding the bridging adenine. The only specific sequence determinants are found in the helix common to the pseudoknot and the hairpin structures.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano K., Kato A., Moriwaki H., Hama C., Shiba K., Mizobuchi K. Positive and negative regulations of plasmid CoLIb-P9 repZ gene expression at the translational level. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3774–3781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Rolley N. J., Jenner A. J., Inglis S. C. Mutational analysis of the RNA pseudoknot component of a coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90361-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénard L., Philippe C., Dondon L., Grunberg-Manago M., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C., Portier C. Mutational analysis of the pseudoknot structure of the S15 translational operator from Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Oct;14(1):31–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachia C., Flamion P. J., Schreiber J. P. Fast preparative separation of 'native' core E coli 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochimie. 1991 May;73(5):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90029-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D. W., Cech T. R. Iron(II)-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid catalyzed cleavage of RNA and DNA oligonucleotides: similar reactivity toward single- and double-stranded forms. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1355–1361. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groebe D. R., Uhlenbeck O. C. Characterization of RNA hairpin loop stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11725–11735. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massire C., Gaspin C., Westhof E. DRAWNA: a program for drawing schematic views of nucleic acids. J Mol Graph. 1994 Sep;12(3):201-6, 196. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(94)80088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Autogenous regulatory site on the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):517–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90634-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Bénard L., Eyermann F., Cachia C., Kirillov S. V., Portier C., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Structural elements of rps0 mRNA involved in the modulation of translational initiation and regulation of E. coli ribosomal protein S15. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2538–2546. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Eyermann F., Bénard L., Portier C., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Ribosomal protein S15 from Escherichia coli modulates its own translation by trapping the ribosome on the mRNA initiation loading site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe C., Portier C., Mougel M., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Target site of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S15 on its messenger RNA. Conformation and interaction with the protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90362-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., Philippe C., Dondon L., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Translational control of ribosomal protein S15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90190-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. K., Draper D. E. Unusual mRNA pseudoknot structure is recognized by a protein translational repressor. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A., Churchill M. E., Kam L. Hydroxyl radical footprinting: a high-resolution method for mapping protein-DNA contacts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:537–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassov V. V., Giegé R., Ebel J. P. Tertiary structure of tRNAs in solution monitored by phosphodiester modification with ethylnitrosourea. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Romby P., Romaniuk P. J., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Computer modeling from solution data of spinach chloroplast and of Xenopus laevis somatic and oocyte 5 S rRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):417–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]