Figure 2. HCV infection in AFC8-hu HSC/Hep mice leads to human immune infiltration and liver injury.
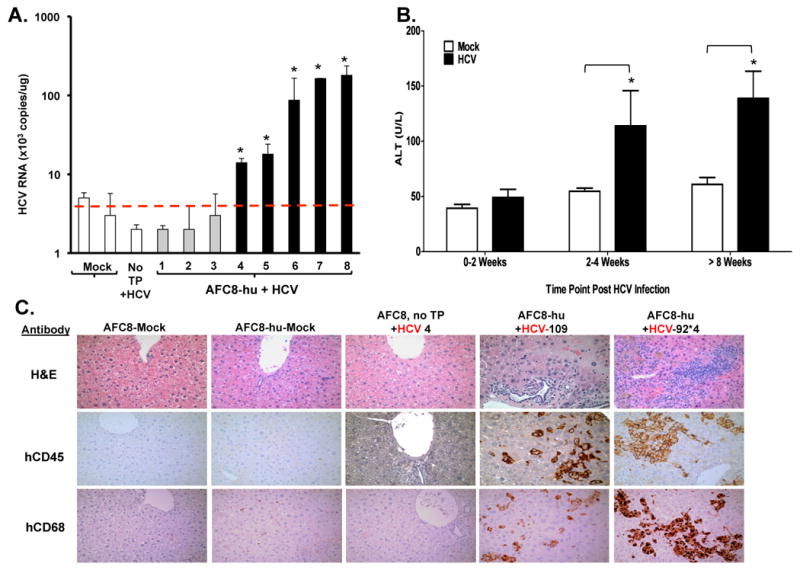
AFC8-hu HSC/Hep mice or control mice were infected with HCV patient isolates (genotype 1a, 1×10e5 i.u./mouse) or control serum. Blood samples were collected at various times after infection. Liver samples were collected at termination time points. (A) HCV genomic RNA was detected in the liver of HCV-infected AFC8-hu mice. Liver tissues were harvested from HCV-infected AFC8-hu or control mice at 70-80 days post-infection. Values represent HCV RNA copy#/ug liver-derived RNA in triplicates. * P <.05. (B) Increased ALT in sera from HCV-infected AFC8-hu or control mice. Data represent mean ± s.e.m (n = 6 mice per group). *, P < .05. (C) Representative liver sections from control/mock, AFC8-hu/mock, control (no transplant)/HCV, and two AFC8-hu/HCV mice were stained to detect leukocyte infiltration with H&E (top panels), or with anti-human CD45 (middle panels) or human CD68 (bottom panels).
