Abstract
The synthesis and DNA binding properties of bis-PNA (peptide nucleic acid) are reported. Two PNA segments each of seven nucleobases in length were connected in a continuous synthesis via a flexible linker composed of three 8-amino-3,6-dioxaoctanoic acid units. The sequence of the first strand was TCTCTTT (C- to N-terminal), while the second strand was TTTCTCT or TTTJTJT, where J is pseudoisocytosine. These bis-PNAs form triple-stranded complexes of somewhat higher thermal stability than monomeric PNA with complementary oligonucleotides and the thermal melting transition shows very little hysteresis. When the J base is placed in the strand parallel to the DNA complement ('Hoogsteen strand'), the DNA binding was pH independent. The bis-PNAs were also superior to monomeric PNAs for targeting double-stranded DNA by strand invasion.
Full text
PDF
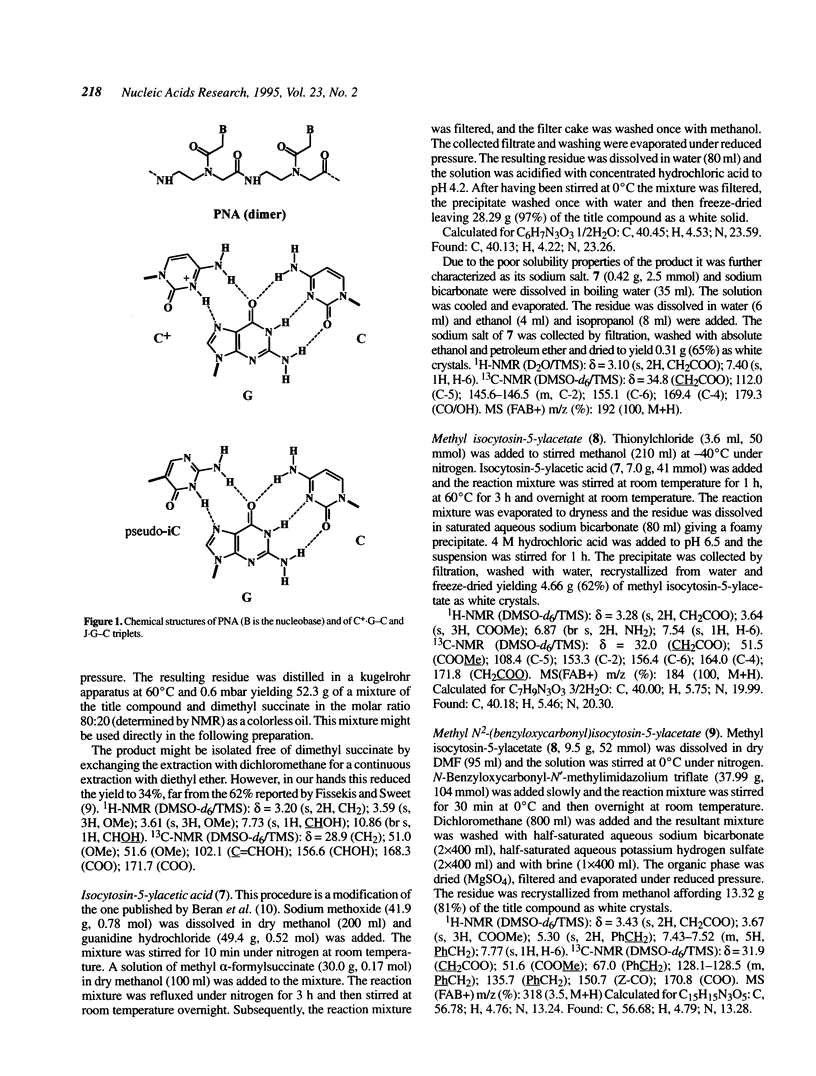

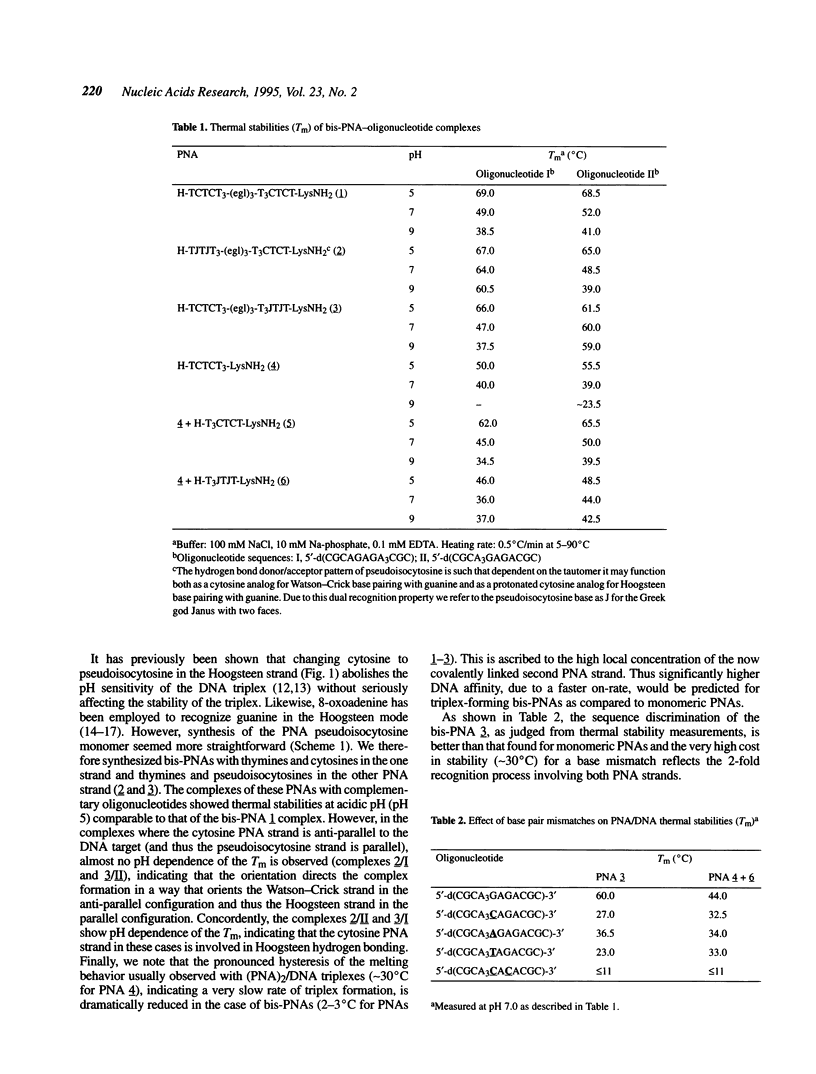
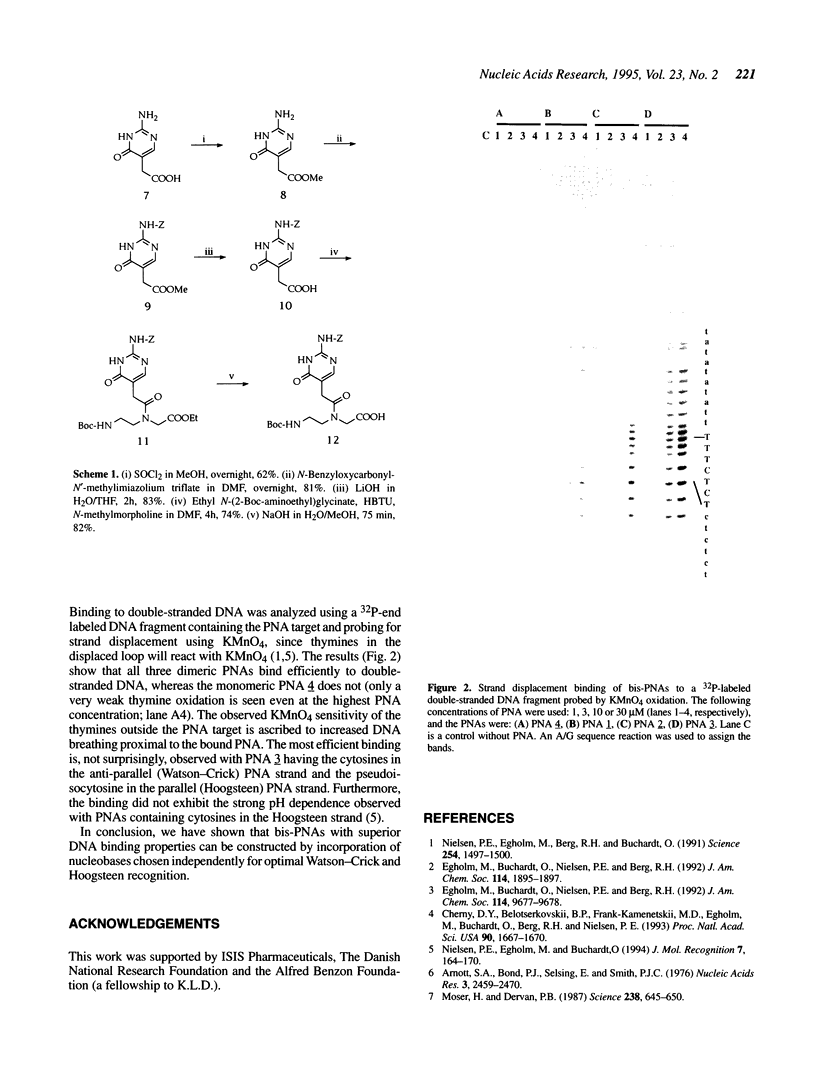

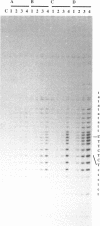
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Bond P. J., Selsing E., Smith P. J. Models of triple-stranded polynucleotides with optimised stereochemistry. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2459–2470. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherny D. Y., Belotserkovskii B. P., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Egholm M., Buchardt O., Berg R. H., Nielsen P. E. DNA unwinding upon strand-displacement binding of a thymine-substituted polyamide to double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1667–1670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egholm M., Buchardt O., Christensen L., Behrens C., Freier S. M., Driver D. A., Berg R. H., Kim S. K., Norden B., Nielsen P. E. PNA hybridizes to complementary oligonucleotides obeying the Watson-Crick hydrogen-bonding rules. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):566–568. doi: 10.1038/365566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fissekis J. D., Sweet F. Synthesis of 5-carboxymethyluridine. A nucleoside from transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 4;9(16):3136–3142. doi: 10.1021/bi00818a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetter M. C., Hobbs F. W. 7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoadenine as a replacement for cytosine in the third strand of triple helices. Triplex formation without hypochromicity. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3249–3254. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk S. H., Milligan J. F., Wadwani S., Moulds C., Froehler B. C., Matteucci M. D. Oligonucleotide-mediated triple helix formation using an N3-protonated deoxycytidine analog exhibiting pH-independent binding within the physiological range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3761–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. S., Bhan P., Cushman C. D., Trapane T. L. Recognition of a guanine-cytosine base pair by 8-oxoadenine. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6788–6793. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Berg R. H., Buchardt O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1962210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E. Uranyl photofootprinting of triple helical DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2735–2739. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]