Abstract
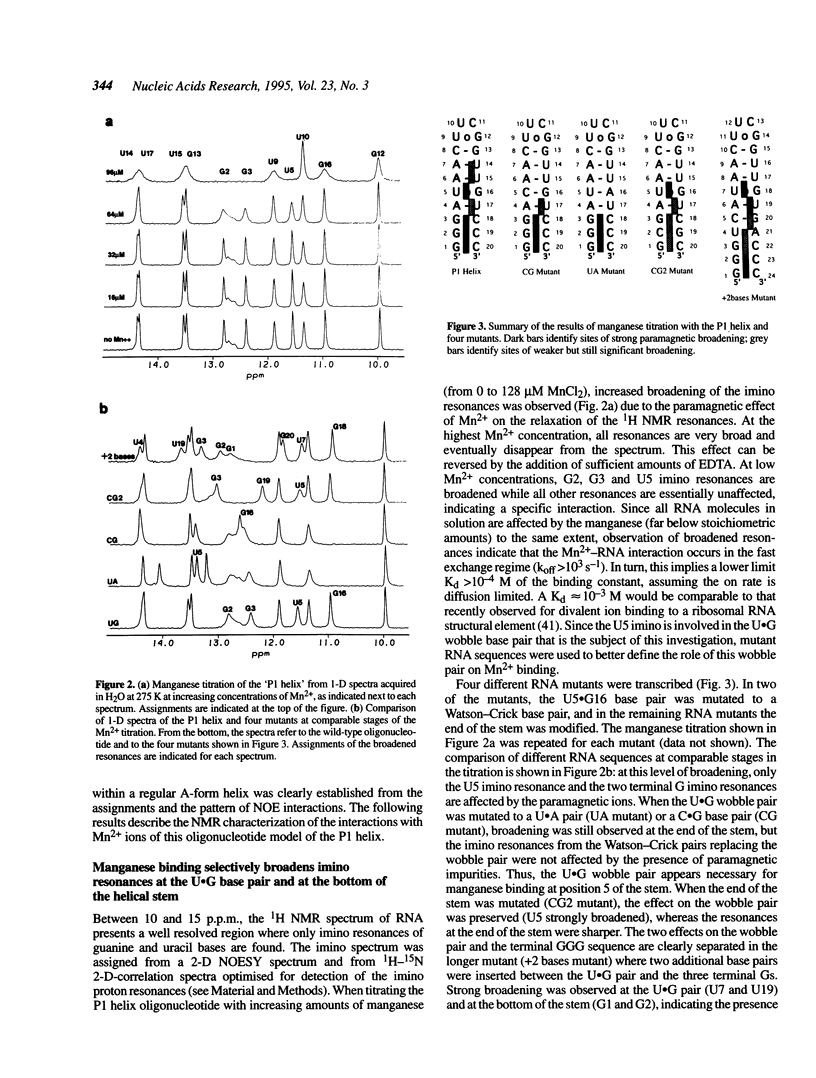
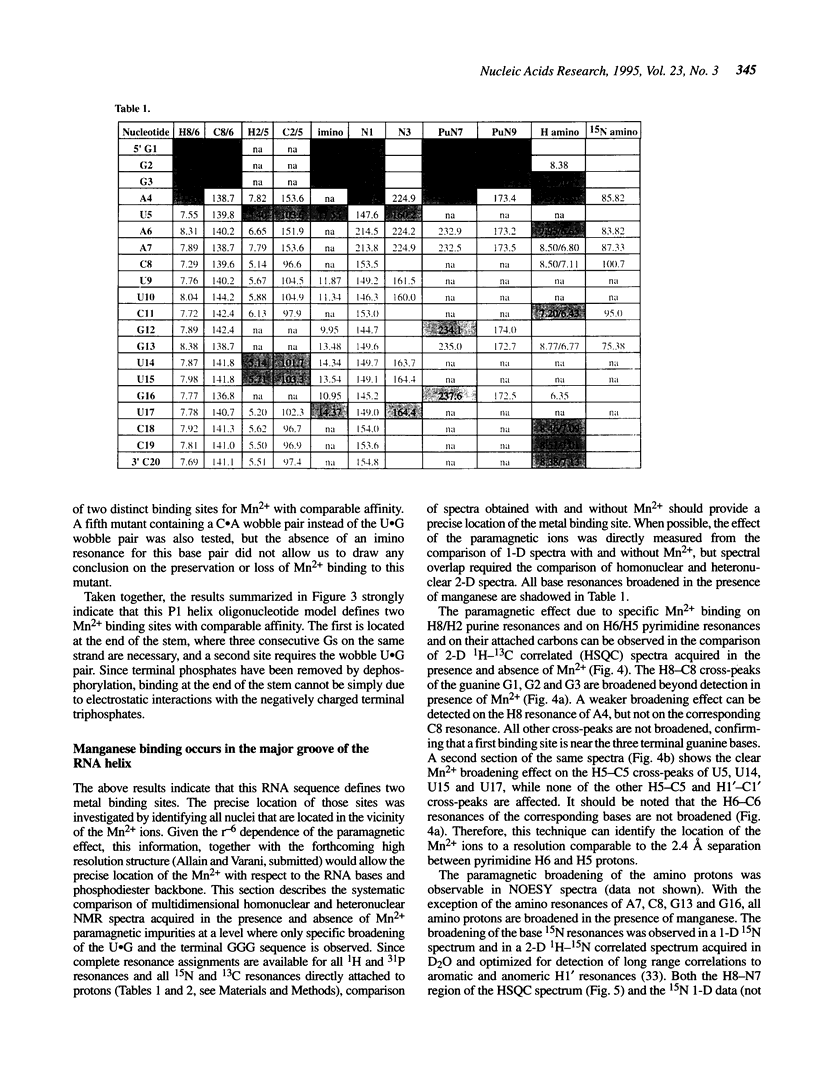
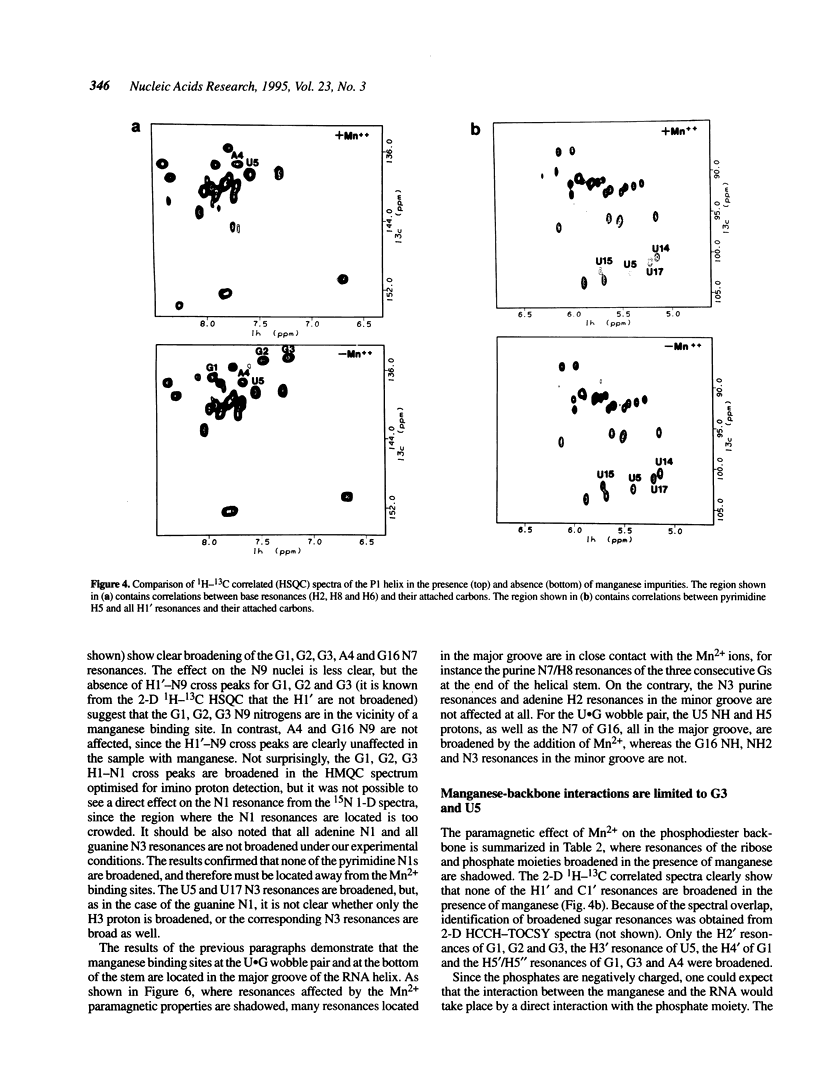
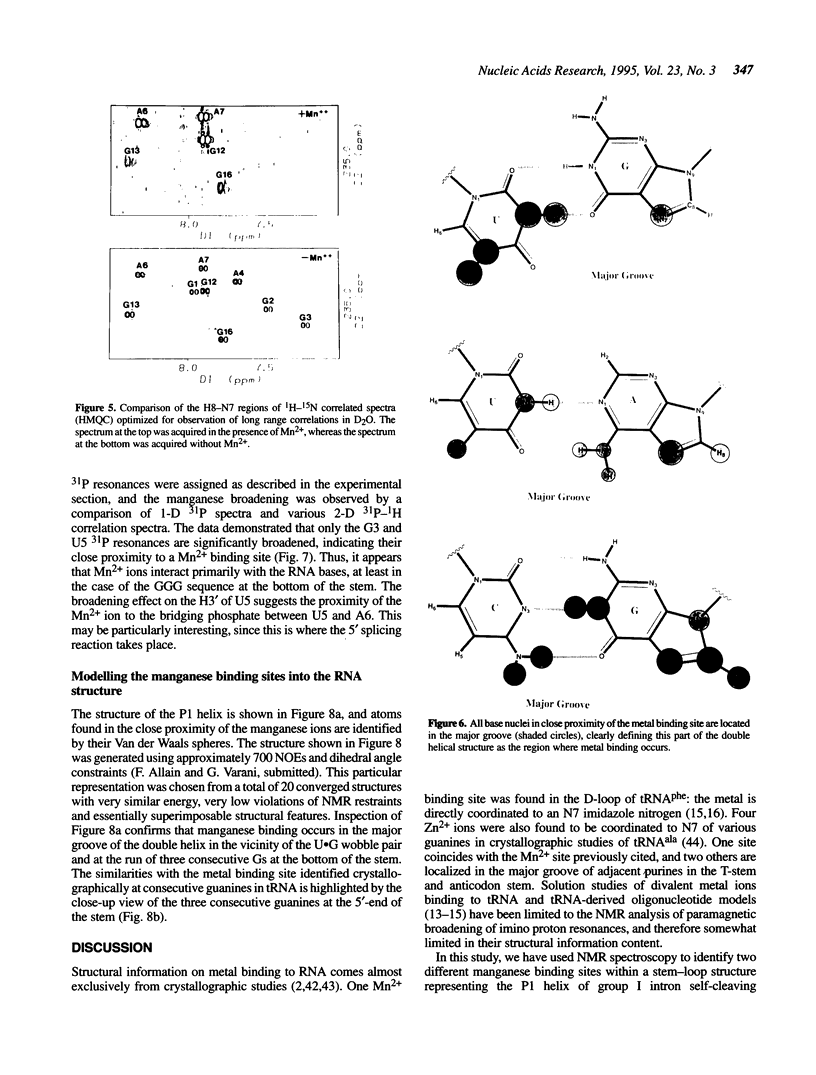
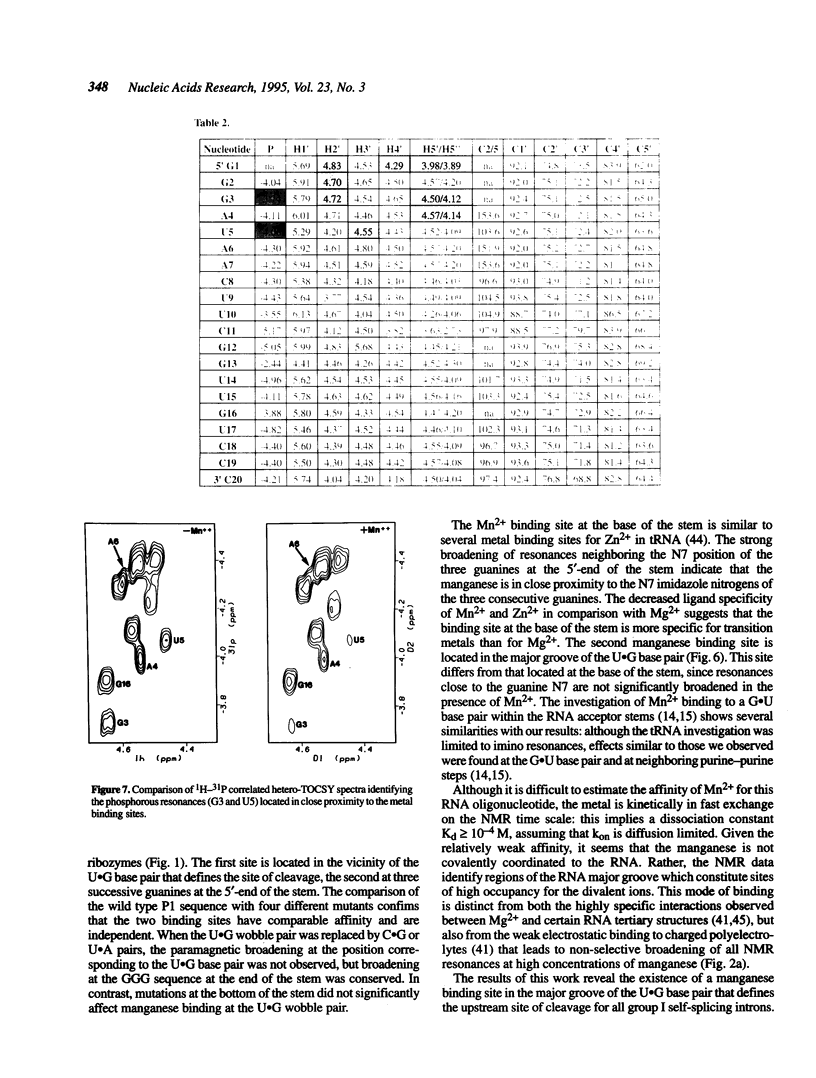
The upstream site of cleavage of all group I self-splicing introns is identified by an absolutely conserved U.G base pair. Although a wobble C.A pair can substitute the U.G pair, all other combinations of nucleotides at this position abolish splicing, suggesting that it is an unusual RNA structure, rather than sequence, that is recognized by the catalytic intron core. RNA enzymes are metalloenzymes, and divalent metal ion binding may be an important requirement for splice site recognition and catalysis. The paramagnetic broadening of NMR resonances upon manganese binding at specific sites was used to probe the interaction between divalent metal ions and an oligonucleotide model of a group I intron ribozyme substrate. Unlike previous studies in which only imino proton resonances were monitored, we have used isotopically labelled RNA and a set of complete spectral assignments to identify the location of the divalent metal binding site with much greater detail than previously possible. Two independent metal binding sites were identified for this oligonucleotide. A first metal binding site is located in the major groove of the three consecutive G.C base pairs at the end of double helical stem. A second site is found in the major groove of the RNA double helix in the vicinity of the U.G base pair. These results suggest that metal ion coordination (or a metal bridge) and tertiary interactions identified biochemically, may be used by group I intron ribozymes for substrate recognition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batey R. T., Inada M., Kujawinski E., Puglisi J. D., Williamson J. R. Preparation of isotopically labeled ribonucleotides for multidimensional NMR spectroscopy of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4515–4523. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Sierzputowska-Gracz H., Guenther R., Everett K., Agris P. F. 5-Methylcytidine is required for cooperative binding of Mg2+ and a conformational transition at the anticodon stem-loop of yeast phenylalanine tRNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):10249–10253. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian E. L., Yarus M. Metal coordination sites that contribute to structure and catalysis in the group I intron from Tetrahymena. Biochemistry. 1993 May 4;32(17):4475–4480. doi: 10.1021/bi00068a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahm S. C., Derrick W. B., Uhlenbeck O. C. Evidence for the role of solvated metal hydroxide in the hammerhead cleavage mechanism. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13040–13045. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudna J. A., Cormack B. P., Szostak J. W. RNA structure, not sequence, determines the 5' splice-site specificity of a group I intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7402–7406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Bax A., Wingfield P. T., Clore G. M. A powerful method of sequential proton resonance assignment in proteins using relayed 15N-1H multiple quantum coherence spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 16;243(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hingerty B., Brown R. S., Jack A. Further refinement of the structure of yeast tRNAPhe. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd R. E., Azhderian E., Reid B. R. Paramagnetic ion effects on the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of transfer ribonucleic acid: assignment of the 15--48 tertiary resonance. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):4012–4017. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Klug A. A crystallographic study of metal-binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 15;111(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg G. W., Schweitzer B. I. Two- and three-dimensional 31P-driven NMR procedures for complete assignment of backbone resonances in oligodeoxyribonucleotides. J Biomol NMR. 1993 Sep;3(5):577–595. doi: 10.1007/BF00174611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing L. G., Gluick T. C., Draper D. E. Stabilization of RNA structure by Mg ions. Specific and non-specific effects. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):577–587. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limmer S., Hofmann H. P., Ott G., Sprinzl M. The 3'-terminal end (NCCA) of tRNA determines the structure and stability of the aminoacyl acceptor stem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6199–6202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikonowicz E. P., Pardi A. An efficient procedure for assignment of the proton, carbon and nitrogen resonances in 13C/15N labeled nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 20;232(4):1141–1156. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikonowicz E. P., Sirr A., Legault P., Jucker F. M., Baer L. M., Pardi A. Preparation of 13C and 15N labelled RNAs for heteronuclear multi-dimensional NMR studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4507–4513. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott G., Arnold L., Limmer S. Proton NMR studies of manganese ion binding to tRNA-derived acceptor arm duplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5859–5864. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Dichtl B., Uhlenbeck O. C. Properties of an in vitro selected Pb2+ cleavage motif. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 16;33(32):9561–9565. doi: 10.1021/bi00198a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. A small metalloribozyme with a two-step mechanism. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):560–563. doi: 10.1038/358560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccirilli J. A., Vyle J. S., Caruthers M. H., Cech T. R. Metal ion catalysis in the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):85–88. doi: 10.1038/361085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pley H. W., Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of a hammerhead ribozyme. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):68–74. doi: 10.1038/372068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tinoco I., Jr Absorbance melting curves of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:304–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M., Murphy F. L., Cech T. R. RNA substrate binding site in the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):123–128. doi: 10.1038/358123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M. Ribozymes: a distinct class of metalloenzymes. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):709–714. doi: 10.1126/science.7688142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. R., Wang J., Sundaralingam M. X-ray diffraction study of the zinc(II) binding sites in yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. Preferential binding of zinc to guanines in purine-purine sequences. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 15;756(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklenár V., Miyashiro H., Zon G., Miles H. T., Bax A. Assignment of the 31P and 1H resonances in oligonucleotides by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklenár V., Peterson R. D., Rejante M. R., Feigon J. Correlation of nucleotide base and sugar protons in a 15N-labeled HIV-1 RNA oligonucleotide by 1H-15N HSQC experiments. J Biomol NMR. 1994 Jan;4(1):117–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00178339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Steitz J. A. A general two-metal-ion mechanism for catalytic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Cech T. R. Tertiary interactions with the internal guide sequence mediate docking of the P1 helix into the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13593–13604. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Cech T. R. Translocation of an RNA duplex on a ribozyme. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Jan;1(1):13–17. doi: 10.1038/nsb0194-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gauss P., Thermes C., Groebe D. R., Gayle M., Guild N., Stormo G., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Uhlenbeck O. C., Tinoco I., Jr CUUCGG hairpins: extraordinarily stable RNA secondary structures associated with various biochemical processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchimaru T., Uebayasi M., Tanabe K., Taira K. Theoretical analyses on the role of Mg2+ ions in ribozyme reactions. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):137–142. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani G., Cheong C., Tinoco I., Jr Structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3280–3289. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr RNA structure and NMR spectroscopy. Q Rev Biophys. 1991 Nov;24(4):479–532. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]