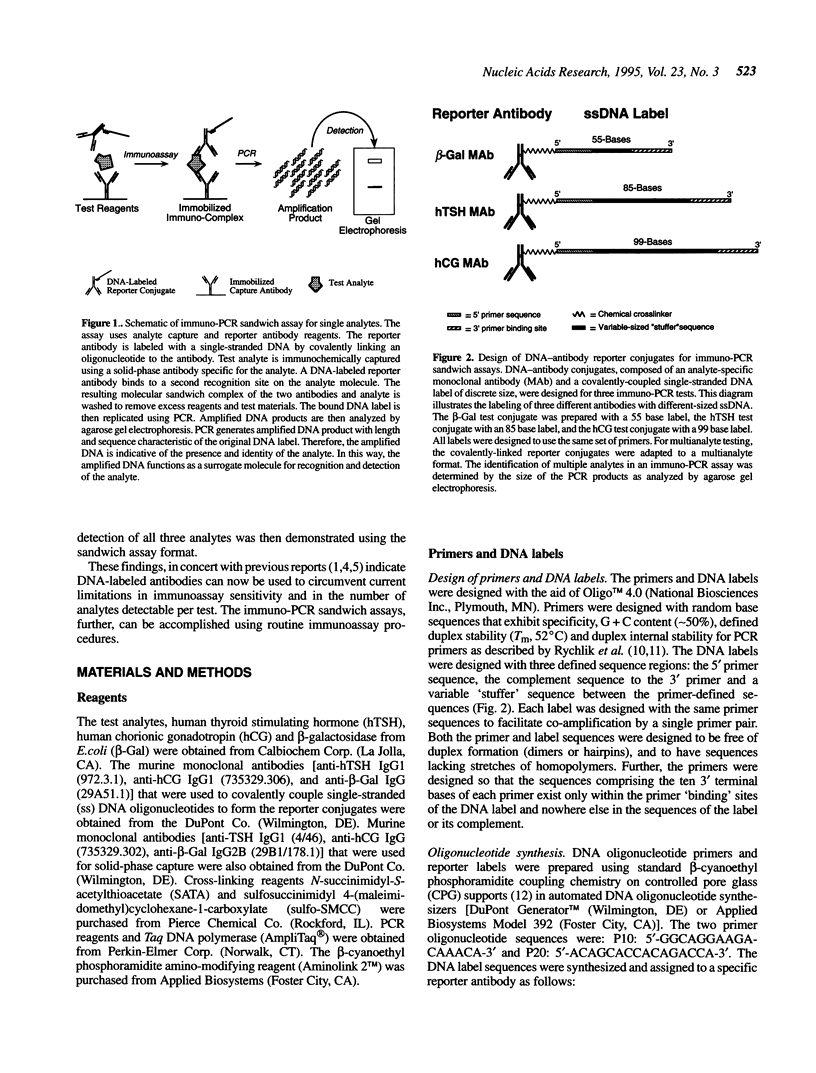
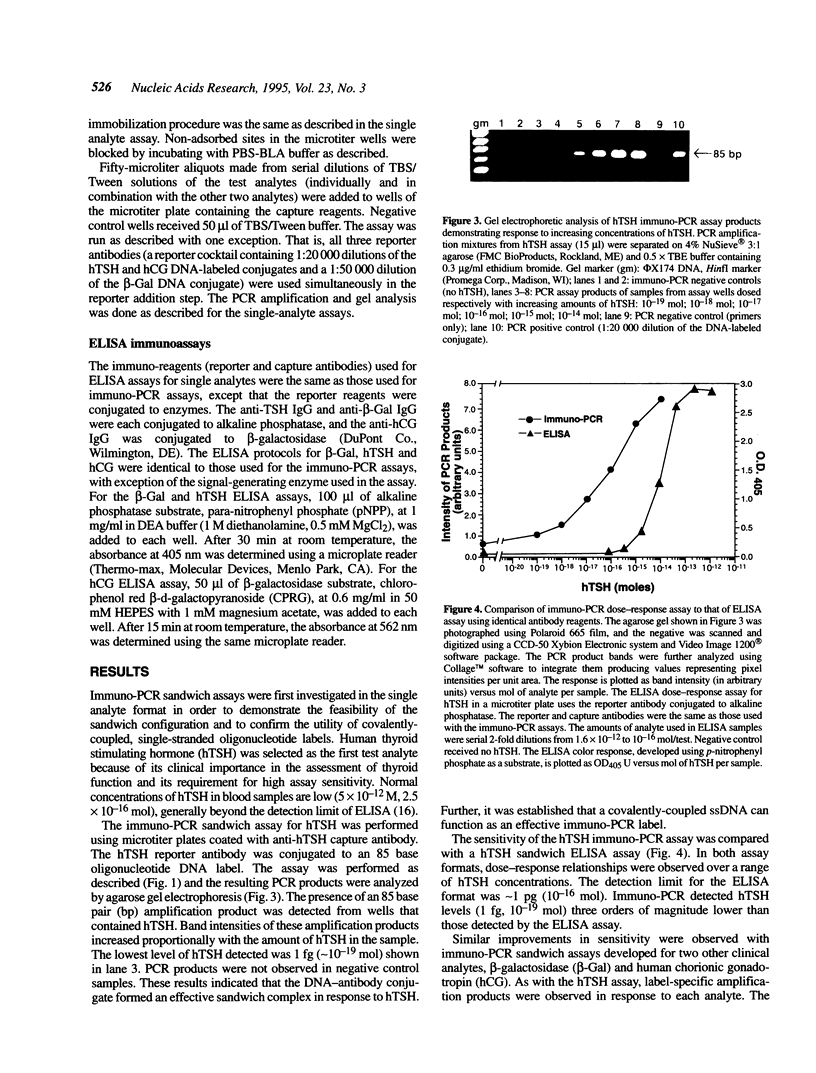
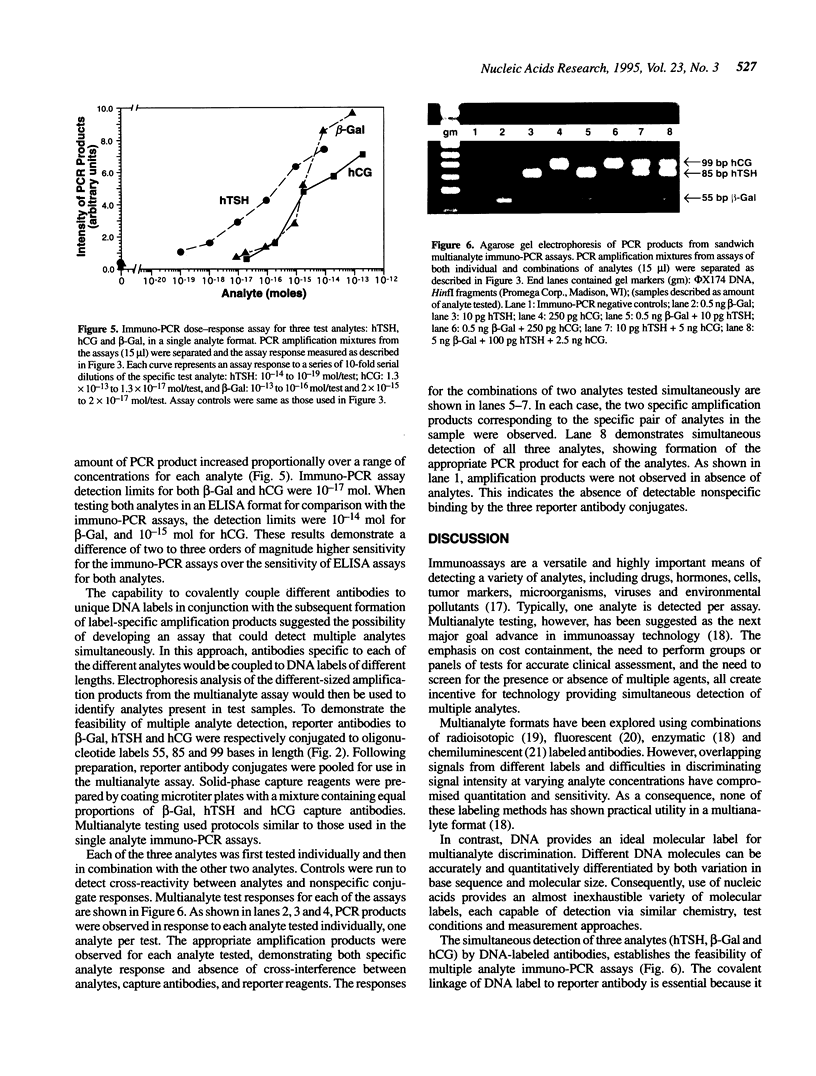
Abstract
A multianalyte immunoassay for simultaneous detection of three analytes (hTSH, hCG and beta-Gal) has been demonstrated using DNA-labeled antibodies and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for amplification of assay response. The labeled antibodies were prepared by covalently coupling uniquely designed DNA oligonucleotides to each of the analyte-specific monoclonal antibodies. Each of the DNA oligonucleotide labels contained the same primer sequences to facilitate co-amplification by a single primer pair. Assays were performed using a two-antibody sandwich assay format and a mixture of the three DNA-labeled antibodies. Dose-response relationships for each analyte were demonstrated. Analytes were detected at sensitivities exceeding those of conventional enzyme immunoassays by approximately three orders of magnitude. Detection limits for hTSH, beta-Gal and hCG were respectively 1 x 10(-19), 1 x 10(-17) and 1 x 10(-17) mol. Given the enormous amplification afforded by PCR and the existing capability to differentiate DNA based on size or sequence differences, the use of DNA-labeled antibodies could provide the basis for the simultaneous detection of many analytes at sensitivities greater than those of existing antigen detection systems. These findings in concert with previous reports suggest this hybrid technology could provide a new generation of ultra-sensitive multianalyte immunoassays.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Aquila R. T., Bechtel L. J., Videler J. A., Eron J. J., Gorczyca P., Kaplan J. C. Maximizing sensitivity and specificity of PCR by pre-amplification heating. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3749–3749. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. C., Gibbs R. A. Multiplex PCR: advantages, development, and applications. PCR Methods Appl. 1994 Feb;3(4):S65–S75. doi: 10.1101/gr.3.4.s65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosling J. P. A decade of development in immunoassay methodology. Clin Chem. 1990 Aug;36(8 Pt 1):1408–1427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakabakos S. E., Christopoulos T. K., Diamandis E. P. Multianalyte immunoassay based on spatially distinct fluorescent areas quantified by laser-excited solid-phase time-resolved fluorometry. Clin Chem. 1992 Mar;38(3):338–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kricka L. J. Multianalyte testing. Clin Chem. 1992 Mar;38(3):327–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. R. Immunoassay of human insulin and growth hormone simultaneously using I-131 and I-125 tracers. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Oct;123(1):230–233. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obzansky D. M., Rabin B. R., Simons D. M., Tseng S. Y., Severino D. M., Eggelte H., Fisher M., Harbron S., Stout R. W., Di Paolo M. J. Sensitive, colorimetric enzyme amplification cascade for determination of alkaline phosphatase and application of the method to an immunoassay of thyrotropin. Clin Chem. 1991 Sep;37(9):1513–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka V., März W., Russ A., Gross W. Immuno-PCR with a commercially available avidin system. Science. 1993 Apr 30;260(5108):698–699. doi: 10.1126/science.8480182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Spencer W. J., Rhoads R. E. Optimization of the annealing temperature for DNA amplification in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6409–6412. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Cantor C. R. A streptavidin-protein A chimera that allows one-step production of a variety of specific antibody conjugates. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Dec;9(12):1378–1381. doi: 10.1038/nbt1291-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Immuno-PCR: very sensitive antigen detection by means of specific antibody-DNA conjugates. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):120–122. doi: 10.1126/science.1439758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Response. Science. 1993 Apr 30;260(5108):699–699. doi: 10.1126/science.260.5108.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Fung S., Hunkapiller M. W., Hunkapiller T. J., Hood L. E. The synthesis of oligonucleotides containing an aliphatic amino group at the 5' terminus: synthesis of fluorescent DNA primers for use in DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2399–2412. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sproat B. S., Beijer B., Rider P. The synthesis of protected 5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxyribonucleoside-3'-O-phosphoramidites; applications of 5'-amino-oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6181–6196. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H., Fisher R. J., Papas T. S. Universal immuno-PCR for ultra-sensitive target protein detection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):6038–6039. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





