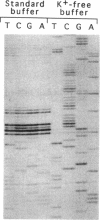
Abstract
Full text
PDFPage 539
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fawcett T. W., Bartlett G. An effective method for eliminating "artifact banding" when sequencing double-stranded DNA templates. Biotechniques. 1990 Jul;9(1):46–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pati U. K., Weissman S. M. The amino acid sequence of the human RNA polymerase II 33-kDa subunit hRPB 33 is highly conserved among eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8400–8403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodford K. J., Howell R. M., Usdin K. A novel K(+)-dependent DNA synthesis arrest site in a commonly occurring sequence motif in eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):27029–27035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]