Abstract
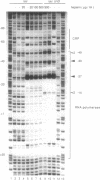
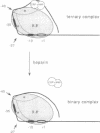
The role of cAMP receptor protein (CRP) in transcription activation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter was investigated focusing on the steps after the formation of open complex. Although CRP binding to the lac DNA is stabilized in the ternary open complex, a high concentration of heparin dissociates CRP from the open complex without affecting the interaction between RNA polymerase and promoter, resulting in a binary complex. The release of CRP is directly shown by Western blotting and DNase I footprinting. The binary complex exhibits a slightly increased gel mobility compared to the ternary complex. The binary complex retains the characteristics of the open complex in footprinting pattern which is essentially identical with that of the open complex of the lac UV5 promoter. The binary complex is competent for transcription. These results indicate that CRP is not necessary for the maintenance of active open complex. In addition, the removal of CRP does not increase the production of abortive RNAs. We conclude that the contact between CRP and RNA polymerase is not essential for transcription activation after the formation of the open complex at the lac promoter. In other words, the role of CRP in the lac promoter is restricted to the steps up to the formation of open complex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., Garges S., Oppenheim A. Promoter resurrection by activators--a minireview. Gene. 1993 Sep 30;132(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90507-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Fujimoto S., Ozaki N. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene for E. coli cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Hanamura A., Tobe T. Semisynthetic promoters activated by cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford J. L., Harman J. G. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):100–122. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.100-122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc H. Mechanism of activation of transcription by the complex formed between cyclic AMP and its receptor in Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Apr;14(2):196–199. doi: 10.1042/bst0140196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle M., Buc H., Travers A. A. DNA deformation in nucleoprotein complexes between RNA polymerase, cAMP receptor protein and the lac UV5 promoter probed by singlet oxygen. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2619–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Ebright R. H. Promoter structure, promoter recognition, and transcription activation in prokaryotes. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):743–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Gralla J. D. Interaction of RNA polymerase with lacUV5 promoter DNA during mRNA initiation and elongation. Footprinting, methylation, and rifampicin-sensitivity changes accompanying transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenchick A., Beabealashvilli R., Mirzabekov A. Topography of interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase subunits with lac UV5 promoter. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 1;128(1):46–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H. Transcription activation at Class I CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Pampeno C., Krakow J. S. Production and properties of the alpha core derived from the cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2469–2473. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R., Iwakura Y., Ishihama A. Heterogeneity of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli. I. A new holoenzyme containing a new sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar;83(3):353–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann H., Ricchetti M., Werel W. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli induces bending or an increased flexibility of DNA by specific complex formation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4379–4381. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka H., Hanamura A., Kunimura T., Aiba H. A lowered concentration of cAMP receptor protein caused by glucose is an important determinant for catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamukai M., Kishimoto J., Utsumi R., Himeno M., Komano T., Aiba H. Negative regulation of adenylate cyclase gene (cya) expression by cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein in Escherichia coli: studies with cya-lac protein and operon fusion plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.872-877.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Buc H., Garges S., Adhya S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnke G., Fritz H. J., Ehring R. Unusual properties of promoter-up mutations in the Escherichia coli galactose operon and evidence suggesting RNA polymerase-induced DNA bending. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):507–513. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Rate-limiting steps in RNA chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5634–5638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menendez M., Kolb A., Buc H. A new target for CRP action at the malT promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4227–4234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W., Schickor P., Meier T., Werel W., Heumann H. Nucleation of RNA chain formation by Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 5;232(1):35–49. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Almes F. J., Heumann H., Porschke D. The structure of the RNA polymerase-promoter complex. DNA-bending-angle by quantitative electrooptics. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):1–6. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees W. A., Keller R. W., Vesenka J. P., Yang G., Bustamante C. Evidence of DNA bending in transcription complexes imaged by scanning force microscopy. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1646–1649. doi: 10.1126/science.8503010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y. L., Garges S., Adhya S., Krakow J. S. Cooperative DNA binding of heterologous proteins: evidence for contact between the cyclic AMP receptor protein and RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4138–4142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S. The lactose operon-controlling elements: a complex paradigm. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(17):2419–2422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinov K., Fenyö D., Severinova E., Mustaev A., Chait B. T., Goldfarb A., Darst S. A. The sigma subunit conserved region 3 is part of "5'-face" of active center of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):20826–20828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Kirkegaard K., Buc H. Changes in the DNA structure of the lac UV5 promoter during formation of an open complex with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2723–2731. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Straney S. B., Crothers D. M. Synergy between Escherichia coli CAP protein and RNA polymerase in the lac promoter open complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90522-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Catabolite activator protein-induced DNA bending in transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90562-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]