Abstract
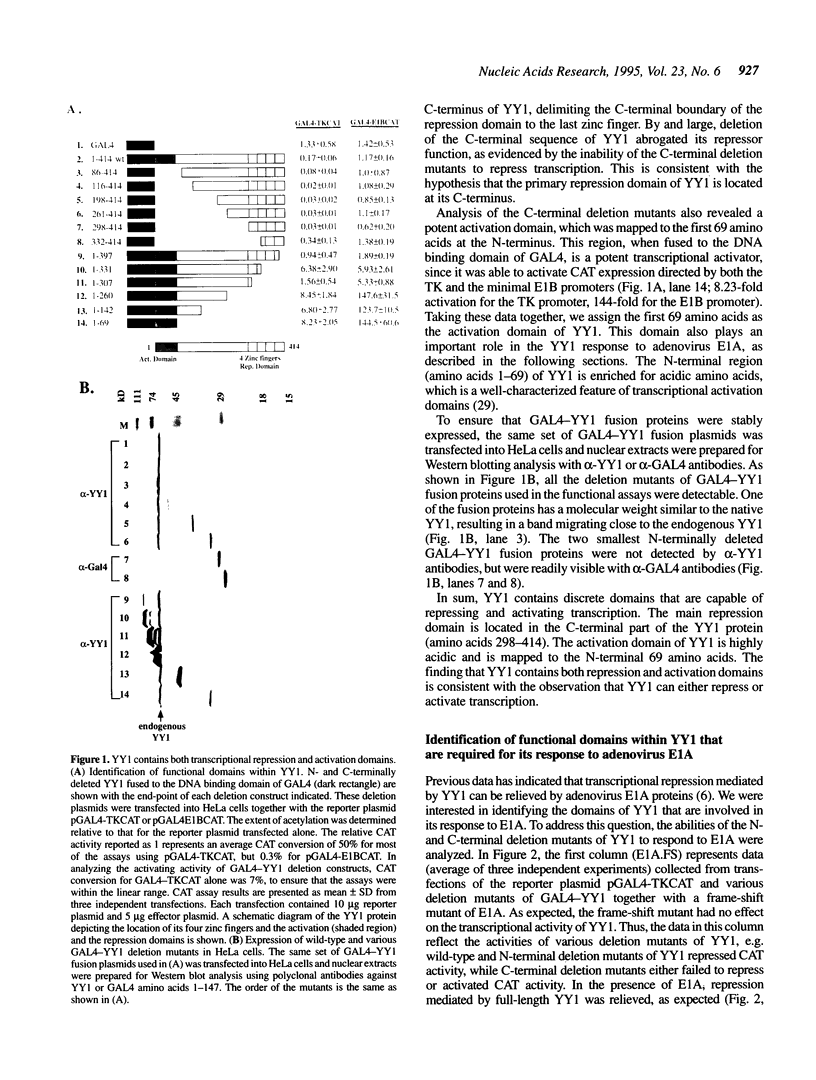
YY1 is a C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor that is a member of the human GLl-Kruppel family of proteins. YY1 represses transcription when bound upstream of transcription initiation sites. The repression can be relieved by adenovirus E1A and activation of target genes occurs. We have mapped the repression domain of YY1 to the C-terminal region, overlapping its DNA binding domain. We have also identified an activation domain within the first 69 amino acids of YY1. The YY1 C-terminal region is involved in physical interactions with E1A and is functionally necessary for YY1 to respond to E1A. This suggests that relief of YY1 repression by E1A involves YY1-E1A physical interactions. Although not involved in interactions with E1A, the N-terminal activation domain is also necessary for YY1 to respond to E1A. Presumably, under repressing conditions, the activation domain is masked by the conformation of YY1, but is released upon binding of E1A and is required to subsequently activate transcription. Consistent with this hypothesis, an ATF-2-YY1 chimeric protein containing the activation domain of ATF-2 and the C-terminal two-thirds of YY1 is still a potent repressor. Unlike the mutant YY1 lacking its own N-terminal activation domain, the chimeric protein is fully responsive to E1A.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu A., Park K., Atchison M. L., Carter R. S., Avadhani N. G. Identification of a transcriptional initiator element in the cytochrome c oxidase subunit Vb promoter which binds to transcription factors NF-E1 (YY-1, delta) and Sp1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4188–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauknecht T., Angel P., Royer H. D., zur Hausen H. Identification of a negative regulatory domain in the human papillomavirus type 18 promoter: interaction with the transcriptional repressor YY1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4607–4617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. S., Shi Y., Shenk T. Adeno-associated virus P5 promoter contains an adenovirus E1A-inducible element and a binding site for the major late transcription factor. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3479–3488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3479-3488.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Becker K. G., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Driggers P. H., Levi B. Z., Appella E., Ozato K. Cloning of a negative transcription factor that binds to the upstream conserved region of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto A., LePage D., Pons G., Mader S. L., Park K., Atchison M. L., Walsh K. Functional antagonism between YY1 and the serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4209–4214. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto A., LePage D., Pons G., Mader S. L., Park K., Atchison M. L., Walsh K. Functional antagonism between YY1 and the serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4209–4214. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Delta, a transcription factor that binds to downstream elements in several polymerase II promoters, is a functionally versatile zinc finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9799–9803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi N., Maguire K., Kralli A., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Weinmann R. Direct interaction between adenovirus E1A protein and the TATA box binding transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5124–5128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Galvin K. M., Shi Y. Evidence for physical interaction between the zinc-finger transcription factors YY1 and Sp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6145–6149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Shi Y., Schwartz R. J. Displacement of BrdUrd-induced YY1 by serum response factor activates skeletal alpha-actin transcription in embryonic myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9814–9818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Zhang Y., Schwartz R. J. Bifunctional transcriptional properties of YY1 in regulating muscle actin and c-myc gene expression during myogenesis. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1047–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kao C. C., Bryant G. O., Liu X., Berk A. J. Adenovirus E1A activation domain binds the basic repeat in the TATA box transcription factor. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. Promoter targeting by adenovirus E1a through interaction with different cellular DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):520–525. doi: 10.1038/368520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis D. M., Somasundaran M., Green M. R. Human transcription factor YY1 represses human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcription and virion production. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):905–910. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.905-910.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M., Dong X. P., Beyer-Finkler E., Stubenrauch F., Fuchs P. G., Pfister H. The E6/E7 promoter of extrachromosomal HPV16 DNA in cervical cancers escapes from cellular repression by mutation of target sequences for YY1. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1460–1466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06400.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo E. A., Shi Y., Shenk T. E., Levine A. J. Negative regulation of the BZLF1 promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3647–3655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3647-3655.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natesan S., Gilman M. Z. DNA bending and orientation-dependent function of YY1 in the c-fos promoter. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2497–2509. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Atchison M. L. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9804–9808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B., Merezhinskaya N., Diffley J. F., Noguchi C. T. Protein-DNA interactions in the epsilon-globin gene silencer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3430–3437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raught B., Khursheed B., Kazansky A., Rosen J. YY1 represses beta-casein gene expression by preventing the formation of a lactation-associated complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1752–1763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs K. J., Saleque S., Wong K. K., Merrell K. T., Lee J. S., Shi Y., Calame K. Yin-yang 1 activates the c-myc promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7487–7495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava A., Calame K. An analysis of genes regulated by the multi-functional transcriptional regulator Yin Yang-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 11;22(24):5151–5155. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.24.5151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava A., Saleque S., Kalpana G. V., Artandi S., Goff S. P., Calame K. Inhibition of transcriptional regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1889–1892. doi: 10.1126/science.8266081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Keegan L. P., Ptashne M. Amino terminus of the yeast GAL4 gene product is sufficient for nuclear localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5951–5955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]