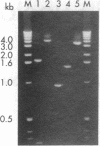
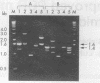
Abstract
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M. PCR amplification of up to 35-kb DNA with high fidelity and high yield from lambda bacteriophage templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2216–2220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Fockler C., Barnes W. M., Higuchi R. Effective amplification of long targets from cloned inserts and human genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5695–5699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., Rajput B., Reich E. The human tissue plasminogen activator gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6972–6985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez O., López-Larrea C. Gene walking by unpredictably primed PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3247–3248. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwahana H., Tsujisawa T., Katashima R., Yoshimoto K., Itakura M. PCR with end trimming and cassette ligation: a rapid method to clone exon-intron boundaries and a 5'-upstream sequence of genomic DNA based on a cDNA sequence. PCR Methods Appl. 1994 Aug;4(1):19–25. doi: 10.1101/gr.4.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Winistorfer S. C. Genome walking with 2- to 4-kb steps using panhandle PCR. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 Feb;2(3):197–203. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.3.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagerström M., Parik J., Malmgren H., Stewart J., Pettersson U., Landegren U. Capture PCR: efficient amplification of DNA fragments adjacent to a known sequence in human and YAC DNA. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Nov;1(2):111–119. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.2.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Gerber A. S., Hartl D. L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):621–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. D., Rabinovitch P. S., Burmer G. C. Targeted gene walking polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):3055–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley J., Butler R., Ogilvie D., Finniear R., Jenner D., Powell S., Anand R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2887–2890. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Jones D. S. Genomic walking and sequencing by oligo-cassette mediated polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3095–3096. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]