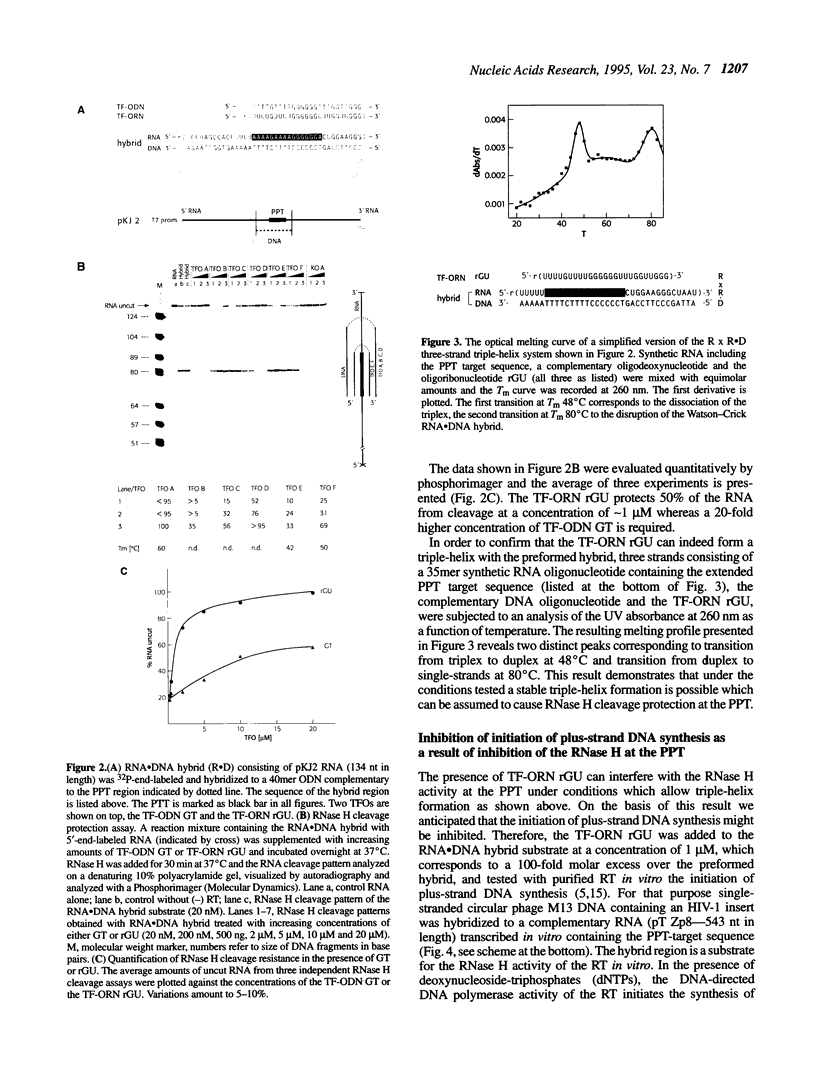
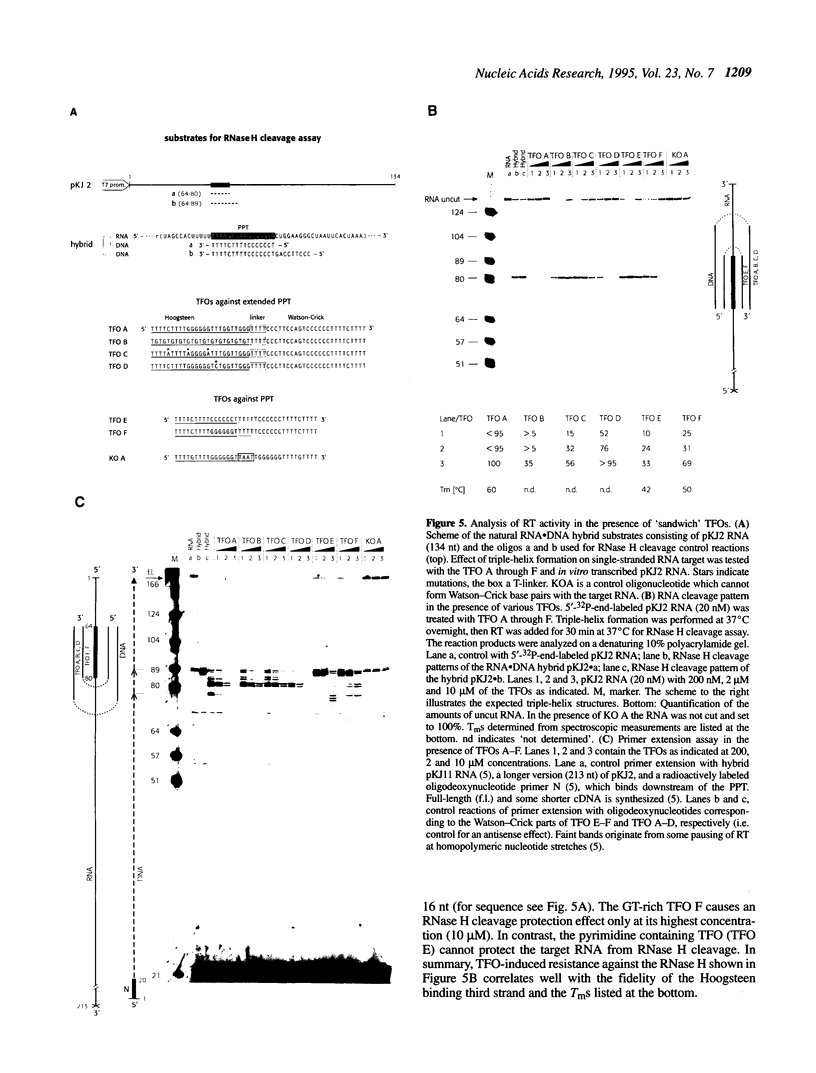
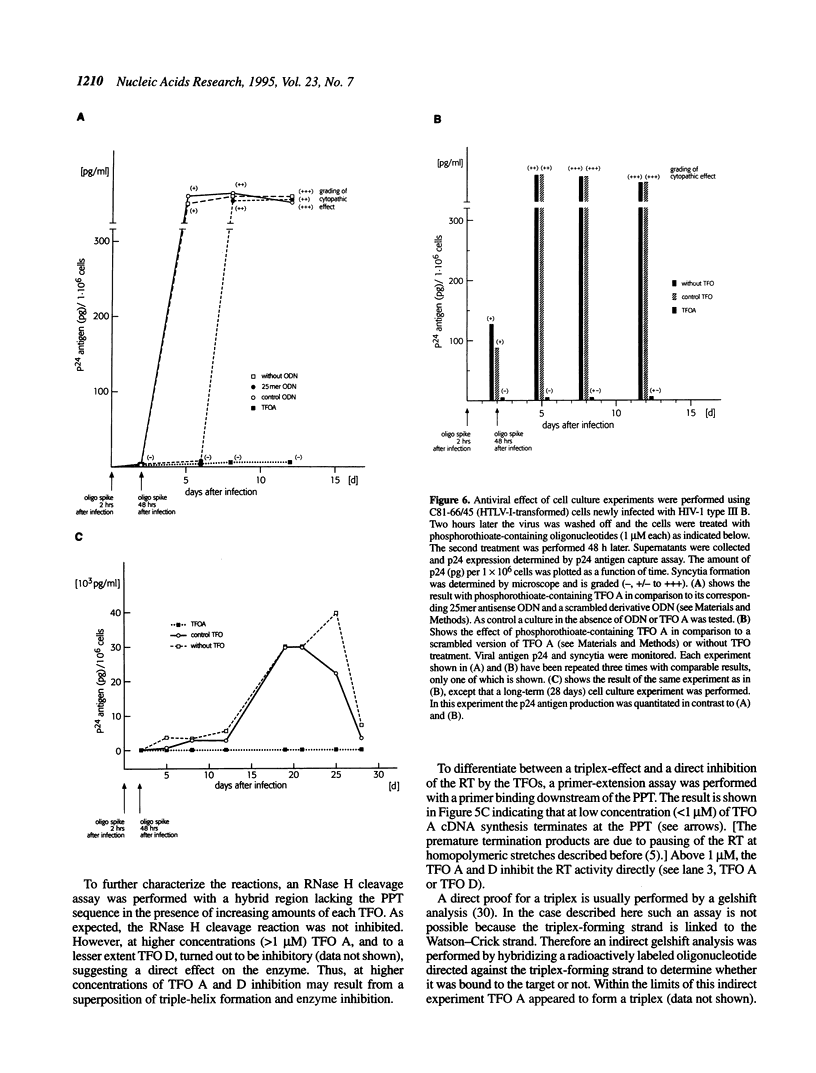
Abstract
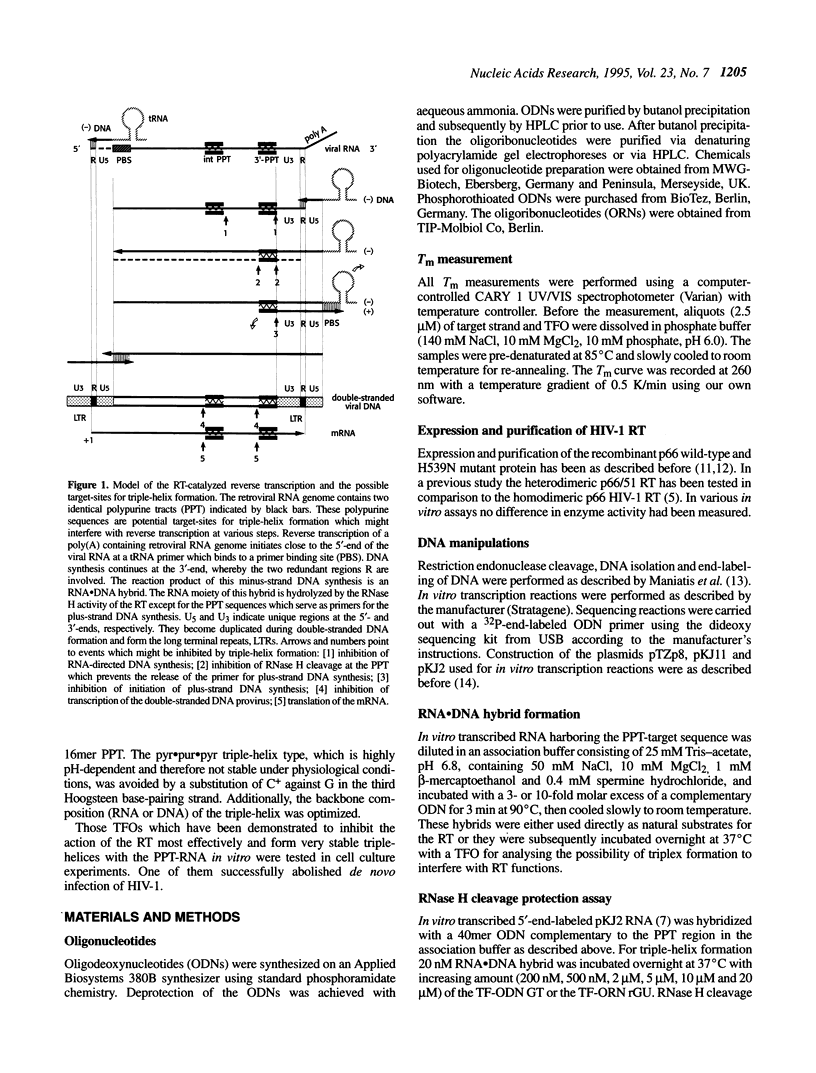
Reverse transcription of retroviral RNA into double-stranded DNA is catalyzed by reverse transcriptase (RT). A highly conserved polypurine tract (PPT) on the viral RNA serves as primer for plus-strand DNA synthesis and is a possible target for triple-helix formation. Triple-helix formation during reverse transcription involves either single-stranded RNA or an RNA.DNA hybrid. The effect of triple-helix formation on reverse transcription has been analyzed here in vitro using a three-strand-system consisting of an RNA.DNA hybrid and triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) consisting either of DNA or RNA. Three strand triple-helices inhibit RNase H cleavage of the PPT-RNA.DNA hybrid and initiation of plus-strand DNA synthesis in vitro. Triple-helix formation on a single-stranded RNA target has also been tested in a two-strand-system with TFOs comprising Watson-Crick and Hoogsteen base-pairing sequences, both targeted to the PPT-RNA, on a single strand connected by a linker (T)4. TFOs prevent RNase H cleavage of the PPT-RNA and initiation of plus-strand DNA synthesis in vitro. In cell culture experiments one TFO is an efficient inhibitor of retrovirus replication, leading to a block of p24 synthesis and inhibition of syncytia formation in newly infected cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charneau P., Alizon M., Clavel F. A second origin of DNA plus-strand synthesis is required for optimal human immunodeficiency virus replication. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2814–2820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2814-2820.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannangeli C., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Oligonucleotide clamps arrest DNA synthesis on a single-stranded DNA target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10013–10017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannangéli C., Rougée M., Garestier T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Triple-helix formation by oligonucleotides containing the three bases thymine, cytosine, and guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8631–8635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannangéli C., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Oligodeoxynucleotide-directed photo-induced cross-linking of HIV proviral DNA via triple-helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4275–4281. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Recognition of thymine adenine.base pairs by guanine in a pyrimidine triple helix motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2549639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Guieysse A. L., Robin P., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. Inhibition of gene expression by triple helix-directed DNA cross-linking at specific sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3501–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical RNA and RNA.DNA by triple helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Moelling K. RNase H activity associated with bacterially expressed reverse transcriptase of human T-cell lymphotropic virus III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B., Purifoy D., Powell K., Darby G. AIDS virus reverse transcriptase defined by high level expression in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3133–3137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02623.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisziewicz J., Sun D., Klotman M., Agrawal S., Zamecnik P., Gallo R. Specific inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by antisense oligonucleotides: an in vitro model for treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11209–11213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölling K., Bolognesi D. P., Bauer H., Büsen W., Plassmann H. W., Hausen P. Association of viral reverse transcriptase with an enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of RNA-DNA hybrids. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 22;234(51):240–243. doi: 10.1038/newbio234240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Stability and properties of double and triple helices: dramatic effects of RNA or DNA backbone composition. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1463–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.1279808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., Giovannangeli C., François J. C., Kurfurst R., Montenay-Garestier T., Asseline U., Saison-Behmoaras T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Triple-helix formation by alpha oligodeoxynucleotides and alpha oligodeoxynucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Schulze T., Larder B. A., Moelling K. Mutations within the RNase H domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase abolish virus infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jan;72(Pt 1):59–66. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., MacDougal S., Gold L. RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann S., Dannull J., Moelling K. The polypurine tract, PPT, of HIV as target for antisense and triple-helix-forming oligonucleotides. Biochimie. 1993;75(1-2):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90027-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann S., Wöhrl B. M., Tisdale M., Moelling K. Enzymatic analysis of two HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mutants with mutations in carboxyl-terminal amino acid residues conserved among retroviral ribonucleases H. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2674–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrl B. M., Moelling K. Interaction of HIV-1 ribonuclease H with polypurine tract containing RNA-DNA hybrids. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10141–10147. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrl B. M., Volkmann S., Moelling K. Mutations of a conserved residue within HIV-1 ribonuclease H affect its exo- and endonuclease activities. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):801–818. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90119-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K., Hobbs C. A., Koch J., Sardaro M., Kutny R., Weis A. L. Elucidation of the sequence-specific third-strand recognition of four Watson-Crick base pairs in a pyrimidine triple-helix motif: T.AT, C.GC, T.CG, and G.TA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Krawczyk S. H., Matteucci M. D., Toole J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10023–10026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]