Abstract
Background:
Bacterial infections remain an important cause of pediatric mortality and morbidity. It might be possible to reduce these factors by early diagnosis and proper management.
Aim:
The aim of the study was to analyze the bacteriological profiles with their antibiogram, and to register the risk factors for septicemia in neonates and infants. Setting and design: This observational cross-sectional study was conducted in a tertiary care teaching hospital at Gangtok, Sikkim, India, and included clinically suspected cases of septicemia in neonates and infants.
Materials and Methods:
Blood culture reports were studied in 363 cases of clinically suspected septicemia in neonates and infants, using the standard technique of Mackie and McCartney. The antibiotic sensitivity was performed by Kirby-Bauer's disc diffusion method. Risk factors for sepsis in the children were registered.
Results:
Blood culture was positive in 22% of cases. Gram-negative septicemia was encountered in 61% of the culture-positive cases. Pseudomonas and Enterobacter species were the predominant pathogens amongst gram-negative organisms. Most gram-negative organisms were sensitive to Amikacin, Ciprofloxacin, and Co-trimoxazole. The most common gram-positive organism isolated was Staphylococcus aureus (97%). More than 70% of Staphylococci isolated were resistant to Penicillin, but were sensitive to Clindamycin (70%) and Vancomycin (40%). The most important risk factors of septicemia in our study population were preterm birth (31%), followed by respiratory distress (5%) and low birth weight (4%).
Conclusion:
As the cultures showed variable antibiogram with complicated patterns of resistance, culture and sensitivity test should be performed in all cases of septicemia.
Keywords: Developing countries, Infant, Neonate, Septicemia
INTRODUCTION
Septicemia constitutes an important cause of morbidity and mortality in the pediatric age group. Blood cultures are not always positive in neonatal septicemia. A combination of clinical, hematological and other microbiological evidence (colony morphology, Gram staining, biochemical properties and sensitivity in the antibiogram) should be used when diagnosing neonatal septicemia. Knowledge of pathogens causing infections in young infants is essential for designing community-based management strategies.[1,2]
Septicemia is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in neonates and children. Numerous risk factors have been identified both in the neonates and children that make them susceptible to infections,[3] which points to the need for bacteriological monitoring in the pediatric wards.[4] The varying microbiological pattern of septicemia in children warrants the need for an ongoing review of the causative organisms and their antimicrobial susceptibility pattern.[5] As gram-negative, multidrug-resistant organisms were the main cause of septicemia in children, great caution is required in selection of antibiotic therapy.[6]
Furthermore, facilities for bacterial culture are not available in most peripheral health facilities in developing countries and neither are pediatricians.Early diagnosis and proper management of neonatal septicemia could bring down the morbidity and mortality substantially. Little is known about the prevalence and incidence of septicemia in the neonates and infants in Sikkim. Hence, the present study was undertaken to study the bacteriological profile and the antimicrobial sensitivity pattern of septicemia in neonates and infants.To the horizon of our knowledge there has been no study done in this field in the state of Sikkim.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study period: January 15, 2007 to January 14, 2008.
Study population: This observational cross-sectional study was carried out at a tertiary care 500 bedded teaching hospital at Gangtok, Sikkim (India) having regular OPD and In-patients department with full-fledged medical and surgical ICU, PICU, and NICU. The study included 363 cases of clinically suspected septicemia in neonates and infants. Signs and symptoms of sepsis included: temperature instability, feeding difficulties, respiratory distress, jaundice, convulsions, and autonomic disturbances. The main outcome measures were microbiologic spectrum of blood cultures and the following risk factors: prematurity (<37 weeks), low birth weight (<2500 g), respiratory distress, and neonatal jaundice.
Data collection procedure: Institutional ethics committee approved the study. All the caregivers of the patients were explained about the purpose of the study and were ensured strict confidentiality. Written informed consents were taken from each of the caregivers of the children prior to the study. Following Helsinki Declaration on research bioethics, the participants and their caregivers were given the options not to participate in the study if they wished. The standard microbiological methods were followed in this study during blood culture and antibiotic sensitivity test. Blood samples were collected with all aseptic precautions for culture and sensitivity studies following universal precautions. Blood cultures were processed using the standard technique described by Mackie and McCartney[7] and the antibiotic sensitivity was performed by Kirby Bauer's disc diffusion method, as recommended in the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) guidelines. The aerobic isolates were studied. Gram staining was performed and organisms were identified based on their colony characteristics and biochemical properties.
Statistical analysis using microsoft excel
The data analysis involved transcription, preliminary data inspection, content analysis, and interpretation. Percentages were used in this study to analyze epidemiological variables.
RESULTS
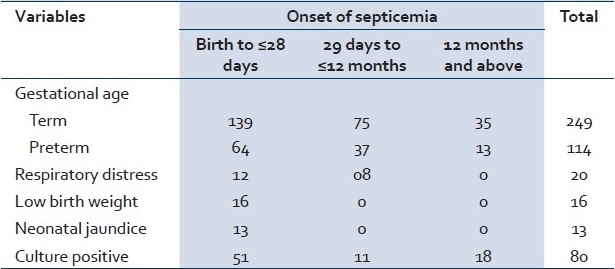
In our study, 363 blood samples were collected from neonates and infants who were admitted with signs and symptoms of sepsis. Out of these, 363 clinically suspected cases of septicemia, 249 (69%) were term and 114 (31%) were preterm babies. The age of onset of septicemia was quite variable in the children in our study. Clinical suspected septicemia was observed in 203 neonates (56%), in 112 infants (31%) from 29 days to12 months of age, and 48 infants (13%) above 12 months of age. The most important risk factor of suspected septicemia in our study population was preterm birth (31%), followed by respiratory distress (5%), low birth weight (4%), and neonatal jaundice (4%). Overall, in the clinically suspected cases of septicemia in our study population a blood culture positivity rate was observed to be 22% of 363 infants [Table 1].
Table 1.
Clinical and demographic characteristics of children with septicemia
The most common gram-positive organism isolated was S. aureus (97%). Only a single isolate of Coagulase negative Staphylococci was found (among the children from 29 days of age up to12 months). The most common gram negative organism were the Enterobacter species (25%) followed by the Pseudomonas species (20%) [Table 2].
Table 2.
Distribution of bacterial isolates
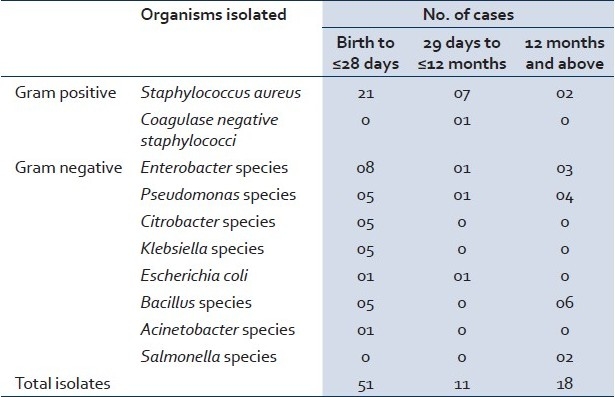
The risk of specific infections was related to the age of the child. Only in neonatal cases Klebsiella, Citrobacter, and Acinetobacter species were isolated. Escherichia coli and Coagulase negative Staphylococci were isolated from cases below one year, whereas Salmonella species were isolated only from two cases after infancy as a causative organism in septicemia [Table 2].
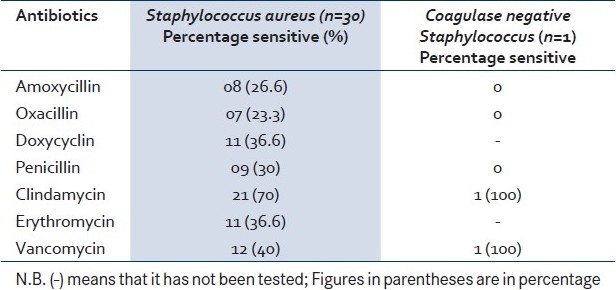
From the antibiotic sensitivity pattern, It is clear that 70% of Staphylococci isolated were resistant to Penicillin. The most effective antibiotic against the Staphylococcal isolate was Clindamycin (70%) followed by Vancomycin (40%). The single isolate of Coagulase negative Staphylococci was sensitive to Clindamycin and Vancomycin. [Table 3]
Table 3.
Sensitivity pattern of the gram positive isolates
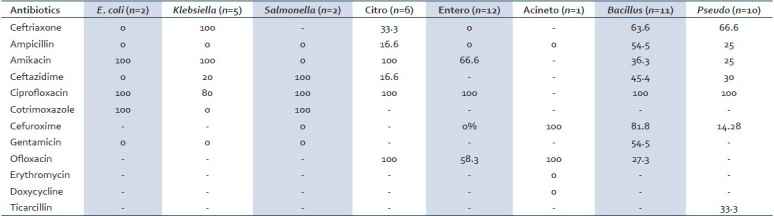
Most of the gram-negative bacteria were sensitive to Ciprofloxacin except one isolate of Klebsiella. Co-trimoxazole was 100% sensitive in E. Coli and Salmonella isolates, but resistant in Klebsiella. All the Citrobacter isolates were sensitive to Amikacin, Ciprofloxacin, and Ofloxacin. Amikacin was effective for all the isolates of Klebsiella species, Citrobacter species, and E. coli. [Table 4]
Table 4.
Sensitivity pattern of the gram-negative isolates (percentage sensitive)
DISCUSSION
For the effectual management of septicemia cases, study of bacteriological profile along with the antimicrobial sensitivity pattern plays a noteworthy role. Out of the 363 clinically suspected cases of sepsis in our study, 80 were culture positive with a blood culture positivity rate of 22%. Gram-negative septicemia was encountered in 61% of the culture positive cases.
A high blood culture positivity rate in septicemic children (56%) had been reported by Sharma et al.[8] However, a lower positivity rate (36%) was observed by Mondal et al,[9] which was comparable with the present study. Chow et al, had reported that 26% of all neonatal septicemias were caused by anerobes.[10] A low blood culture isolation rate in this study might be due to several reasons, like administration of antibiotics before blood collection or anerobic bacteraemia.
Mathur et al, observed that gram-negative species were found in 87% of neonates. Klebsiella species and Enterobacter species were the predominant gram-negative species. Of gram-positive species, S. aureus was mainly isolated (79.06%). Salmonella species were isolated in 2% of cases (comparable to our findings).[11]
The antimicrobial sensitivity pattern differs in different studies as well as at different times in the same hospital in Indian and overseas studies.[12–14] This is mainly a result of indiscriminate use of antibiotics. In our study, we observed that penicillin resistance was found in 70% of the S. aureus strains and the single Coagulase negative staphylococci (CoNS) strain. Similar high rate of penicillin resistance against S.aureus (95%) and CoNS (90%) was seen in a study conducted in Lucknow.[4] In our study, S. aureus showed a sensitivity of 70% to Clindamycin and 40% to Vancomycin. Most of the gram-negative organisms were sensitive to Amikacin, Ciprofloxacin, and Co-trimoxazole. Multiple drug resistance was seen in Enterobacter, E.coli, Klebsiella, and Salmonella species.
A systematic review from the literature for studies from developing countries find that most hospital infections in the first week of life are due to gram-negative pathogens, namely Klebsiella species (25%), E. coli (15%). Strains of Staphylococcus aureus (18%) and Group B streptococci (GBS) were relatively uncommon (7%), although regional differences existed. After the first week of life, S. aureus (14%), GBS (12%), Streptococcus pneumoniae (12%), and nontyphoidal Salmonella species (13%) were most frequent. S. pneumoniae (27%) was the most common during the postneonatal period.[2]
Infections are the single largest cause of neonatal deaths globally. According to National Neonatal Perinatal Database (2002-03), the incidence of neonatal sepsis in India was 30 per 1000 live-births; Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus were the two most common organisms isolated.[15]
There is neither any routine for analyzing blood cultures in suspected septicemia nor for antibiotic treatment of neonates/infants with suspected sepsis in our centre.
We have conducted this study to describe the antibiotic susceptibility pattern to propose our “Hospital Infection Committee” to formulate a revised standard operating procedure.
The strength of this study lies in describing patterns of microbiological behavior from an area where this is not routinely done. This study presented an analysis of septicemia in a tertiary healthcare center in northeastern India.
CONCLUSION
Local microbiological databases suggesting the best choice of antibiotics for different age groups are important for the local physicians when treatment of the septic infant has to be initiated before the result of the blood culture is known. The authors suggest that a local dynamic database has to be established. This should contain relevant data on the positive blood cultures.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Sanghvi KP, Tudehope DI. Neonatal bacterial sepsis in a neonatal intensive care unit: A 5 year analysis. J Paediatr Child Health. 1996;32:333–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1996.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zaidi AK, Thaver D, Ali SA, Khan TA. Pathogens associated with sepsis in newborns and young infants in developing countries. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28:S10–8. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181958769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Meremkwer MM, Nwachukwu CE, Asuquo AE, Okebe J, Utsalo SJ. Bacterial isolates from blood cultures of children with suspected septicemia in Calabar, Nigeria. BMC Infect Dis. 2005;5:110–5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-5-110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roy I, Jain A, Kumar M, Agarwal SK. Bacteriology of neonatal septicaemia in a tertiary care hospital of northern India. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2002;20:156–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Anuradha DE, Saraswathi K, Gogate A, Fernandes AR. Bacteremia in hospitalised children: A one year prospective study. Indian J Med Microbiol. 1995;13:72–5. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sharma M, Yadav A, Yadav S, Goel N, Chaudhury U. Microbial profile of septicemia in children. Indian J Pract Doct. 2008;5:16–8. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Collee JG, Marr W. Mackie and McCartney Practical Medical Microbiology. In: Collee JG, Fraser AG, Marmion BP, Simmons A, editors. Culture of Bacteria. 14th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1996. pp. 113–29. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sharma PP, Halder D, Dutta AK, Dutta R, Bhatnagar S, Bali A, et al. Bacteriological profile of neonatal septicemia. Indian Pediatr. 1987;24:1011–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mondal GP, Raghavan M, Bhat BV, Srinivasan S. Neonatal septicemia among inborn and outborn babies in a referral hospital. Indian J Pediatr. 1991;58:529–33. doi: 10.1007/BF02750936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chow AW, Leake RD, Yamauchi T, Anthony BF, Guze LB. The significance of anerobes in neonatal bacteremia: Analysis of 23 cases and review of literature. Pediatrics. 1974;54:736–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mathur M, Shah H, Dixit K, Khambadkone S, Chakrapani A, Irani S. Bacteriological profile of neonatal septicemia cases (for the year 1990-91) J Postgrad Med. 1994;40:18–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Freedam RM, Ingram DI, Gross I. A half century of neonatal sepsis at Yale. Am J Dis Child. 1981;13:140–4. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130260032010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Somu N, Shetty MV, Moses LG, Subramaniam L, Raju VB. A critical analysis of septicemia in infancy. Indian Pediatr. 1976;13:443–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bhakoo ON, Agarwal KC, Narang A. Prognosis and the treatment of neonatal septicemia: A clinicobacterial study of 100 cases. Indian Pediatr. 1974;11:519–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sankar MJ, Agarwal R, Deorari AK, Paul VK. Sepsis in the newborn. Indian J Pediatr. 2008;75:261–6. doi: 10.1007/s12098-008-0056-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


