Abstract
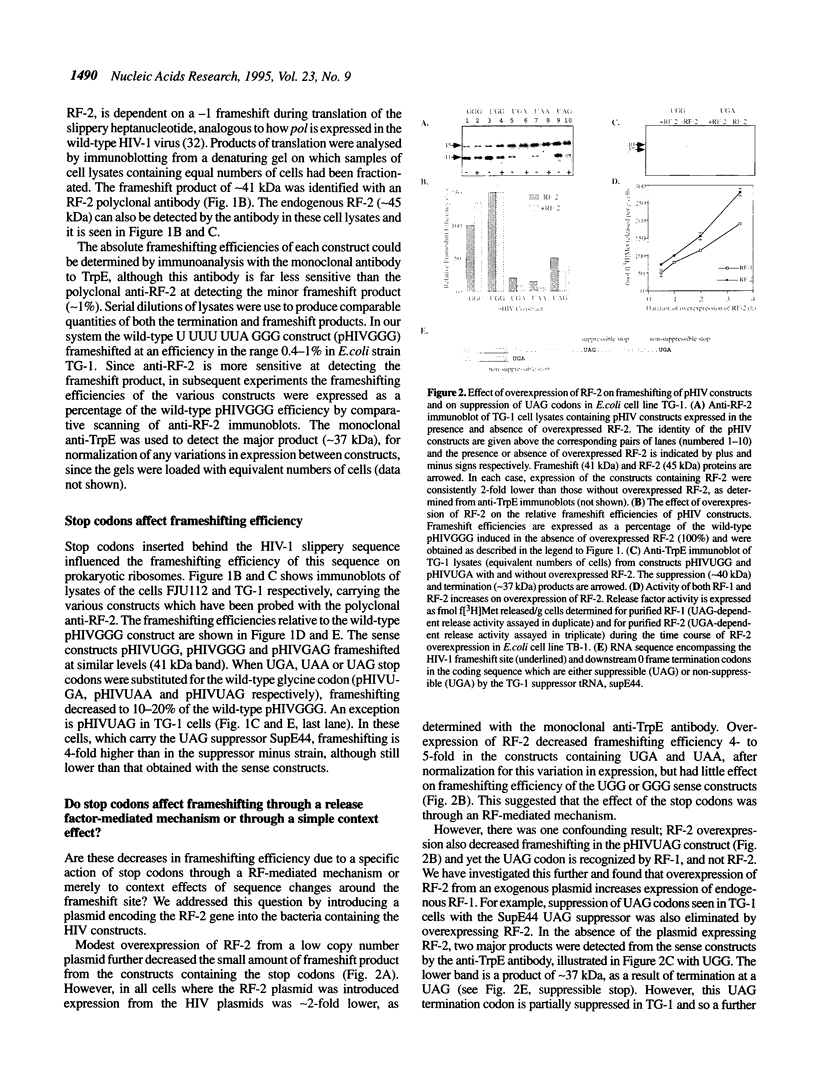
The mechanism favoured for -1 frameshifting at typical retroviral sites is a pre-translocation simultaneous slippage model. An alternative post-translocation mechanism would also generate the same protein sequence across the frameshift site and therefore in this study the strategic placement of a stop codon has been used to distinguish between the two mechanisms. A 26 base pair frameshift sequence from the HIV-1 gag-pol overlap has been modified to include a stop codon immediately 3' to the heptanucleotide frameshift signal, where it often occurs naturally in retroviral recoding sites. Stop codons at the 3'-end of the heptanucleotide sequence decreased the frame-shifting efficiency on prokaryote ribosomes and the recording event was further depressed when the levels of the release factors in vivo were increased. In the presence of elevated levels of a defective release factor 2, frameshifting efficiency in vivo was increased in the constructs containing the stop codons recognized specifically by that release factor. These results are consistent with the last six nucleotides of the heptanucleotide slippery sequence occupying the ribosomal E and P sites, rather than the P and A sites, with the next codon occupying the A site and therefore with a post-translocation rather than a pre-translocation -1 slippage model.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamski F. M., McCaughan K. K., Jørgensen F., Kurland C. G., Tate W. P. The concentration of polypeptide chain release factors 1 and 2 at different growth rates of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 6;238(3):302–308. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkov A. L., Korolev S. V., Kisselev L. L. Termination of translation in bacteria may be modulated via specific interaction between peptide chain release factor 2 and the last peptidyl-tRNA(Ser/Phe). Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2891–2897. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Elseviers D., Gorini L. Low activity of -galactosidase in frameshift mutants of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1192–1195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Weiss R. B., Gesteland R. F. Ribosome gymnastics--degree of difficulty 9.5, style 10.0. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brault V., Miller W. A. Translational frameshifting mediated by a viral sequence in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2262–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I. Probing the mechanism of ribosomal frameshifting on viral RNAs. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Nov;21(4):822–826. doi: 10.1042/bst0210822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M., Fayet O. Translational frameshifting in the control of transposition in bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Feb;7(4):497–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J. J., Belcourt M., Farabaugh P. J. Efficient translational frameshifting occurs within a conserved sequence of the overlap between the two genes of a yeast Ty1 transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6816–6820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigen W. J., Cook R. G., Tate W. P., Caskey C. T. Bacterial peptide chain release factors: conserved primary structure and possible frameshift regulation of release factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3616–3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam E., Pleij K., Draper D. Structural and functional aspects of RNA pseudoknots. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11665–11676. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donly B. C., Edgar C. D., Adamski F. M., Tate W. P. Frameshift autoregulation in the gene for Escherichia coli release factor 2: partly functional mutants result in frameshift enhancement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6517–6522. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J. Alternative readings of the genetic code. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):591–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90507-M. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Weiss R. B., Atkins J. F. Recoding: reprogrammed genetic decoding. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1640–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.1529352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramstat A., Prüfer D., Rohde W. The nucleic acid-binding zinc finger protein of potato virus M is translated by internal initiation as well as by ribosomal frameshifting involving a shifty stop codon and a novel mechanism of P-site slippage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep 25;22(19):3911–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.19.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Oroszlan S. The where, what and how of ribosomal frameshifting in retroviral protein synthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90159-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Madhani H. D., Masiarz F. R., Varmus H. E. Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Power M. D., Masiarz F. R., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Varmus H. E. Characterization of ribosomal frameshifting in HIV-1 gag-pol expression. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):280–283. doi: 10.1038/331280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen F., Adamski F. M., Tate W. P., Kurland C. G. Release factor-dependent false stops are infrequent in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):41–50. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen F., Kurland C. G. Processivity errors of gene expression in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 20;215(4):511–521. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. H., Lommel S. A. Identification and analysis of the site of -1 ribosomal frameshifting in red clover necrotic mosaic virus. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):574–582. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):142–148. doi: 10.1038/342142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa S., Bishop D. H. Identification and analysis of the gag-pol ribosomal frameshift site of feline immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90004-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. Errors and alternatives in reading the universal genetic code. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):273–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.273-298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin N. T., Chamorro M., Varmus H. E. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag-pol frameshifting is dependent on downstream mRNA secondary structure: demonstration by expression in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5147–5151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5147-5151.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom E., Kahana C. Polyamines regulate the expression of ornithine decarboxylase antizyme in vitro by inducing ribosomal frame-shifting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3959–3963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., Brown C. M. Translational termination: "stop" for protein synthesis or "pause" for regulation of gene expression. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2443–2450. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchihashi Z. Translational frameshifting in the Escherichia coli dnaX gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2457–2462. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F., Stansfield I. Termination of protein synthesis. Mol Biol Rep. 1994 May;19(3):171–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00986959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Ribosomal frameshifting from -2 to +50 nucleotides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;39:159–183. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60626-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Slippery runs, shifty stops, backward steps, and forward hops: -2, -1, +1, +2, +5, and +6 ribosomal frameshifting. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:687–693. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Shuh M., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. E. coli ribosomes re-phase on retroviral frameshift signals at rates ranging from 2 to 50 percent. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W., Braddock M., Adams S. E., Rathjen P. D., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. HIV expression strategies: ribosomal frameshifting is directed by a short sequence in both mammalian and yeast systems. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1159–1169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelverton E., Lindsley D., Yamauchi P., Gallant J. A. The function of a ribosomal frameshifting signal from human immunodeficiency virus-1 in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(2):303–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]