Abstract
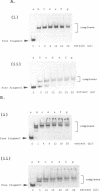
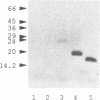
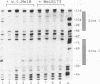
A set of nested deletions has been made in the Escherichia coli melR gene, encoding the MelR transcription activator protein. Expression of the resulting melR derivatives led to the production of nine MelR proteins with N-terminal deletions of different lengths. The properties of the shortened proteins have been studied both in vivo and in vitro. None of the truncated proteins activate transcription from the E.coli melAB promoter but three; MelR220, MelR183 and MelR173, inhibit activation of the melAB promoter by chromosomally-encoded full-length MelR. In gel retardation assays, both MelR183 and MelR173 clearly retard DNA fragments carrying the melAB promoter. MelR173 has been overproduced in a T7 expression system and shown to be stable in vivo for up to 2 h. DNAase I footprinting assays of partially purified protein show that it binds to the melAB promoter, protecting the same sites as the full-length protein. This fragment may be suitable for further structure/function studies of this class of transcription activator.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. L., Berry R. W., Telser A. A sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system that separates peptides and proteins in the molecular weight range of 2500 to 90,000. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;132(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. Determining residue-base interactions between AraC protein and araI DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):607–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustos S. A., Schleif R. F. Functional domains of the AraC protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5638–5642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carra J. H., Schleif R. F. Formation of AraC-DNA sandwiches. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):435–438. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell R., Webster C., Busby S. Studies on the binding of the Escherichia coli MelR transcription activator protein to operator sequences at the MelAB promoter. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):501–508. doi: 10.1042/bj2870501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caswell R., Williams J., Lyddiatt A., Busby S. Overexpression, purification and characterization of the Escherichia coli MelR transcription activator protein. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):493–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2870493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P., Lee J. H., Burke K., Wilcox G. Mutations in the araC gene of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 which affect both activator and auto-regulatory functions of the AraC protein. Gene. 1992 Aug 1;117(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90486-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. A., Coleman K. J., Compton B. E., Kavanagh B. M., Keevil C. W. Nitrite and ammonia assimilation by anaerobic continuous cultures of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Nov;85(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francklyn C. S., Lee N. AraC proteins with altered DNA sequence specificity which activate a mutant promoter in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4400–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallegos M. T., Michán C., Ramos J. L. The XylS/AraC family of regulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):807–810. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Chan B., Kolb A., Fox J., Busby S. Alterations in the binding site of the cyclic AMP receptor protein at the Escherichia coli galactose operon regulatory region. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):809–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2530809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodberg J., Dunn J. J. ompT encodes the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease that cleaves T7 RNA polymerase during purification. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1245-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Wallace J. C., Brown J. P. Finding protein similarities with nucleotide sequence databases. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:111–132. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain H., Grove J., Griffiths L., Busby S., Cole J. A seven-gene operon essential for formate-dependent nitrite reduction to ammonia by enteric bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Apr;12(1):153–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon K. P., Lee N. L. Activation of ara operons by a truncated AraC protein does not require inducer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michán C., Kessler B., de Lorenzo V., Timmis K. N., Ramos J. L. XylS domain interactions can be deduced from intraallelic dominance in double mutants of Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Nov;235(2-3):406–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00279387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Michan C., Rojo F., Dwyer D., Timmis K. Signal-regulator interactions. Genetic analysis of the effector binding site of xylS, the benzoate-activated positive regulator of Pseudomonas TOL plasmid meta-cleavage pathway operon. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90358-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Rojo F., Zhou L., Timmis K. N. A family of positive regulators related to the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid XylS and the Escherichia coli AraC activators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2149–2152. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S., Buc H. On the action of the cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein complex at the Escherichia coli lactose and galactose promoter regions. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90855-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster C., Gardner L., Busby S. The Escherichia coli melR gene encodes a DNA-binding protein with affinity for specific sequences located in the melibiose-operon regulatory region. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster C., Gaston K., Busby S. Transcription from the Escherichia coli melR promoter is dependent on the cyclic AMP receptor protein. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster C., Kempsell K., Booth I., Busby S. Organisation of the regulatory region of the Escherichia coli melibiose operon. Gene. 1987;59(2-3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Michan C., Webster C., Busby S. Interactions between the Escherichia coli MelR transcription activator protein and operator sequences at the melAB promoter. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 15;300(Pt 3):757–763. doi: 10.1042/bj3000757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L. M., Timmis K. N., Ramos J. L. Mutations leading to constitutive expression from the TOL plasmid meta-cleavage pathway operon are located at the C-terminal end of the positive regulator protein XylS. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3707–3710. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3707-3710.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]