Abstract
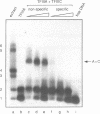
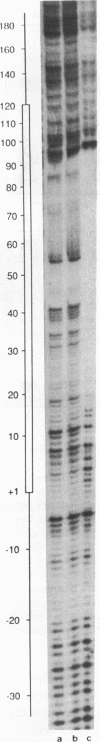
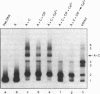
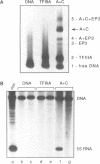
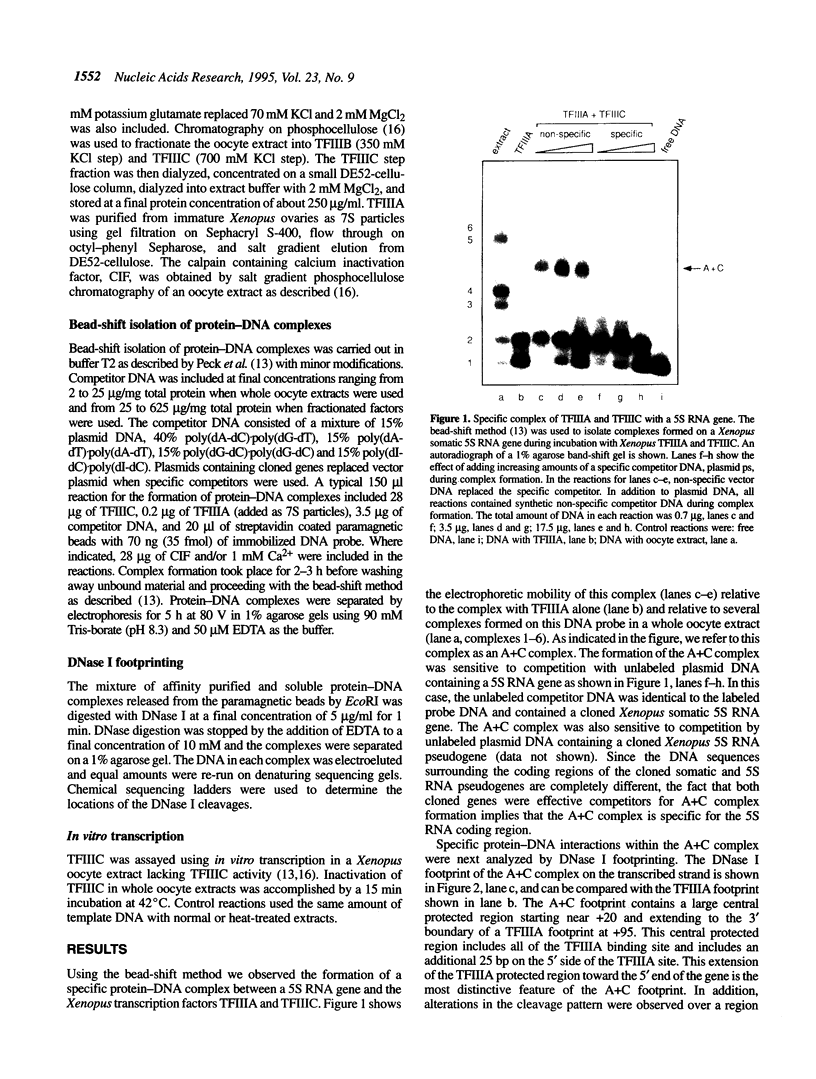
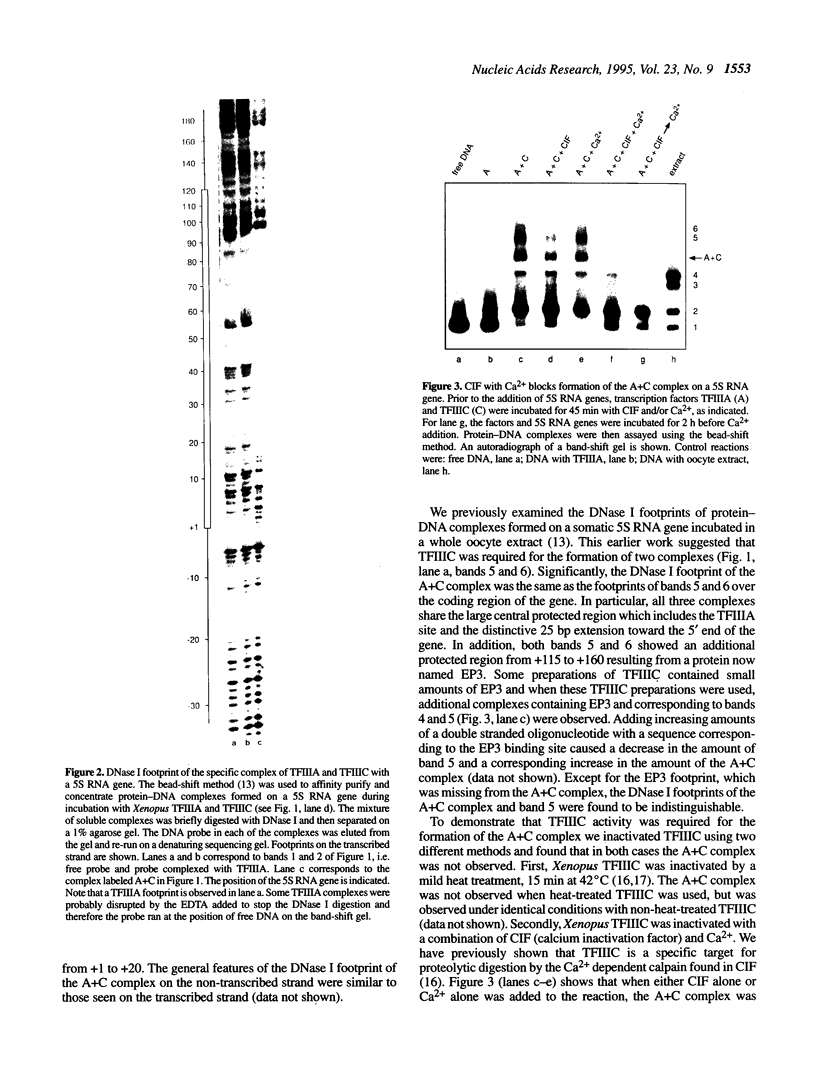
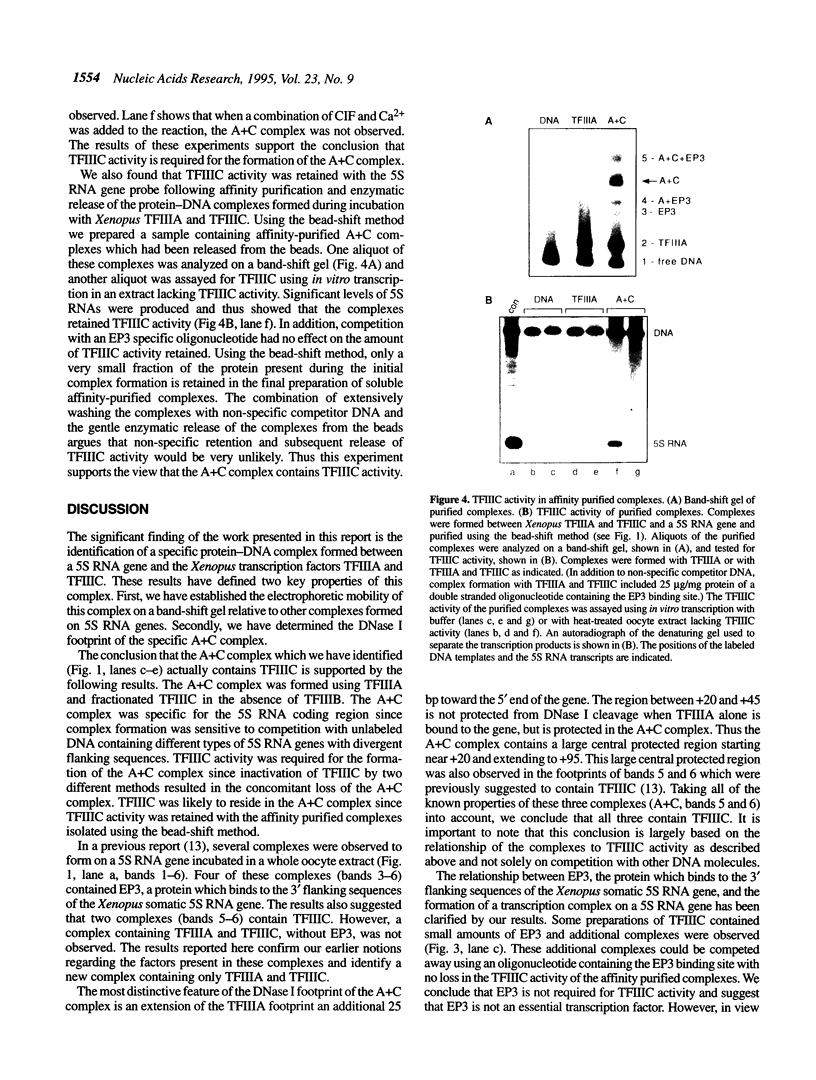
Using fractionated Xenopus transcription factors we have identified and characterized a unique protein-DNA complex formed between TFIIIA, TFIIIC and a 5S RNA gene. The formation of this complex was blocked by specific competitor DNAs and by the inactivation of TFIIIC using two different methods. In addition, TFIIIC activity was retained when the complexes were affinity purified using a reversibly immobilized DNA template. The TFIII(A+C)-5S RNA gene complex has a distinct electrophoretic mobility on band-shift gels and a unique DNase I footprint. The characteristic feature of the DNase I footprint is a TFIIIC-dependent extension of the TFIIIA footprint an additional 25 bp toward the 5' end of the gene. This indicates a direct interaction between Xenopus TFIIIC and the template DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun B. R., Bartholomew B., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Topography of transcription factor complexes on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5 S RNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1063–1077. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90315-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun B. R., Riggs D. L., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Multiple states of protein-DNA interaction in the assembly of transcription complexes on Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2530–2534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Ge H., Wang Z., Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Unique TATA-binding protein-containing complexes and cofactors involved in transcription by RNA polymerases II and III. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2749–2762. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipev C. C., Wolffe A. P. Chromosomal organization of Xenopus laevis oocyte and somatic 5S rRNA genes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Gottesfeld J. M. Chromosomal footprinting of transcriptionally active and inactive oocyte-type 5S RNA genes of Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6031–6037. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase III (C) and its transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):412–416. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90166-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J., Tullius T. D., Wolffe A. P. A protein-protein interaction is essential for stable complex formation on a 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6009–6012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. J., Romaniuk P. J., Gottesfeld J. M. Interaction of Xenopus TFIIIC with the TFIIIA.5 S RNA gene complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18190–18198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. J., You Q. M., Romaniuk P. J., Gottesfeld J. M. Additional intragenic promoter elements of the Xenopus 5S RNA genes upstream from the TFIIIA-binding site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5166–5176. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovelman R., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of two forms of human transcription factor IIIC. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24446–24456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Etoile N. D., Fahnestock M. L., Shen Y., Aebersold R., Berk A. J. Human transcription factor IIIC box B binding subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1652–1656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagna G., Kovelman R., Sukegawa J., Roeder R. G. Cloning and characterization of an evolutionarily divergent DNA-binding subunit of mammalian TFIIIC. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3053–3064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Bartilson M., DeRisi J. L. Bead-shift isolation of protein--DNA complexes on a 5S RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):443–449. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Azer K. Sequence differences upstream of the promoters are involved in the differential expression of the Xenopus somatic and oocyte 5S RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3391–3403. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. R., Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Purification of human transcription factor IIIC and its binding to the gene for ribosomal 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5003–5016. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel C. W., Peck L. J. Kinetic control of 5 S RNA gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90517-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturges M. R., Peck L. J. Calcium-dependent inactivation of RNA polymerase III transcription. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5712–5719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. DNA replication in vitro erases a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Morse R. H. The transcription complex of the Xenopus somatic 5 S RNA gene. A functional analysis of protein-DNA interactions outside of the internal control region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4592–4599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription fraction TFIIIC can regulate differential Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Boulanger P. A., Berk A. J. Resolution of human transcription factor TFIIIC into two functional components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]