Abstract
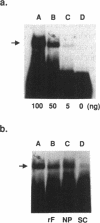
HOX11 is a homeobox-containing oncogene of specific T-cell leukemias. We determined the DNA binding specificity of the Hox11 protein by using a novel technique of random oligonucleotide selection developed in this study. The optimal Hox11 binding sequence, GGCGGTAAGTGG, contained a core TAAGTG motif that is consistent with a prediction based on the residues at specific positions that potentially make DNA base contacts and models of homeodomain-DNA interaction proposed from studies with other homeodomains. The specific interaction between Hox11 and the selected optimal binding sequence was further confirmed by band-shift and DNA competition assays. Given that the Hox11 homeodomain shares low homology with other well studied homeodomains, the presence of a predictable recognition core motif in its optimal binding sequence supports the notion that different homeodomains interact with DNA in a similar manner, through highly conserved residues at specific positions that allow contact with DNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Lotem J., Sachs L. Inhibition of specific pathways of myeloid cell differentiation by an activated Hox-2.4 homeobox gene. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Oct;3(10):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear T. N., Sanchez-Garcia I., Rabbitts T. H. The HOX11 gene encodes a DNA-binding nuclear transcription factor belonging to a distinct family of homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4431–4435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubé I. D., Kamel-Reid S., Yuan C. C., Lu M., Wu X., Corpus G., Raimondi S. C., Crist W. M., Carroll A. J., Minowada J. A novel human homeobox gene lies at the chromosome 10 breakpoint in lymphoid neoplasias with chromosomal translocation t(10;14). Blood. 1991 Dec 1;78(11):2996–3003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Furukubo-Tokunaga K., Schier A. F., Resendez-Perez D., Affolter M., Otting G., Wüthrich K. Homeodomain-DNA recognition. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. A genetic model for interaction of the homeodomain recognition helix with DNA. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1671176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. DNA specificity of the bicoid activator protein is determined by homeodomain recognition helix residue 9. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1275–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatano M., Roberts C. W., Minden M., Crist W. M., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulation of a homeobox gene, HOX11, by the t(10;14) in T cell leukemia. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1676542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Warrior R., Manak J., Levine M. DNA-binding activities of the Drosophila melanogaster even-skipped protein are mediated by its homeo domain and influenced by protein context. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4598–4607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Müller U., Li X., Ma L., Luo W., Haworth I. S., Klisak I., Sparkes R., Warman M. L., Mulliken J. B. A mutation in the homeodomain of the human MSX2 gene in a family affected with autosomal dominant craniosynostosis. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90379-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Activation and repression of transcription by homoeodomain-containing proteins that bind a common site. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):744–749. doi: 10.1038/336744a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Murre C., Sun X. H., Baltimore D. A new homeobox gene contributes the DNA binding domain of the t(1;19) translocation protein in pre-B ALL. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen C., Schughart K., Ruddle F. H. Early evolutionary origin of major homeodomain sequence classes. Genomics. 1993 Oct;18(1):54–70. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. A., Gonzalez-Sarmiento R., Kees U. R., Lampert F., Dear N., Boehm T., Rabbitts T. H. HOX11, a homeobox-containing T-cell oncogene on human chromosome 10q24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8900–8904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. A homeodomain substitution changes the regulatory specificity of the deformed protein in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L., McGinnis W. Mapping functional specificity in the Dfd and Ubx homeo domains. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1071–1081. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu M., Gong Z. Y., Shen W. F., Ho A. D. The tcl-3 proto-oncogene altered by chromosomal translocation in T-cell leukemia codes for a homeobox protein. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2905–2910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07840.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourse J., Mellentin J. D., Galili N., Wilkinson J., Stanbridge E., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. Chromosomal translocation t(1;19) results in synthesis of a homeobox fusion mRNA that codes for a potential chimeric transcription factor. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90657-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J. The interaction with DNA of wild-type and mutant fushi tarazu homeodomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3967–3974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju K., Tang S., Dubé I. D., Kamel-Reid S., Bryce D. M., Breitman M. L. Characterization and developmental expression of Tlx-1, the murine homolog of HOX11. Mech Dev. 1993 Nov;44(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90016-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. W., Shutter J. R., Korsmeyer S. J. Hox11 controls the genesis of the spleen. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):747–749. doi: 10.1038/368747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., McGinnis W., Carrasco A. E., De Robertis E. M., Gehring W. J. Fly and frog homoeo domains show homologies with yeast mating type regulatory proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):70–71. doi: 10.1038/310070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Gönczy P., Vashishtha M., Harris E., Desplan C. A single amino acid can determine the DNA binding specificity of homeodomain proteins. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Wilson D., Desplan C. The homeodomain: a new face for the helix-turn-helix? Bioessays. 1992 Mar;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. B., Ghysdael J., Owen M. J. Identification of nucleotide preferences in DNA sequences recognised specifically by c-Ets-1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):699–704. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]