Abstract
Characterization of the regulatory elements involved in V(D)J recombination is crucial for understanding development of the B and T cell immune repertoire. Previously we have shown that the chicken immunoglobulin lambda light chain gene (CLLCG) undergoes lymphoid-specific rearrangement in transgenic mice. The whole gene is only 10 kb in length and contains all phylogenetically conserved target sites for recombinational and transcriptional regulation. In this study we have localized an enhancer element in a region 4 kb downstream of the constant (C) region. The 467 bp element can be subdivided into three subfragments. The previously detected silencer element on the V-J intervening sequence is shown to be localized on a 500 bp fragment. Partial silencer activity is retained on a 250 bp fragment, which includes an octamer motif. By mutational analysis this octamer is shown to be essential for B cell- but not for T cell-specific silencer function. The silencer represses transcription directed by heterologous elements like the SV 40 promoter or the Ig kappa 3' enhancer. We propose that transcription of the unrearranged and rearranged Ig genes is regulated by complex interactions between different modules from the promoter, enhancer and silencer, which is eliminated by recombination during B cell development.
Full text
PDF

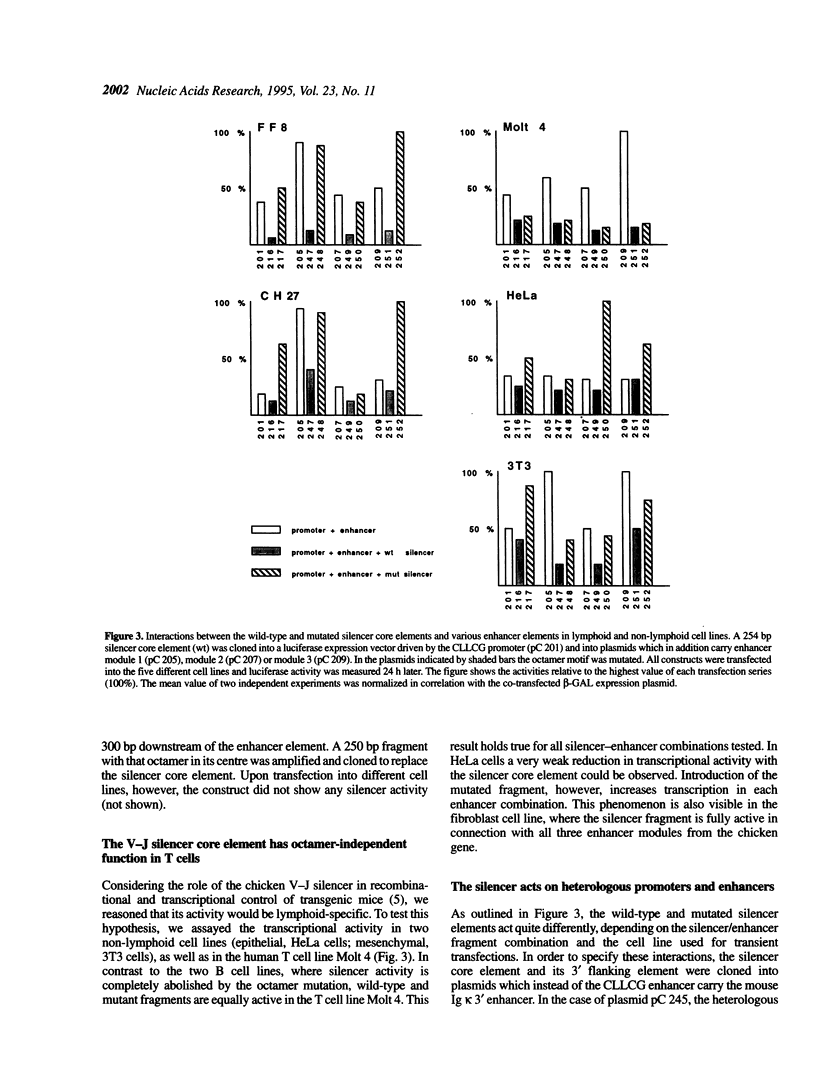

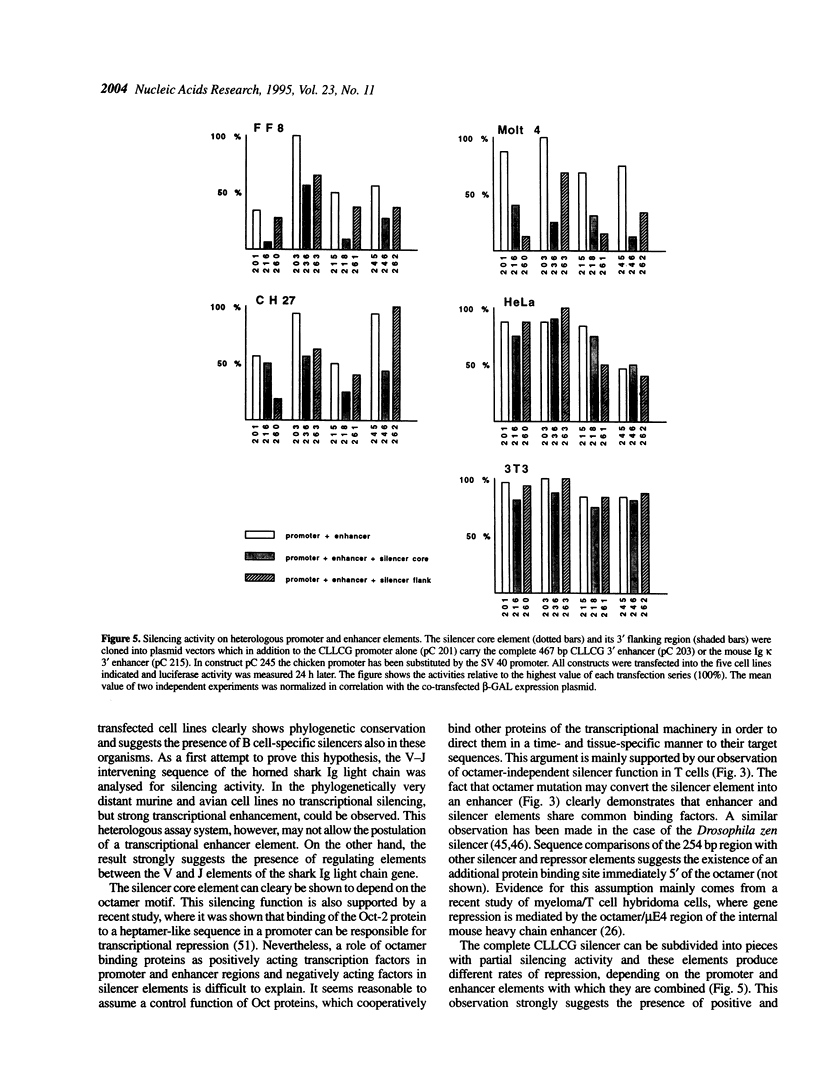

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Oltz E. M., Young F., Gorman J., Taccioli G., Chen J. VDJ recombination. Immunol Today. 1992 Aug;13(8):306–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Wood C., Thomas E., Boss M., Coffman R., Rosenberg N., Tonegawa S., Baltimore D. Ordered rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region segments. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1209–1219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benatar T., Tkalec L., Ratcliffe M. J. Stochastic rearrangement of immunoglobulin variable-region genes in chicken B-cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7615–7619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucchini D., Reynaud C. A., Ripoche M. A., Grimal H., Jami J., Weill J. C. Rearrangement of a chicken immunoglobulin gene occurs in the lymphoid lineage of transgenic mice. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):409–411. doi: 10.1038/326409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K. L. Immunoglobulin gene transcription: molecular mechanisms. Trends Genet. 1989 Dec;5(12):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. Identification of an octamer-binding site in the mouse kappa light-chain immunoglobulin enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4239–4247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson S. J., Yoon S. O., Chikaraishi D. M., Lillycrop K. A., Latchman D. S. The Oct-2 transcription factor represses tyrosine hydroxylase expression via a heptamer TAATGARAT-like motif in the gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1023–1028. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferradini L., Reynaud C. A., Lauster R., Weill J. C. Rearrangement of the chicken lambda light chain locus: a silencer/antisilencer regulation. Semin Immunol. 1994 Jun;6(3):165–173. doi: 10.1006/smim.1994.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti R. A., Leibold W. HLA--D typing with lymphoblastoid cell lines. IV. Allelic relationships. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Jan;13(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb01134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goraya T. Y., Kessler S. P., Kumar R. S., Douglas J., Sen G. C. Identification of positive and negative transcriptional regulatory elements of the rabbit angiotensin-converting enzyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1194–1201. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant P. A., Arulampalam V., Ahrlund-Richter L., Pettersson S. Identification of Ets-like lymphoid specific elements within the immunoglobulin heavy chain 3' enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4401–4408. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Cai H., Zhou Q., Levine M. Conversion of a dorsal-dependent silencer into an enhancer: evidence for dorsal corepressors. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3201–3209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler I., Schreiber E., Müller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W. Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2001–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirov N., Zhelnin L., Shah J., Rushlow C. Conversion of a silencer into an enhancer: evidence for a co-repressor in dorsal-mediated repression in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3193–3199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenson P., Rine J. Silencers, silencing, and heritable transcriptional states. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):543–560. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.543-560.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauster R., Reynaud C. A., Mårtensson I. L., Peter A., Bucchini D., Jami J., Weill J. C. Promoter, enhancer and silencer elements regulate rearrangement of an immunoglobulin transgene. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4615–4623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. Regulation of the immunoglobulin gene transcription. Biochimie. 1990 Jan;72(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90167-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Suzuki T., Mori N., Greengard P. Identification of a functional silencer element involved in neuron-specific expression of the synapsin I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1460–1464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Tjoelker L. W., Thompson C. B. Avian B-cell development: generation of an immunoglobulin repertoire by gene conversion. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:219–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. B., Sharpe M. J., Surani M. A., Neuberger M. S. The importance of the 3'-enhancer region in immunoglobulin kappa gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5609–5615. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. L., Feldhaus A. L., Rooney J. W., Rhodes L. D., Sibley C. H., Singh H. Regulation and a possible stage-specific function of Oct-2 during pre-B-cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4885–4894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Iacomini J., Johnson R. S., Herrup K., Tonegawa S., Papaioannou V. E. RAG-1-deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson I. L., Leanderson T. Transient gene expression in untransformed lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1499–1502. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourbakhsh M., Hoffmann K., Hauser H. Interferon-beta promoters contain a DNA element that acts as a position-independent silencer on the NF-kappa B site. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):451–459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Schatz D. G., Gorka C., Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1517–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.2360047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell C. A., Arnold L. W., Lutz P. M., LoCascio N. J., Willoughby P. B., Haughton G. Cross-reactive idiotypes and common antigen binding specificities expressed by a series of murine B-cell lymphomas: etiological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3799–3803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Gifford A. M., Baltimore D. Silencing of the expression of the immunoglobulin kappa gene in non-B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1431–1437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Atchison M. L. Functional characterization of the developmentally controlled immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer: regulation by Id, a repressor of helix-loop-helix transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1040–1047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Imhof B. A., Anquez V., Weill J. C. Emergence of committed B lymphoid progenitors in the developing chicken embryo. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4349–4358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin C. M., Storb U. Two conserved essential motifs of the murine immunoglobulin lambda enhancers bind B-cell-specific factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):309–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela K., Baltimore D. Negative regulation of immunoglobulin kappa light-chain gene transcription by a short sequence homologous to the murine B1 repetitive element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3698–3705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Schlissel M. S. V(D)J recombination: molecular biology and regulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:359–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamblott M. J., Litman G. W. Genomic organization and sequences of immunoglobulin light chain genes in a primitive vertebrate suggest coevolution of immunoglobulin gene organization. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3733–3739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Lieberman S., Eckhardt L. A. The octamer/mu E4 region of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer mediates gene repression in myeloma x T-lymphoma hybrids. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3530–3540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Rathbun G., Lam K. P., Oltz E. M., Stewart V., Mendelsohn M., Charron J., Datta M., Young F., Stall A. M. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):855–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Birshtein B. K. NF-HB (BSAP) is a repressor of the murine immunoglobulin heavy-chain 3' alpha enhancer at early stages of B-cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3611–3622. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover D. M., Zehner Z. E. Identification of a cis-acting DNA antisilencer element which modulates vimentin gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2230–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomilin N. V., Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Ariga H. Transcription and replication silencer element is present within conserved region of human Alu repeats interacting with nuclear protein. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80707-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Oketani M., Watanabe T. Positive and negative regulation of immunoglobulin gene expression by a novel B-cell-specific enhancer element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weill J. C., Reynaud C. A. The chicken B cell compartment. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1094–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.3317827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. Alpha beta lineage-specific expression of the alpha T cell receptor gene by nearby silencers. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]