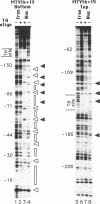
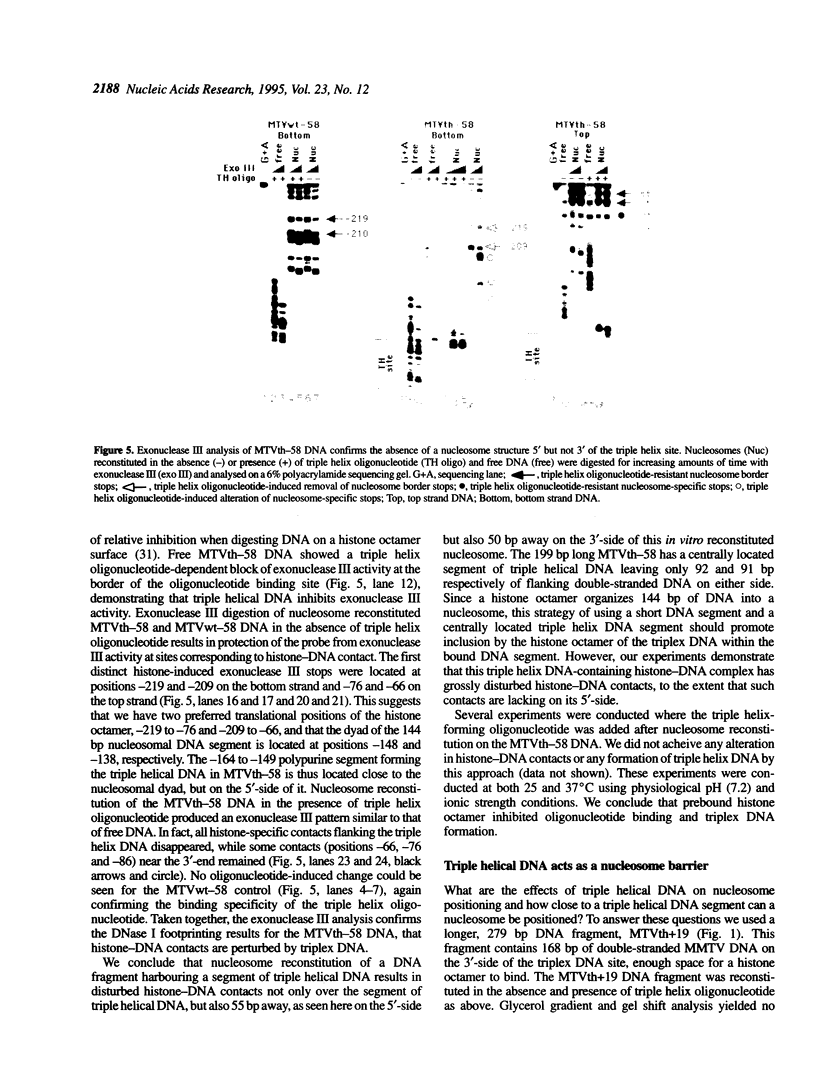
Abstract
Oligonucleotides which form triple helical complexes on double-stranded DNA have been previously reported to selectively inhibit transcription both in vitro and in vivo by physically blocking RNA polymerase or transcription factor access to the DNA template. Here we show that a 16mer oligonucleotide, which forms triple helix DNA by binding to a 16 bp homopurine segment, alters the formation of histone-DNA contacts during in vitro nucleosome reconstitution. This effect was DNA sequence-specific and required the oligonucleotide to be present during in vitro nucleosome reconstitution. Binding of the triple helix oligonucleotide on a 199 bp mouse mammary tumour virus promoter DNA fragment with a centrally located triplex DNA resulted in interruption of histone-DNA contacts flanking the triplex DNA segment. When nucleosome reconstitution is carried out on a longer, 279 bp DNA fragment with an asymmetrically located triplex site, nucleosome formation occurred at the border of the triple helical DNA. In this case the triplex DNA functioned as a nucleosome barrier. We conclude that triplex DNA cannot be accommodated within a nucleosome context and thus may be used to site-specifically manipulate nucleosome organization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer T. K., Lefebvre P., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1347958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arents G., Moudrianakis E. N. Topography of the histone octamer surface: repeating structural motifs utilized in the docking of nucleosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10489–10493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Rories C., Hager G. L. Evidence that nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter adopt specific translational positions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):865–870. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Kühnel B. Distinct sequence elements involved in the glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Mann R. K., Grunstein M. Nucleosome loss activates CUP1 and HIS3 promoters to fully induced levels in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1621–1629. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehler B. C., Ng P. G., Matteucci M. D. Synthesis of DNA via deoxynucleoside H-phosphonate intermediates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5399–5407. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Histone function in transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:643–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Kim U. J., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Depletion of histone H4 and nucleosomes activates the PHO5 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2221–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Nguyen D., Martinez R., Edwards C. A. Triple-helix formation is compatible with an adjacent DNA-protein complex. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 4;31(4):993–998. doi: 10.1021/bi00119a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk S. H., Milligan J. F., Wadwani S., Moulds C., Froehler B. C., Matteucci M. D. Oligonucleotide-mediated triple helix formation using an N3-protonated deoxycytidine analog exhibiting pH-independent binding within the physiological range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3761–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. L., Archer T. K. Nucleosome-mediated disruption of transcription factor-chromatin initiation complexes at the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):32–41. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Wrange O. Translational positioning of a nucleosomal glucocorticoid response element modulates glucocorticoid receptor affinity. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2471–2482. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losa R., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes in vitro through a nucleosome core without displacing it. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):801–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd DNA triple-helix formation: an approach to artificial gene repressors? Bioessays. 1992 Dec;14(12):807–815. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd Inhibition of T7 RNA polymerase initiation by triple-helical DNA complexes: a model for artificial gene repression. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7587–7594. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson C. E., Shim E. Y., Friedman D. S., Zaret K. S. An active tissue-specific enhancer and bound transcription factors existing in a precisely positioned nucleosomal array. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Eriksson P., Wrange O. Quantitative analysis of the glucocorticoid receptor-DNA interaction at the mouse mammary tumor virus glucocorticoid response element. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17222–17229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Wrange O. Inhibition of chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes correlates with derepression of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5259–5265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Wrange O. Specific glucocorticoid receptor binding to DNA reconstituted in a nucleosome. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3073–3079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay N. Deletion analysis of a DNA sequence that positions itself precisely on the nucleosome core. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild C., Claret F. X., Wahli W., Wolffe A. P. A nucleosome-dependent static loop potentiates estrogen-regulated transcription from the Xenopus vitellogenin B1 promoter in vitro. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):423–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning: occurrence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:143–184. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60841-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter U., Svaren J., Schmitz J., Schmid A., Hörz W. A nucleosome precludes binding of the transcription factor Pho4 in vivo to a critical target site in the PHO5 promoter. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4848–4855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallrath L. L., Lu Q., Granok H., Elgin S. C. Architectural variations of inducible eukaryotic promoters: preset and remodeling chromatin structures. Bioessays. 1994 Mar;16(3):165–170. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription: in tune with the histones. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):13–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holde K., Zlatanova J. Unusual DNA structures, chromatin and transcription. Bioessays. 1994 Jan;16(1):59–68. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]