Abstract
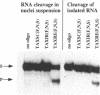
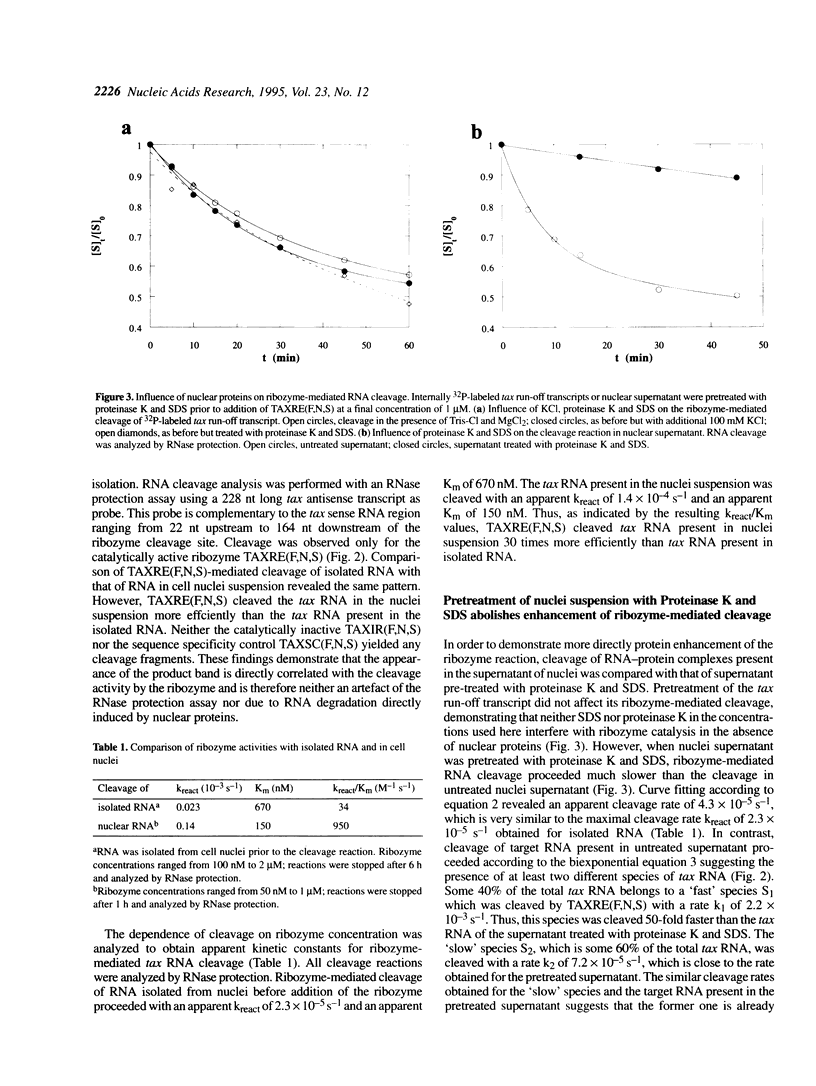
Ribozymes containing 2'-fluoro- and 2'-amino-modified pyrimidine nucleosides in combination with terminal phosphorothioate linkages were targeted against HTLV-I tax RNA. In order to examine the activity of such chemically modified ribozymes in the nuclear environment, they were incubated with nuclei of a Tax-transformed mouse fibroblast cell line. Ribozyme cleavage of tax RNA was analyzed by the RNase protection assay. Comparison of the cleavage of tax RNA isolated nuclei with that of tax RNA present in nuclei suspension revealed a 30 times more efficient cleavage of the latter one. Pre-treatment with proteinase K and SDS abolished the enhancement of the ribozyme-mediated RNA cleavage. Catalytically inactive ribozymes did not yield any cleavage products. These results demonstrate an augmenting effect of nuclear proteins on the ribozyme-mediated RNA cleavage.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertrand E. L., Rossi J. J. Facilitation of hammerhead ribozyme catalysis by the nucleocapsid protein of HIV-1 and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2904–2912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand E., Pictet R., Grange T. Can hammerhead ribozymes be efficient tools to inactivate gene function? Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):293–300. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron F. H., Jennings P. A. Specific gene suppression by engineered ribozymes in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Birnstiel M. L. Ribozyme mediated destruction of RNA in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3861–3866. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Rogers J. Design and specificity of hammerhead ribozymes against calretinin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5171–5178. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Kinetics of intermolecular cleavage by hammerhead ribozymes. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12042–12054. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher T. L., Terhorst T., Cao X., Wagner R. W. Intracellular disposition and metabolism of fluorescently-labeled unmodified and modified oligonucleotides microinjected into mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3857–3865. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of plus and minus RNAs of a virusoid and a structural model for the active sites. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Gerlach W. L. Simple RNA enzymes with new and highly specific endoribonuclease activities. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):585–591. doi: 10.1038/334585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich O., Benseler F., Fahrenholz A., Eckstein F. High activity and stability of hammerhead ribozymes containing 2'-modified pyrimidine nucleosides and phosphorothioates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2131–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich O., Eckstein F. Hammerhead ribozyme-mediated cleavage of the long terminal repeat RNA of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich O., Pieken W., Eckstein F. Chemically modified RNA: approaches and applications. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):90–96. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7678566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Khosla M., Tsuchihashi Z., Karpel R. L. An RNA chaperone activity of non-specific RNA binding proteins in hammerhead ribozyme catalysis. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2913–2924. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel K. J., Herschlag D., Uhlenbeck O. C. A kinetic and thermodynamic framework for the hammerhead ribozyme reaction. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 22;33(11):3374–3385. doi: 10.1021/bi00177a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel K. J., Pardi A., Uhlenbeck O. C., Koizumi M., Ohtsuka E., Uesugi S., Cedergren R., Eckstein F., Gerlach W. L., Hodgson R. Numbering system for the hammerhead. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3252–3252. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehntopf M., Brach M. A., Licht T., Petschauer S., Karawajew L., Kirschning C., Herrmann F. Ribozyme-mediated cleavage of the MDR-1 transcript restores chemosensitivity in previously resistant cancer cells. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4645–4652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Kiehntopf M., Herrmann F., Brach M. A. Functional NF-IL6/CCAAT enhancer-binding protein is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducible expression of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CSF), but not the granulocyte/macrophage CSF or interleukin 6 gene in human fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):793–798. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Kitajima I., Shinohara T., Minor T., Bibbs L., Bilakovics J., Nerenberg M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax transformation is associated with increased uptake of oligodeoxynucleotides in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25881–25888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange W., Cantin E. M., Finke J., Dölken G. In vitro and in vivo effects of synthetic ribozymes targeted against BCR/ABL mRNA. Leukemia. 1993 Nov;7(11):1786–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Mechti N., Degols G., Gagnor C., Lebleu B. Intracellular distribution of microinjected antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2702–2706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loke S. L., Stein C. A., Zhang X. H., Mori K., Nakanishi M., Subasinghe C., Cohen J. S., Neckers L. M. Characterization of oligonucleotide transport into living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3474–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marschall P., Thomson J. B., Eckstein F. Inhibition of gene expression with ribozymes. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1994 Oct;14(5):523–538. doi: 10.1007/BF02088835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerenberg M., Hinrichs S. H., Reynolds R. K., Khoury G., Jay G. The tat gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 induces mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1324–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.2888190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella G., Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I. Nuclease resistant ribozymes with high catalytic activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1913–1919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieken W. A., Olsen D. B., Benseler F., Aurup H., Eckstein F. Kinetic characterization of ribonuclease-resistant 2'-modified hammerhead ribozymes. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):314–317. doi: 10.1126/science.1857967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prody G. A., Bakos J. T., Buzayan J. M., Schneider I. R., Bruening G. Autolytic processing of dimeric plant virus satellite RNA. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4745.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner D. E., Stormo G. D., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence requirements of the hammerhead RNA self-cleavage reaction. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10695–10702. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Cantin E. M., Chang P. S., Zaia J. A., Ladne P. A., Stephens D. A., Rossi J. J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1222–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.2107573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M. Interaction between tumour necrosis factor alpha ribozyme and cellular proteins. Involvement in ribozyme stability and activity. J Mol Biol. 1994 Oct 7;242(5):619–629. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinecke P., Herget T., Schreier P. H. Expression of a chimeric ribozyme gene results in endonucleolytic cleavage of target mRNA and a concomitant reduction of gene expression in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1525–1530. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05197.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Cech T. R. Tethering ribozymes to a retroviral packaging signal for destruction of viral RNA. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1566–1569. doi: 10.1126/science.8248806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchihashi Z., Khosla M., Herschlag D. Protein enhancement of hammerhead ribozyme catalysis. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.7692597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usman N., Cedergren R. Exploiting the chemical synthesis of RNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Sep;17(9):334–339. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90306-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Z., Whitton J. L. An anti-lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus ribozyme expressed in tissue culture cells diminishes viral RNA levels and leads to a reduction in infectious virus yield. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1840–1847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1840-1847.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakubov L. A., Deeva E. A., Zarytova V. F., Ivanova E. M., Ryte A. S., Yurchenko L. V., Vlassov V. V. Mechanism of oligonucleotide uptake by cells: involvement of specific receptors? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6454–6458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. H., Usman N., Chartrand P., Cedergren R. Minimum ribonucleotide requirement for catalysis by the RNA hammerhead domain. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):5005–5009. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]