Abstract
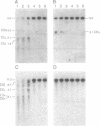
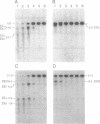
In this study, a determination was made of the chromatin structure of the rat growth hormone (GH) gene locus by DNase I sensitivity analysis using GC [GH+, prolactin (PRL)-], 235 (GH-, PRL+), GH3 (GH+, PRL+) and liver (GH-, PRL-) cells. From 7 kb upstream from the transcription start site to 19 kb downstream from the polyadenylation site, two major DNase I-hypersensitive sites (M-DHS; UIA, UIIA) and three M-DHS (DIA, DII, DIII) were found within 2 kb upstream and 7 kb downstream regions, respectively. Two minor DHS (m-DHS; UIB, UIIB) in the upstream region and one m-DHS (DIB) downstream were shown to be associated with M-DHS. Thus, a total of five M-DHS and three m-DHS were mapped on the rat GH gene locus. Among these, five (UIIB, UIA, UIB, DIB, DIA) including two (UIA, DIA) M-DHS were specific for GH-producing cells. UIIA and DIII were M-DHS only in PRL-producing 235 cells while the major hypersensitivity of DII was detected in GH-producing cells and liver cells. Assessment of the enhancing activity of the DHS regions indicated novel enhancers in one upstream and two downstream regions that function well with the GH promoter in GC cells. These enhancers, each appearing different, coincided with m-DHS but not M-DHS in GC cells, and were not activated by Pit-1. Based on these observations, the following functions of five M-DHS and three m-DHS regions were defined: enhancer; locus control region (LCR); switch region serving for conversion from GH/PRL-producing cells to PRL-producing cells; and a region having a structural function in chromatin.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiss L. E., Bennett A., Friedman J. M., Darnell J. E., Jr DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking region of the rat serum albumin gene: correlation between chromatin structure and transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6504–6508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft F. C. Measurement of growth hormone synthesis by rat pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):1014–1021. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Mathews L. S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Dwarf mice produced by genetic ablation of growth hormone-expressing cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):453–461. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifer C., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Sippel A. E. Tissue specific and position independent expression of the complete gene domain for chicken lysozyme in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2843–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Heyman R. A., Arias C., Sawchenko P. E., Evans R. M. Transgenic mice with inducible dwarfism. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):538–541. doi: 10.1038/339538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain A., Dupouy J. P., Dubois M. P. Ontogenesis of cells producing polypeptide hormones (ACTH, MSH, LPH, GH, prolactin) in the fetal hypophysis of the rat: influence of the hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Feb 28;196(3):409–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00234737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. N., Koike S., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Maurer R. A. Both Pit-1 and the estrogen receptor are required for estrogen responsiveness of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1964–1971. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon N., Grosveld F. Transcriptional regulation of multigene loci: multilevel control. Trends Genet. 1993 Apr;9(4):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90208-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. Expression of GHF-1 protein in mouse pituitaries correlates both temporally and spatially with the onset of growth hormone gene activity. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):809–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90095-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Weber J. L., Gorski J. Chromatin structure, transcription, and methylation of the prolactin gene domain in pituitary tumors of Fischer 344 rats. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7086–7093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Boockfor F. R., Frawley L. S. Ontogeny of prolactin cells in neonatal rats: initial prolactin secretors also release growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1985 Jul;117(1):187–195. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Albert V. R., Chen R. P., Crenshaw 3d E. B., Elsholtz H. P., He X., Kapiloff M. S., Mangalam H. J., Swanson L. W., Treacy M. N. A family of POU-domain and Pit-1 tissue-specific transcription factors in pituitary and neuroendocrine development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:773–791. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kladde M. P., D'Cunha J., Gorski J. Multiple transitions to non-B-DNA structures occur in the distal regulatory region of the rat prolactin gene. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):344–367. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Chromatin structure and transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:563–587. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.003023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavin T. N., Baxter J. D., Horita S. The thyroid hormone receptor binds to multiple domains of the rat growth hormone 5'-flanking sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9418–9426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin S. M., När A. M., Kalla K. A., Sack R. A., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of a novel zinc finger protein binding a conserved element critical for Pit-1-dependent growth hormone gene expression. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1674–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira S. A., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Glass C. K., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of rat growth hormone genomic sequences targeting pituitary expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4755–4759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira S. A., Kalla K. A., Glass C. K., Drolet D. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Synergistic interactions between Pit-1 and other elements are required for effective somatotroph rat growth hormone gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 May;7(5):694–701. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.5.8316253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangalam H. J., Albert V. R., Ingraham H. A., Kapiloff M., Wilson L., Nelson C., Elsholtz H., Rosenfeld M. G. A pituitary POU domain protein, Pit-1, activates both growth hormone and prolactin promoters transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):946–958. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A., Notides A. C. Identification of an estrogen-responsive element from the 5'-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4247–4254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Eberhardt N. L. Structure and evolution of the growth hormone gene family. Endocr Rev. 1983 Spring;4(2):97–130. doi: 10.1210/edrv-4-2-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Franco R., Lira S. A., Albert V. R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Discrete cis-active genomic sequences dictate the pituitary cell type-specific expression of rat prolactin and growth hormone genes. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):557–562. doi: 10.1038/322557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll C. S., Mayer G. L., Russell S. M. Structural features of prolactins and growth hormones that can be related to their biological properties. Endocr Rev. 1986 May;7(2):169–203. doi: 10.1210/edrv-7-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Harigai T., Kaneko T., Sato Y., Ihara S., Kawauchi H. Pit-1/GH factor-1 involvement in the gene expression of somatolactin. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Jan;8(1):109–115. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.1.8152425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Mochizuki E., Mori Y., Aizawa A., Harigai T. The regulatory region and transcription factor required for the expression of rat and salmon pituitary hormone-encoding genes show cell-type and species specificity. Gene. 1995 Feb 14;153(2):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00736-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranjape S. M., Kamakaka R. T., Kadonaga J. T. Role of chromatin structure in the regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:265–297. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond M. J., Nansel D. D., Burrows G. H., Neaves W. B., Porter J. C. A new clonal strain of rat pituitary tumour cells: a model for non-regulated secretion of prolactin. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Aug;106(4):459–470. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1060459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jagodzinski L. L., Yang M., Bonner J. Fine structure and evolution of the rat serum albumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):871–883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Yang M., Bonner J. Nucleotide sequence of cloned rat serum albumin messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):243–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence and amplification in bacteria of structural gene for rat growth hormone. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):486–494. doi: 10.1038/270486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama Y., Rand-Weaver M., Kawauchi H., Ono M. Gene structure of chum salmon somatolactin, a presumed pituitary hormone of the growth hormone/prolactin family. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;5(6):778–786. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-6-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Karin M. Transcriptional control of GH expression and anterior pituitary development. Endocr Rev. 1993 Dec;14(6):670–689. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-6-670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y. G., Daikoku S. An immunohistochemical study on the cytogenesis of adenohypophysial cells in fetal rats. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Adler S., Nelson C., Greene G. L., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. A single domain of the estrogen receptor confers deoxyribonucleic acid binding and transcriptional activation of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;2(1):14–21. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-1-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Analysis of hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:269–289. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]