Abstract
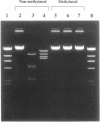
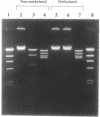
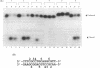
To develop restriction enzymes that are useful for genome analysis, we previously performed screening and isolated Sse8387I from Streptomyces sp. strain 8387. Sse8387I is a restriction enzyme that recognizes 5'-CCTGCA/GG-3' and cleaves DNA at the site shown by the diagonal (Nucleic Acid Res., 18, 5637-5640). The present study evaluated the effects of methylation that is important when Sse8387I is used for genome analysis. Sse8387I lost cleavage activity after methylation of adenine or methylation of cytosine at any site in the recognition sequence. However, the recognition sequence of Sse8387I contains no CG sequence, which is the mammalian methylation sequence. In addition, we evaluated the effects of methylation of CG at sites other than the recognition sequence. The cleavage activity of Sse8387I was maintained even when CG sequences were present immediately before or after, or near the recognition sequence, and cytosine was methylated. These results suggest that CG methylation does not affect the cleavage activity of Sse8387I. Therefore, Sse8387I seems to be very useful for mammalian genome analysis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kotani H., Nomura Y., Kawashima Y., Sagawa H., Takagi M., Kita A., Ito H., Kato I. Sse8387I, a new type-II restriction endonuclease that recognizes the octanucleotide sequence 5'-CCTGCAGG-3'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5637–5640. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Nelson M., Raschke E. Effect of site-specific modification on restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep;22(17):3640–3659. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.17.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. M., Miceli S. M., Lechevalier M. P., Roberts R. J. FseI, a new type II restriction endonuclease that recognizes the octanucleotide sequence 5' GGCCGGCC 3'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2061–2064. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nur I., Szyf M., Razin A., Glaser G., Rottem S., Razin S. Procaryotic and eucaryotic traits of DNA methylation in spiroplasmas (mycoplasmas). J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.19-24.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiang B. Q., Schildkraut I. A type II restriction endonuclease with an eight nucleotide specificity from Streptomyces fimbriatus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4507–4516. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiang B. Q., Schildkraut I. NotI and SfiI: restriction endonucleases with octanucleotide recognition sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:15–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renbaum P., Abrahamove D., Fainsod A., Wilson G. G., Rottem S., Razin A. Cloning, characterization, and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene coding for the CpG DNA methylase from Spiroplasma sp. strain MQ1(M.SssI). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1145–1152. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Macelis D. REBASE--restriction enzymes and methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep;22(17):3628–3639. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.17.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L., Gold L., Kutter E. A gene of bacteriophage T4 whose product prevents true late transcription on cytosine-containing T4 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3098–3102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]