Abstract
Transfer RNA-guanine ribosyltransferase (TGRase) irreversibly incorporates queuine into the first position in the anticodon of four tRNA isoacceptors. Rat brain protein kinase C (PKC) was shown to stimulate rat liver TGRase activity. TGRase preparations derived from rat liver have been observed to decrease in activity over time in storage at -20 or -70 degrees C. Contamination of the samples by phosphatases was indicated by a p-nitrophenylphosphate conversion test. The addition of micromolar concentrations of the phosphatase inhibitors sodium pyrophosphate and sodium fluoride into TGRase isolation buffers resulted in a greater return of TGRase activity than without these inhibitors. Inactive TGRase preparations were reactivated to their original activity with the addition of PKC. In assays combining both TGRase and PKC enzymes, inhibitors of protein kinase C (sphingosine, staurosporine, H-7 and calphostin C) all blocked the reactivation of TGRase, whereas activators of protein kinase C (calcium, diacylglycerol and phosphatidyl serine) increased the activity of TGRase. None of the PKC modulators affected TGRase activity directly. Alkaline phosphatase, when added to assays, decreased the activity of TGRase and also blocked the reactivation of TGRase with PKC. Denaturing PAGE and autoradiography was performed on TGRase isolates that had been labelled with 32P by PKC. The resulting strong 60 kDa band (containing the major site for phosphorylation) and weak 34.5 kDa band (containing the TGRase activity) are suggested to associate to make up a 104 kDa heterodimer that comprises the TGRase enzyme. This was corroberated by native and denaturing size-exclusion chromatography. These results suggest that PKC-dependent phosphorylation of TGRase is tied to efficient enzymatic function and therefore control of the queuine modification of tRNA.
Full text
PDF

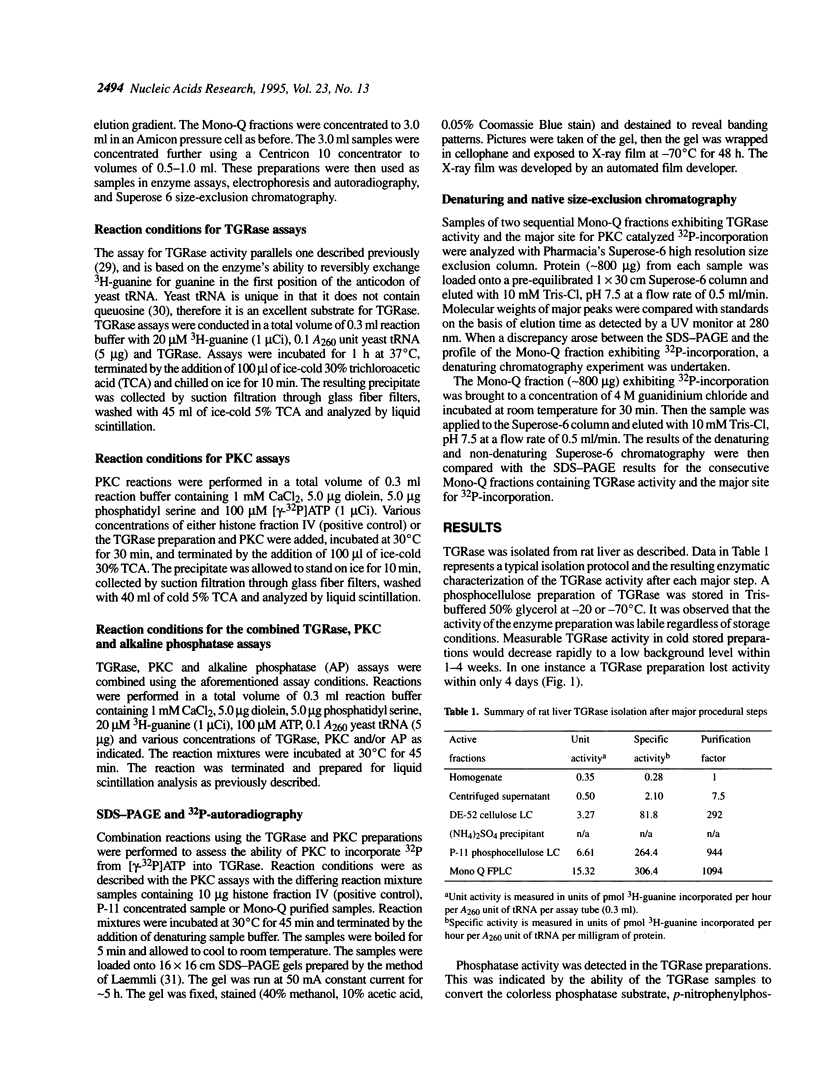
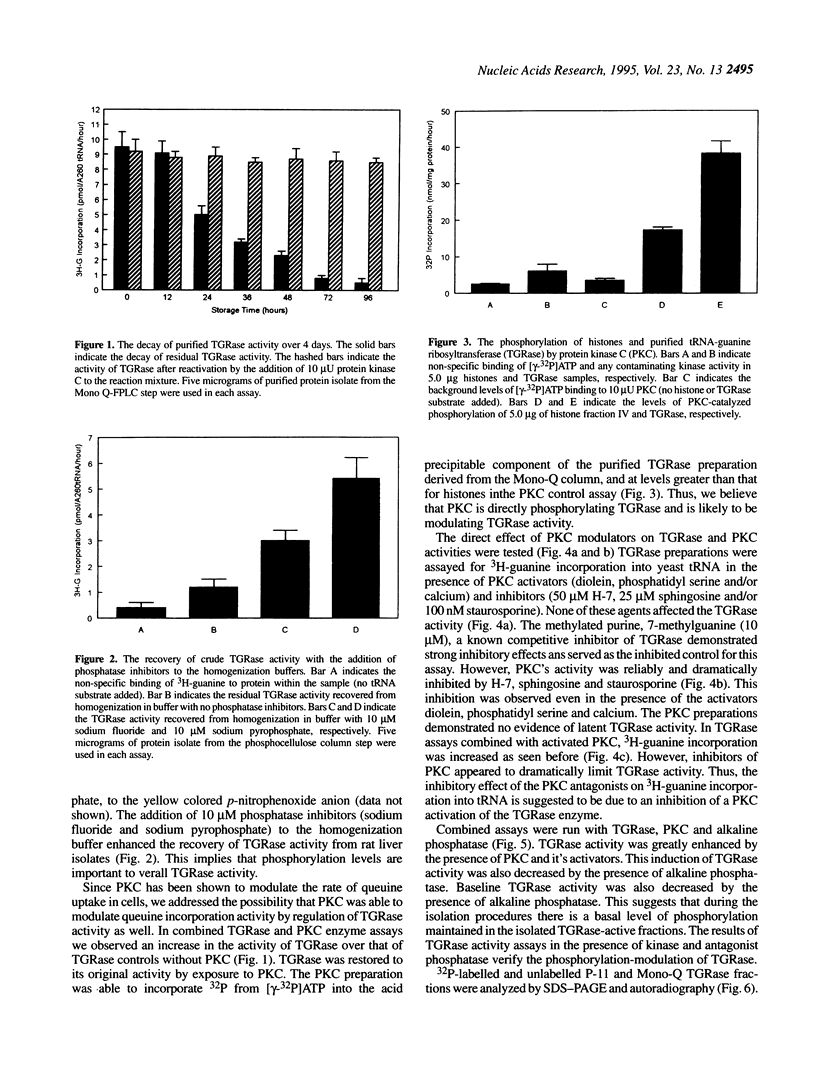

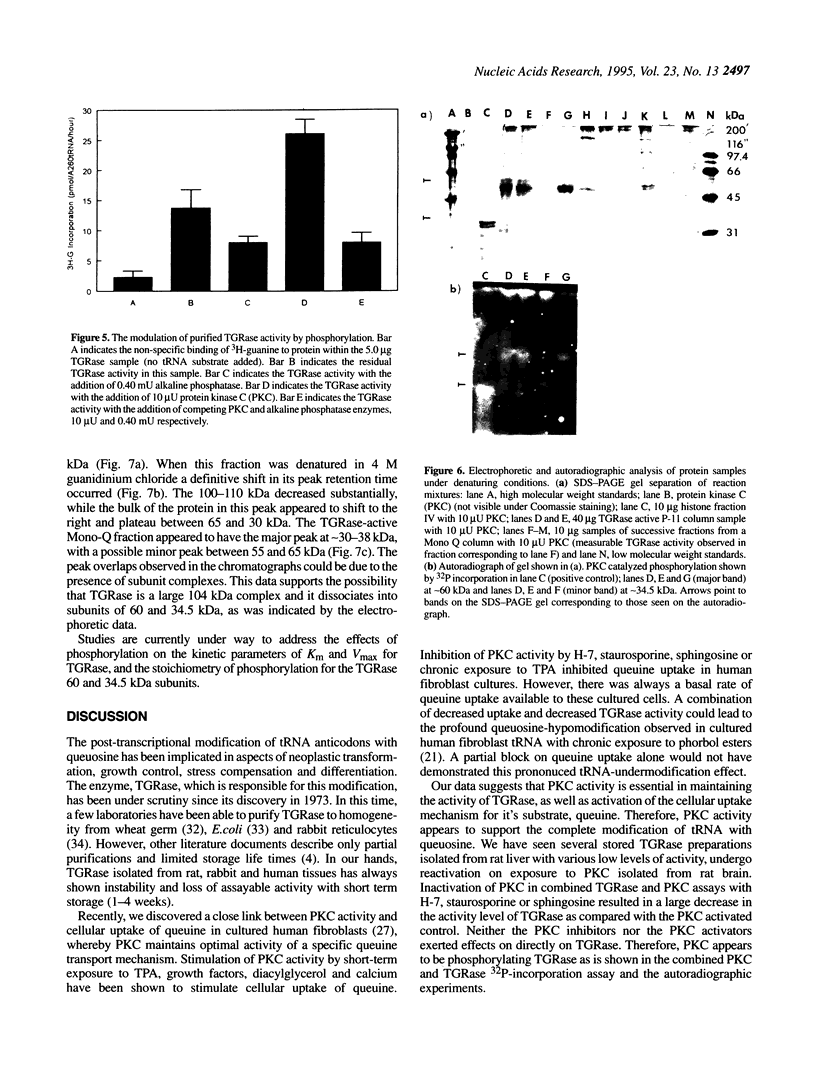
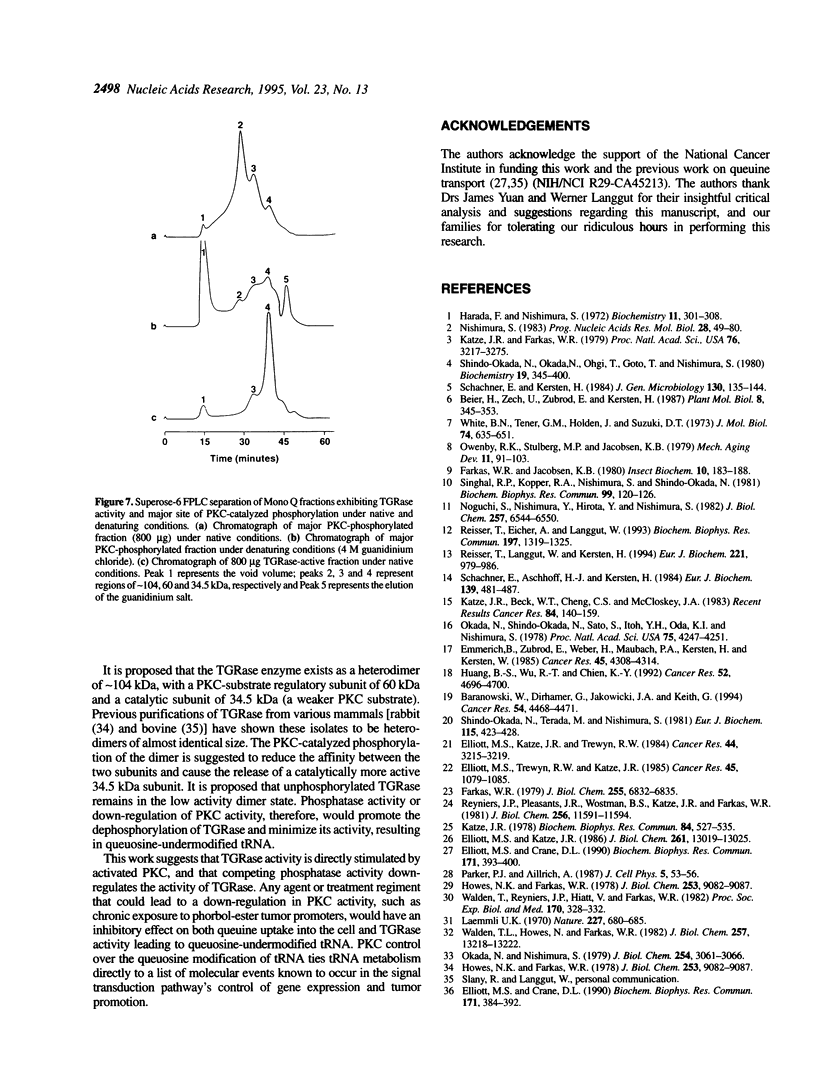
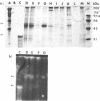
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baranowski W., Dirheimer G., Jakowicki J. A., Keith G. Deficiency of queuine, a highly modified purine base, in transfer RNAs from primary and metastatic ovarian malignant tumors in women. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4468–4471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. S., Crane D. L. Interferon induced inhibition of queuine uptake in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91405-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. S., Crane D. L. Protein kinase C modulation of queuine uptake in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91406-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. S., Katze J. R. Inhibition of queuine uptake in diploid human fibroblasts by phorbol-12,13-didecanoate. Requirement for a factor derived from early passage cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13019–13025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. S., Katze J. R., Trewyn R. W. Relationship between a tumor promoter-induced decrease in queuine modification of transfer RNA in normal human cells and the expression of an altered cell phenotype. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3215–3219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. S., Trewyn R. W., Katze J. R. Inhibition of queuine uptake in cultured human fibroblasts by phorbol-12,13-didecanoate. Cancer Res. 1985 Mar;45(3):1079–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich B., Zubrod E., Weber H., Maubach P. A., Kersten H., Kersten W. Relationship of queuine-lacking transfer RNA to the grade of malignancy in human leukemias and lymphomas. Cancer Res. 1985 Sep;45(9):4308–4314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas W. R. Effect of diet on the queuosine family of tRNAs of germ-free mice. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6832–6835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Nishimura S. Possible anticodon sequences of tRNA His , tRNA Asm , and tRNA Asp from Escherichia coli B. Universal presence of nucleoside Q in the first postion of the anticondons of these transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):301–308. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes N. K., Farkas W. R. Studies with a homogeneous enzyme from rabbit erythrocytes catalyzing the insertion of guanine into tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9082–9087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes N. K., Farkas W. R. Studies with a homogeneous enzyme from rabbit erythrocytes catalyzing the insertion of guanine into tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9082–9087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B. S., Wu R. T., Chien K. Y. Relationship of the queuine content of transfer ribonucleic acids to histopathological grading and survival in human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4696–4700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze J. R., Beck W. T., Cheng C. S., McCloskey J. A. Why is tumor tRNA hypomodified with respect to Q nucleoside? Recent Results Cancer Res. 1983;84:146–159. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81947-6_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze J. R. Q-factor: a serum component required for the appearance of nucleoside Q in tRNA in tissue culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S. Structure, biosynthesis, and function of queuosine in transfer RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:49–73. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y., Nishimura S. Isolation and characterization of an Escherichia coli mutant lacking tRNA-guanine transglycosylase. Function and biosynthesis of queuosine in tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6544–6550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Nishimura S. Isolation and characterization of a guanine insertion enzyme, a specific tRNA transglycosylase, from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3061–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Shindo-Okada N., Sato S., Itoh Y. H., Oda K., Nishimura S. Detection of unique tRNA species in tumor tissues by Escherichia coli guanine insertion enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owenby R. K., Stulberg M. P., Jacobson K. B. Alteration of the Q family of transfer RNAs in adult Drosophila melanogaster as a function of age, nutrition, and genotype. Mech Ageing Dev. 1979 Sep;11(2):91–103. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(79)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisser T., Eicher A., Langgut W. Mitogenic stimulation of HeLa cells increases the activity of the anoxic stress protein, LDH 6/k: suppression by queuine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 30;197(3):1319–1325. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisser T., Langgut W., Kersten H. The nutrient factor queuine protects HeLa cells from hypoxic stress and improves metabolic adaptation to oxygen availability. Eur J Biochem. 1994 May 1;221(3):979–986. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyniers J. P., Pleasants J. R., Wostmann B. S., Katze J. R., Farkas W. R. Administration of exogenous queuine is essential for the biosynthesis of the queuosine-containing transfer RNAs in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11591–11594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner E., Aschhoff H. J., Kersten H. Specific changes in lactate levels, lactate dehydrogenase patterns and cytochrome b559 in Dictyostelium discoideum caused by queuine. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 15;139(3):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo-Okada N., Okada N., Ohgi T., Goto T., Nishimura S. Transfer ribonucleic acid guanine transglycosylase isolated from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 22;19(2):395–400. doi: 10.1021/bi00543a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo-Okada N., Terada M., Nishimura S. Changes in amount of hypo-modified tRNA having guanine in place of queuine during erythroid differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal R. P., Kopper R. A., Nishimura S., Shindo-Okada N. Modification of guanine to queuine in transfer RNAs during development and aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 16;99(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91721-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden T. L., Jr, Howes N., Farkas W. R. Purification and properties of guanine, queuine-tRNA transglycosylase from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13218–13222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden T., Reyniers J. P., Hiatt V., Farkas W. R. Yeast cells cannot incorporate queuine into their tRNA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jul;170(3):328–332. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. N., Tener G. M. Activity of a transfer RNA modifying enzyme during the development of Drosophila and its relationship to the su(s) locus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):635–651. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]