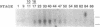Abstract
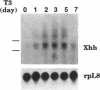
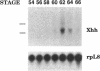
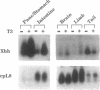
The hedgehog family of proteins have been implicated as important signaling molecules in establishing cell positional information and tissue patterning. Here we present the cloning and characterization of a hedgehog homologue from Xenopus laevis similar to the sonic class of vertebrate hedgehog genes. We isolated Xenopus hedgehog (Xhh) from a subtractive hybridization screen designed to identify genes induced by thyroid hormone during metamorphosis of the X.laevis gastrointestinal tract. In the intestine, Xhh mRNA expression was up-regulated at the climax of metamorphosis (stage 62) when intestinal epithelium underwent morphogenesis. Treatment of pre-metamorphic tadpoles with exogenous thyroid hormone (TH) resulted in a similar pattern of Xhh induction. Furthermore, TH induction was resistant to inhibitors of protein synthesis suggesting that Xhh is a direct thyroid hormone response gene. The expression and TH regulation of Xhh was not limited to the intestine, but was also observed in the limb and a mixture of pancreas and stomach. Throughout development, Xhh mRNA was present at varying levels with the earliest expression being detected at neurula stage. The highest levels of Xhh were observed between stages 33 and 40 shortly before tadpole feeding begins. Whole mount in situ hybridization analysis of Xhh expression in pre-hatching, stage 32 tadpoles demonstrated staining in the notochord and floor plate similar to that observed for other vertebrate hedgehog genes. Together, these data suggest a putative role for Xhh in organ development during both amphibian embryogenesis and metamorphosis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basler K., Struhl G. Compartment boundaries and the control of Drosophila limb pattern by hedgehog protein. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):208–214. doi: 10.1038/368208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckbinder L., Brown D. D. Thyroid hormone-induced gene expression changes in the developing frog limb. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25786–25791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. T., López A., von Kessler D. P., Chiang C., Simandl B. K., Zhao R., Seldin M. F., Fallon J. F., Beachy P. A. Products, genetic linkage and limb patterning activity of a murine hedgehog gene. Development. 1994 Nov;120(11):3339–3353. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.11.3339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M. L., Jamrich M. A novel, activin-inducible, blastopore lip-specific gene of Xenopus laevis contains a fork head DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):599–608. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echelard Y., Epstein D. J., St-Jacques B., Shen L., Mohler J., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1417–1430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Tessier-Lavigne M. Patterning of mammalian somites by surface ectoderm and notochord: evidence for sclerotome induction by a hedgehog homolog. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., Wolff T., Rubin G. M. The TGF beta homolog dpp and the segment polarity gene hedgehog are required for propagation of a morphogenetic wave in the Drosophila retina. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):913–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heemskerk J., DiNardo S. Drosophila hedgehog acts as a morphogen in cellular patterning. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):449–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helbing C., Gergely G., Atkinson B. G. Sequential up-regulation of thyroid hormone beta receptor, ornithine transcarbamylase, and carbamyl phosphate synthetase mRNAs in the liver of Rana catesbeiana tadpoles during spontaneous and thyroid hormone-induced metamorphosis. Dev Genet. 1992;13(4):289–301. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Frank D., Bolce M. E., Brown B. D., Sive H. L., Harland R. M. Localization of specific mRNAs in Xenopus embryos by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):325–330. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Schmidt G. W. Rapid, reversible staining of northern blots prior to hybridization. Biotechniques. 1988 Mar;6(3):196-7, 199-200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Localized hedgehog activity controls spatial limits of wingless transcription in the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):560–562. doi: 10.1038/366560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Pattern formation. Hedgehog points the way. Curr Biol. 1994 Apr 1;4(4):347–350. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W., Taylor A. M., Nakano Y. Role of the Drosophila patched gene in positional signalling. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):184–187. doi: 10.1038/353184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuya-Oka A., Shimozawa A. Development of the connective tissue in the digestive tract of the larval and metamorphosing Xenopus laevis. Anat Anz. 1987;164(2):81–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuya-Oka A., Shimozawa A. Induction of metamorphosis by thyroid hormone in anuran small intestine cultured organotypically in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1991 Nov;27A(11):853–857. doi: 10.1007/BF02630987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Riddle R. D., Tabin C. Ectopic expression of Sonic hedgehog alters dorsal-ventral patterning of somites. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori A., Brown D. D. The regulation of thyroid hormone receptor beta genes by thyroid hormone in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara A., Baker B. S., Tata J. R. Developmental and regional expression of thyroid hormone receptor genes during Xenopus metamorphosis. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):933–943. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordylewski L. Light and electron microscopic observations of the development of intestinal musculature in Xenopus. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1983;97(4):719–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S., Concordet J. P., Ingham P. W. A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1431–1444. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer E., Nelson C. E., Johnson R. L., Morgan B. A., Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog and Fgf-4 act through a signaling cascade and feedback loop to integrate growth and patterning of the developing limb bud. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):993–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Porter J. A., Sun B. I., Beachy P. A. Autoproteolysis in hedgehog protein biogenesis. Science. 1994 Dec 2;266(5190):1528–1537. doi: 10.1126/science.7985023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., von Kessler D. P., Parks S., Beachy P. A. Secretion and localized transcription suggest a role in positional signaling for products of the segmentation gene hedgehog. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):33–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90264-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C., Zhou Y., Beachy P. A., Moses K. The segment polarity gene hedgehog is required for progression of the morphogenetic furrow in the developing Drosophila eye. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):927–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90536-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. A., Dixon K. E. Cell specialization in the epithelium of the small intestine of feeding Xenopus laevis tadpoles. J Anat. 1978 May;126(Pt 1):133–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAvoy J. W., Dixon K. E. Cell specialization in the small intestinal epithelium of adult Xenopus laevis: functional aspects. J Anat. 1978 Feb;125(Pt 2):237–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAvoy J. W., Dixon K. E. Cell specialization in the small intestinal epithelium of adult Xenopus laevis: structural aspects. J Anat. 1978 Jan;125(Pt 1):155–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler J., Vani K. Molecular organization and embryonic expression of the hedgehog gene involved in cell-cell communication in segmental patterning of Drosophila. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):957–971. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niswander L., Jeffrey S., Martin G. R., Tickle C. A positive feedback loop coordinates growth and patterning in the vertebrate limb. Nature. 1994 Oct 13;371(6498):609–612. doi: 10.1038/371609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):795–801. doi: 10.1038/287795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle R. D., Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1401–1416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Augsburger A., Heemskerk J., Korzh V., Norlin S., Ruiz i Altaba A., Tanabe Y., Placzek M., Edlund T., Jessell T. M. Floor plate and motor neuron induction by vhh-1, a vertebrate homolog of hedgehog expressed by the notochord. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):761–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90514-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. J., Galton V. A. Regulation of c-erbA-alpha messenger RNA species in tadpole erythrocytes by thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–208. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Brown D. D. The earliest changes in gene expression in tadpole intestine induced by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20312–20317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Hayes W. P. Thyroid hormone-dependent regulation of the intestinal fatty acid-binding protein gene during amphibian metamorphosis. Dev Biol. 1994 Jan;161(1):48–58. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Liang V. C. Cloning and characterization of the ribosomal protein L8 gene from Xenopus laevis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 1;1217(2):227–228. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C. Hedgehog, the floor plate, and the zone of polarizing activity. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Eaton S., Kornberg T. B. The Drosophila hedgehog gene is expressed specifically in posterior compartment cells and is a target of engrailed regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2635–2645. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Kornberg T. B. Hedgehog is a signaling protein with a key role in patterning Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro S., Michiue T., Higashijima S., Zenno S., Ishimaru S., Takahashi F., Orihara M., Kojima T., Saigo K. Structure and expression of hedgehog, a Drosophila segment-polarity gene required for cell-cell communication. Gene. 1993 Feb 28;124(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90392-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Brown D. D. Thyroid hormone-induced gene expression program for amphibian tail resorption. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16270–16278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Brown D. D. A correlation of thyroid hormone receptor gene expression with amphibian metamorphosis. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1917–1924. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Shi Y. B., Brown D. D. Xenopus laevis alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7090–7094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizato K. Biochemistry and cell biology of amphibian metamorphosis with a special emphasis on the mechanism of removal of larval organs. Int Rev Cytol. 1989;119:97–149. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60650-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]