Abstract
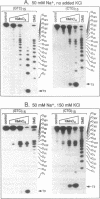
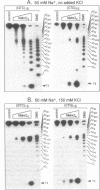
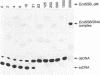
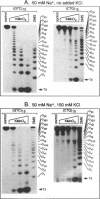
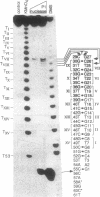
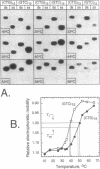
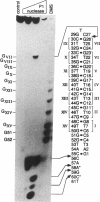
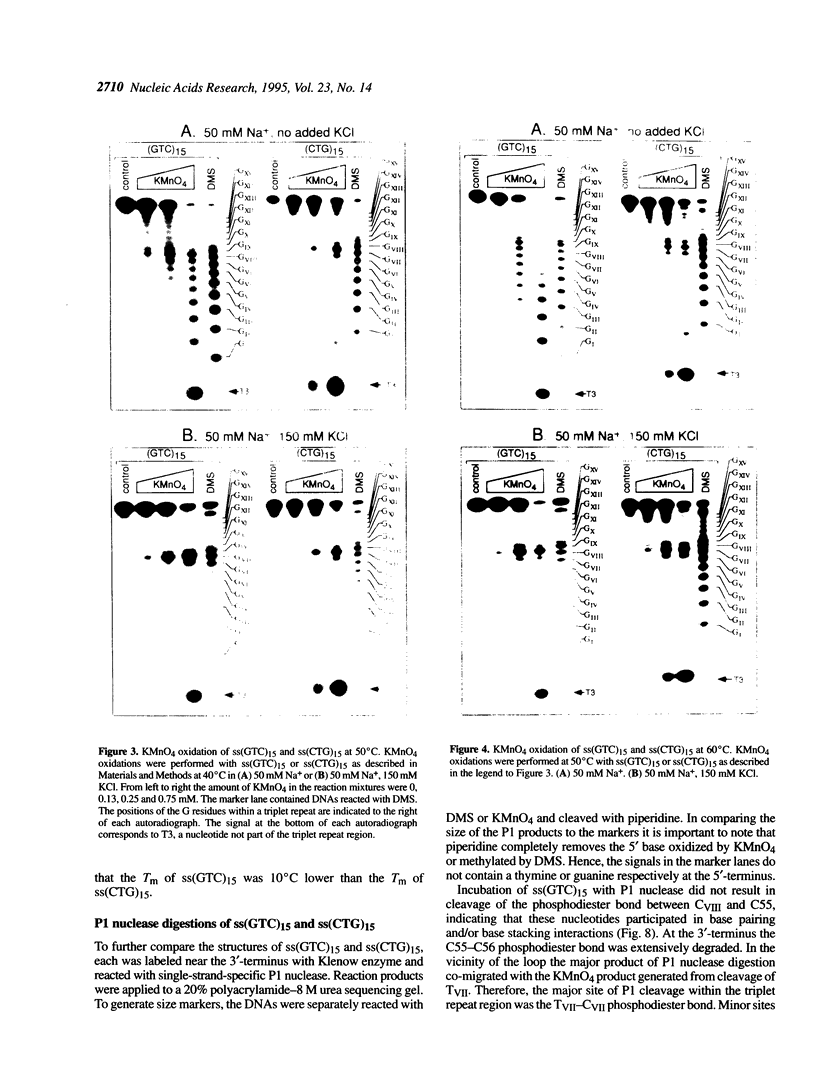
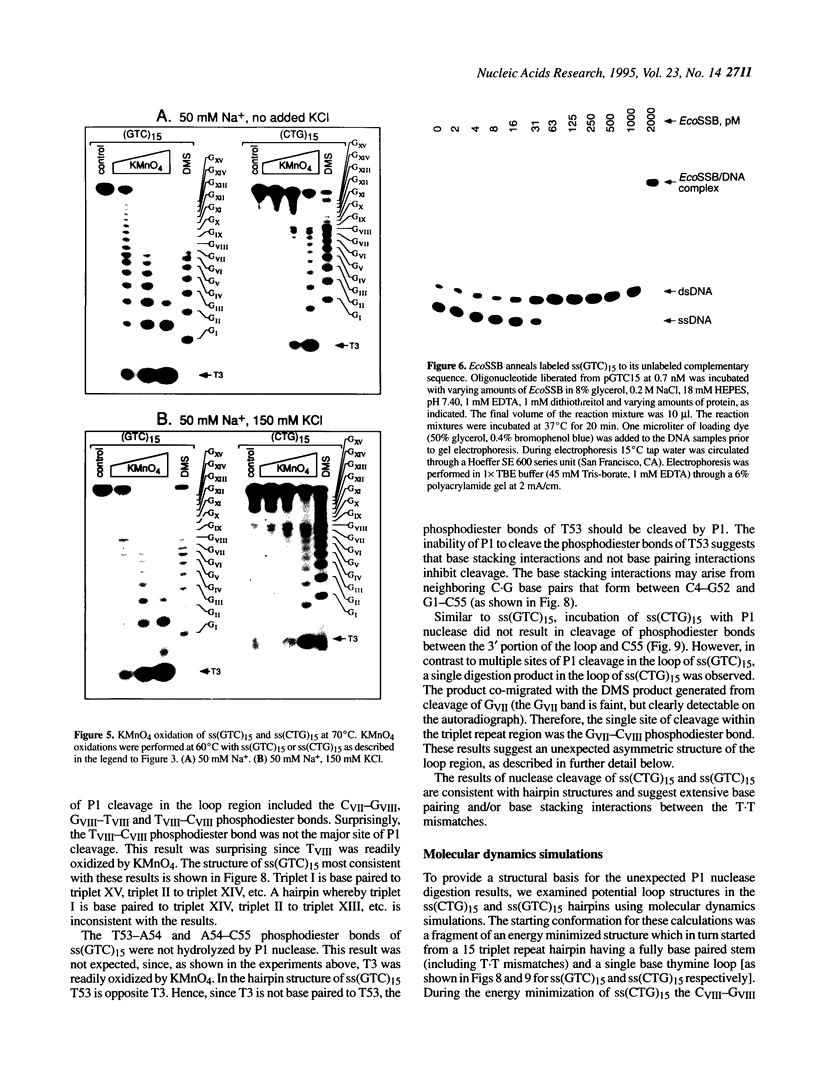
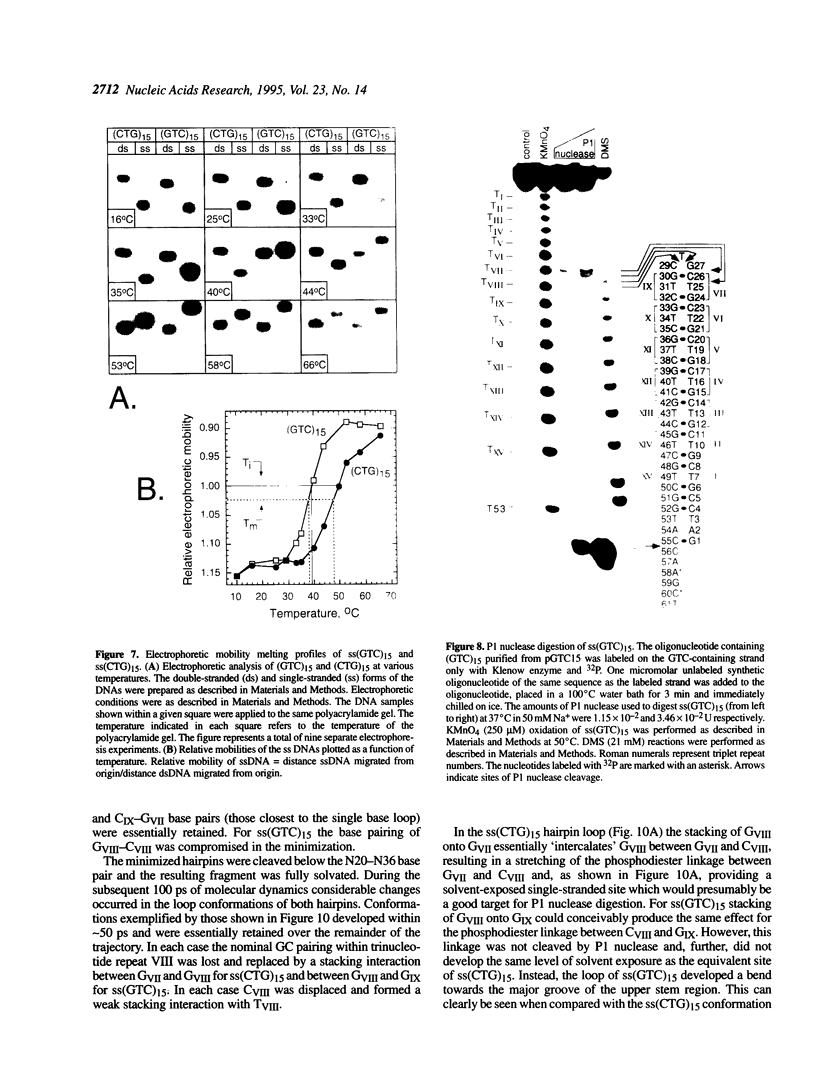
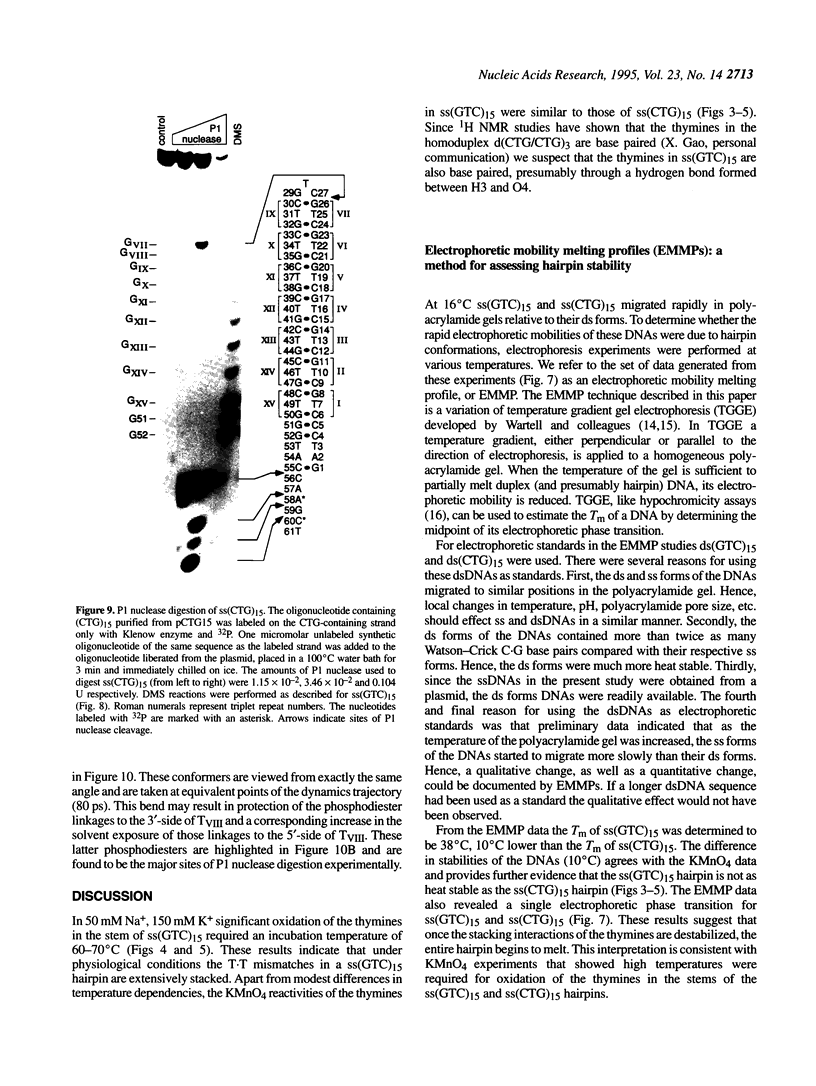
The structure of a single-stranded (ss) oligonucleotide containing (GTC)15 [ss(GTC)15] was examined. As a control, parallel studies were performed with ss(CTG)15, an oligonucleotide that forms a hairpin. Electrophoretic mobility, KMnO4 oxidation and P1 nuclease studies demonstrate that, similar to ss(CTG)15, ss(GTC)15 forms a hairpin containing base paired and/or stacked thymines in the stem. Electrophoretic mobility melting profiles performed in approximately 1 mM Na+ revealed that the melting temperature of ss(GTC)15 and ss(CTG)15 were 38 and 48 degrees C respectively. The loop regions of ss(GTC)15 and ss(CTG)15 were cleaved by single-strand-specific P1 nuclease at the T25-C29 and G26-C27 phosphodiester bonds respectively (where the loop apex of the DNAs is T28). Molecular dynamics simulations suggested that in ss(GTC)15 the loop was bent towards the major groove of the stem, apparently causing an increased exposure of the T25-C29 region to solvent. In ss(CTG)15 guanine--guanine stacking caused a separation of the G26 and C27 bases, resulting in exposure of the intervening phosphodiester to solvent. The results suggest that ss(GTC)15 and ss(CTG)15 form similar, but distinguishable, hairpin structures.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayatsu H., Ukita T. The selective degradation of pyrimidines in nucleic acids by permanganate oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke S. H., Wartell R. M. Influence of nearest neighbor sequence on the stability of base pair mismatches in long DNA; determination by temperature-gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5137–5143. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Ferrari M. E. Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein: multiple DNA-binding modes and cooperativities. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:527–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. G., Rich A. Detection of an unusual distortion in A-tract DNA using KMnO4: effect of temperature and distamycin on the altered conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3421–3429. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitas M., Yu A., Dill J., Kamp T. J., Chambers E. J., Haworth I. S. Hairpin properties of single-stranded DNA containing a GC-rich triplet repeat: (CTG)15. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Mar 25;23(6):1050–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.6.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tinoco I., Jr Absorbance melting curves of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:304–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Schmid C. W. Pyrimidine-specific chemical reactions useful for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4613–4619. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlötterer C., Tautz D. Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):211–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gunsteren W. F., Berendsen H. J., Geurtsen R. G., Zwinderman H. R. A molecular dynamics computer simulation of an eight-base-pair DNA fragment in aqueous solution: comparison with experimental two-dimensional NMR data. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;482:287–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Hosseini S. H., Moran C. P., Jr Detecting base pair substitutions in DNA fragments by temperature-gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2699–2705. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab F. Enzyme probes in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:294–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12018-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]