Abstract
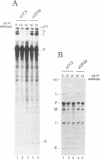
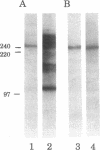
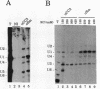
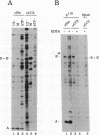
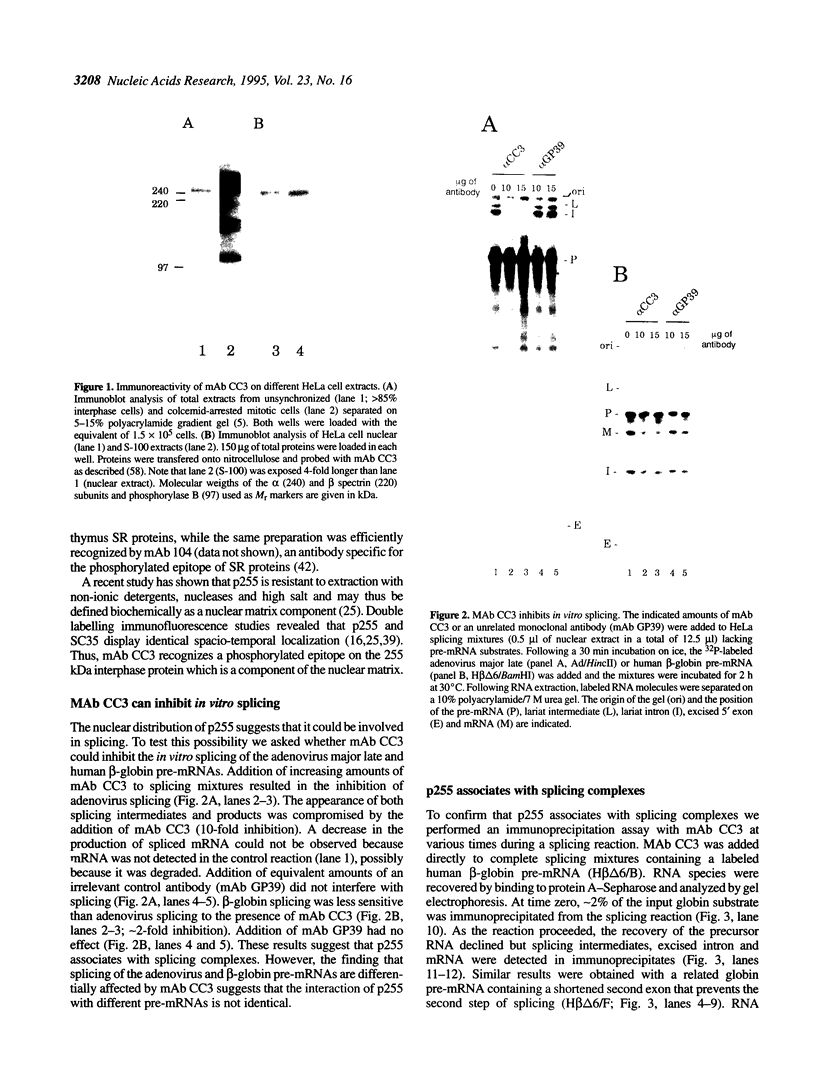
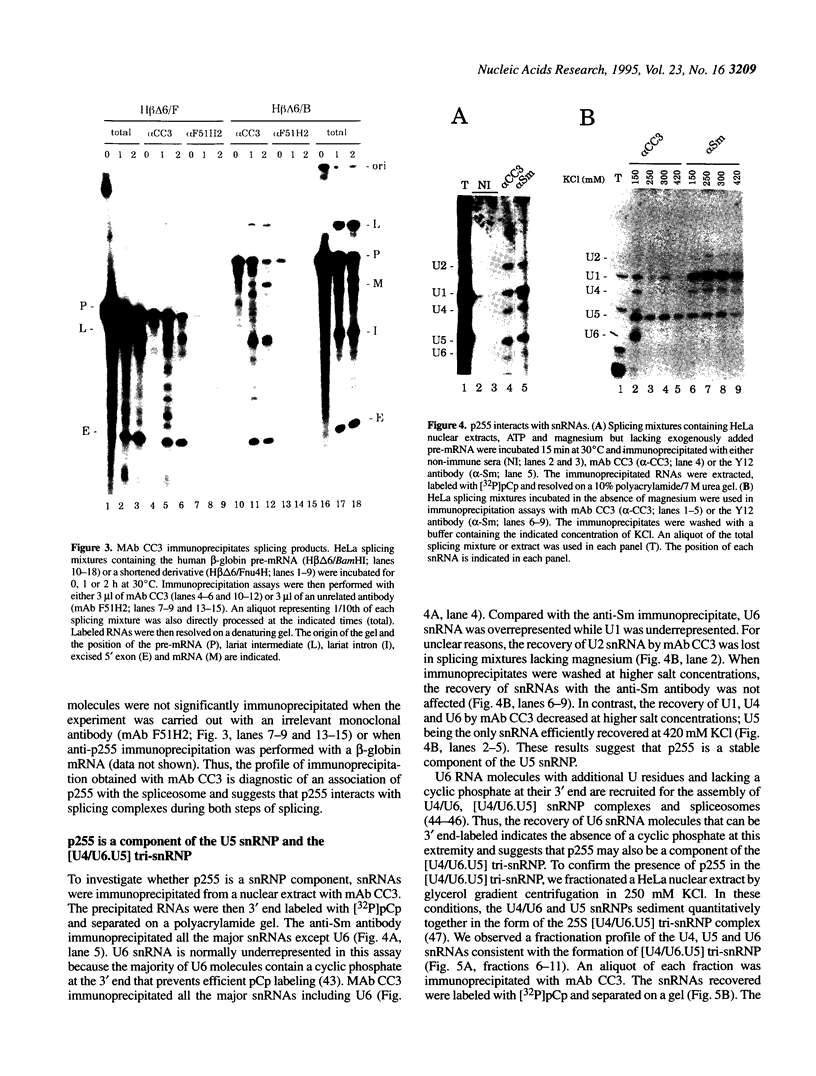
The monoclonal antibody CC3 recognizes a phosphorylated epitope present on an interphase protein of 255 kDa. Previous work has shown that p255 is localized mainly to nuclear speckles and remains associated with the nuclear matrix scaffold following extraction with non-ionic detergents, nucleases and high salt. The association of p255 with splicing complexes is suggested by the finding that mAb CC3 can inhibit in vitro splicing and immunoprecipitate pre-messenger RNA and splicing products. Small nuclear RNA immunoprecipitation assays show that p255 is a component of the U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) and the [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNP complex. In RNase protection assays, mAb CC3 immunoprecipitates fragments containing branch site and 3' splice site sequences. As predicted for a [U4/U6.U5]-associated component, the recovery of the branch site-protected fragment requires binding of U2 snRNP and is inhibited by EDTA. p255 may correspond to the previously identified p220 protein, the mammalian analogue of the yeast PRP8 protein. Our results suggest that changes in the phosphorylation of p255 may be part of control mechanisms that interface splicing activity with nuclear organization.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. J., Bach M., Lührmann R., Beggs J. D. Conservation between yeast and man of a protein associated with U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):819–821. doi: 10.1038/342819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M., Winkelmann G., Lührmann R. 20S small nuclear ribonucleoprotein U5 shows a surprisingly complex protein composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6038–6042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens S. E., Lührmann R. Immunoaffinity purification of a [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNP from human cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1439–1452. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens S. E., Tyc K., Kastner B., Reichelt J., Lührmann R. Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RNP) U2 contains numerous additional proteins and has a bipartite RNP structure under splicing conditions. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):307–319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisotto S., Lauriault P., Duval M., Vincent M. Colocalization of a high molecular mass phosphoprotein of the nuclear matrix (p255) with spliceosomes. J Cell Sci. 1995 May;108(Pt 5):1873–1882. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.5.1873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe B. J., Nickerson J. A., Issner R., Penman S., Sharp P. A. Association of nuclear matrix antigens with exon-containing splicing complexes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):593–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blencowe B. J., Sproat B. S., Ryder U., Barabino S., Lamond A. I. Antisense probing of the human U4/U6 snRNP with biotinylated 2'-OMe RNA oligonucleotides. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brancolini C., Schneider C. Change in the expression of a nuclear matrix-associated protein is correlated with cellular transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6936–6940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman D. B., Du L., Li Y., Ribisi S., Warren S. L. Cytostellin distributes to nuclear regions enriched with splicing factors. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):387–396. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Steitz J. A. Multiple interactions between the splicing substrate and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in spliceosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):281–293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevenger C. V., Epstein A. L. Identification of a nuclear protein component of interchromatin granules using a monoclonal antibody and immunogold electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Mar;151(1):194–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton D. A., Szilak I., Cleveland D. W. Primary structure of NuMA, an intranuclear protein that defines a novel pathway for segregation of proteins at mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1395–1408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific labeling of 3' termini of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Blanco M. A., Anderson G. J., Beggs J., Sharp P. A. A mammalian protein of 220 kDa binds pre-mRNAs in the spliceosome: a potential homologue of the yeast PRP8 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozani O., Patton J. G., Reed R. A novel set of spliceosome-associated proteins and the essential splicing factor PSF bind stably to pre-mRNA prior to catalytic step II of the splicing reaction. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3356–3367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Affinity chromatography of splicing complexes: U2, U5, and U4 + U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in the spliceosome. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1294–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.3638792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gui J. F., Lane W. S., Fu X. D. A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):678–682. doi: 10.1038/369678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Spector D. L. In vivo evidence that transcription and splicing are coordinated by a recruiting mechanism. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90159-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Spliceosome assembly involves the binding and release of U4 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):411–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., La Branche H., Kornblihtt A. R., Chabot B. A splicing enhancer in the human fibronectin alternate ED1 exon interacts with SR proteins and stimulates U2 snRNP binding. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2405–2417. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Cyclic 2',3'-phosphates and nontemplated nucleotides at the 3' end of spliceosomal U6 small nuclear RNA's. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.1549778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan A. M., Query C. C., Allerson C. R., Chen S., Verdine G. L., Sharp P. A. Dynamic association of proteins with the pre-mRNA branch region. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3008–3020. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P. T., Lamond A. I. Regulation of mammalian spliceosome assembly by a protein phosphorylation mechanism. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5679–5688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P., Lamond A. I. Ser/Thr-specific protein phosphatases are required for both catalytic steps of pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5263–5269. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud S., Reed R. A functional association between the 5' and 3' splice site is established in the earliest prespliceosome complex (E) in mammals. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1008–1020. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaud S., Reed R. An ATP-independent complex commits pre-mRNA to the mammalian spliceosome assembly pathway. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2534–2546. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson J. A., Krockmalnic G., Wan K. M., Turner C. D., Penman S. A normally masked nuclear matrix antigen that appears at mitosis on cytoskeleton filaments adjoining chromosomes, centrioles, and midbodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):977–987. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome: unraveling the ties that bind. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. G., Porro E. B., Galceran J., Tempst P., Nadal-Ginard B. Cloning and characterization of PSF, a novel pre-mRNA splicing factor. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):393–406. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A. L., Steitz J. A. The mammalian analogue of the yeast PRP8 splicing protein is present in the U4/5/6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle and the spliceosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8742–8746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Singer R. H. RNA travel: tracks from DNA to cytoplasm. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):399–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90373-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Split genes and RNA splicing. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):805–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea J. E., Toyn J. H., Johnston L. H. The budding yeast U5 snRNP Prp8 is a highly conserved protein which links RNA splicing with cell cycle progression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 25;22(25):5555–5564. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.25.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Harris S. G., Zillmann M., Berget S. M. Evidence that a nuclear matrix protein participates in premessenger RNA splicing. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jun;182(2):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. The U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs as active site components of the spliceosome. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1989–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.8266094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3467–3481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. RNA processing. Cycling splicing factors. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):604–604. doi: 10.1038/369604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staknis D., Reed R. Direct interactions between pre-mRNA and six U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins during spliceosome assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):2994–3005. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staknis D., Reed R. SR proteins promote the first specific recognition of Pre-mRNA and are present together with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle in a general splicing enhancer complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7670–7682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Forne T., Jeanteur P., Cathala G., Brunel C. Mammalian U6 small nuclear RNA undergoes 3' end modifications within the spliceosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1641–1650. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Kornstädt U., Rossi F., Jeanteur P., Cathala G., Brunel C., Lührmann R. Thiophosphorylation of U1-70K protein inhibits pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):283–286. doi: 10.1038/363283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigelkamp S., Whittaker E., Beggs J. D. Interaction of the yeast splicing factor PRP8 with substrate RNA during both steps of splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):320–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terns M. P., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3'-end-dependent formation of U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3032–3040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeau A., Duchaine J., Simard J. L., Vincent M. Localization of molecules with restricted patterns of expression in morphogenesis: an immunohistochemical approach. Histochem J. 1989 Jun;21(6):348–356. doi: 10.1007/BF01798498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeau A., Vincent M. Monoclonal antibody CC-3 recognizes phosphoproteins in interphase and mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Franchi L. Identification of protein antigens associated with the nuclear matrix and with clusters of interchromatin granules in both interphase and mitotic cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Mar;87(Pt 2):269–282. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utans U., Behrens S. E., Lührmann R., Kole R., Krämer A. A splicing factor that is inactivated during in vivo heat shock is functionally equivalent to the [U4/U6.U5] triple snRNP-specific proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):631–641. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan K. M., Nickerson J. A., Krockmalnic G., Penman S. The B1C8 protein is in the dense assemblies of the nuclear matrix and relocates to the spindle and pericentriolar filaments at mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):594–598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. Interactions of small nuclear RNA's with precursor messenger RNA during in vitro splicing. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1918–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1411506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. Site-specific cross-linking of mammalian U5 snRNP to the 5' splice site before the first step of pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2542–2553. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y., Johnson C. V., Dobner P. R., Lawrence J. B. Higher level organization of individual gene transcription and RNA splicing. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1326–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.8446901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yean S. L., Lin R. J. U4 small nuclear RNA dissociates from a yeast spliceosome and does not participate in the subsequent splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5571–5577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Biochemical characterization of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor: an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor with a novel intranuclear distribution. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Parent A., Silverstein S., Efstratiadis A. Pre-mRNA splicing and the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng C., He D., Berget S. M., Brinkley B. R. Nuclear-mitotic apparatus protein: a structural protein interface between the nucleoskeleton and RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1505–1509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Taneja K. L., Singer R. H., Green M. R. Localization of pre-mRNA splicing in mammalian nuclei. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):809–812. doi: 10.1038/372809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]