Abstract
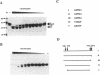
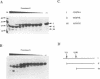
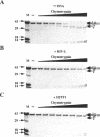
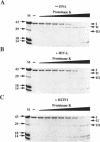
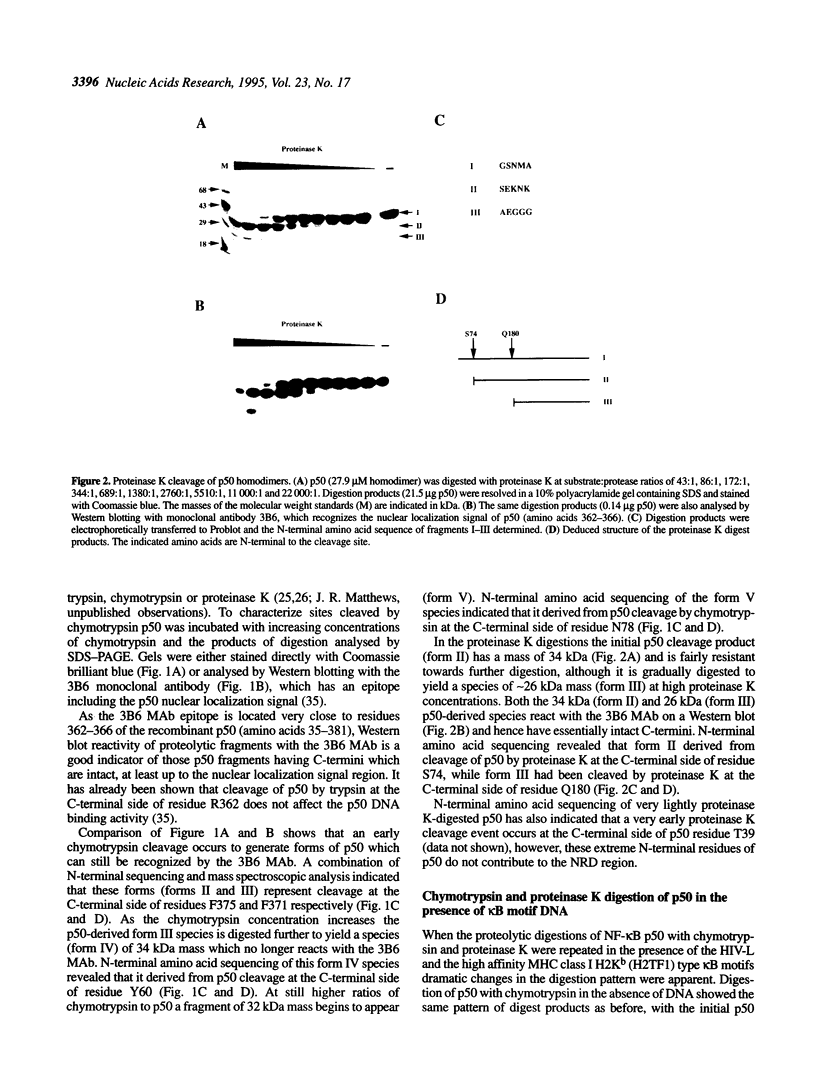
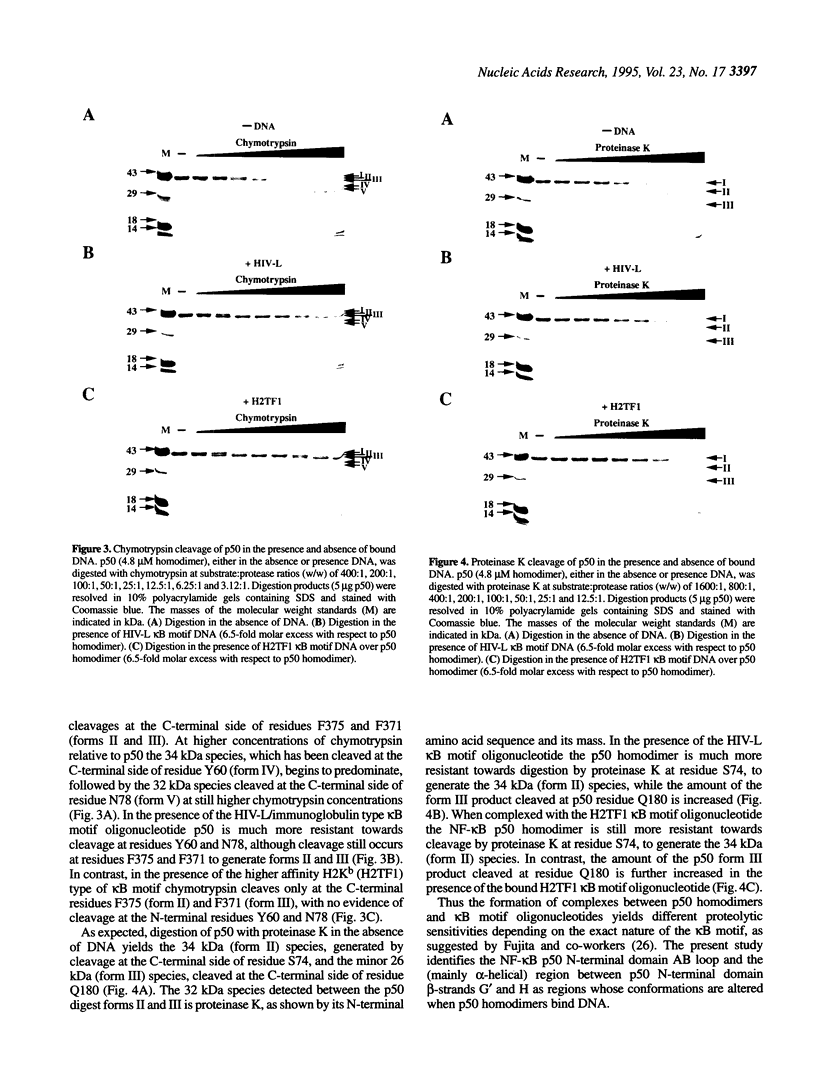
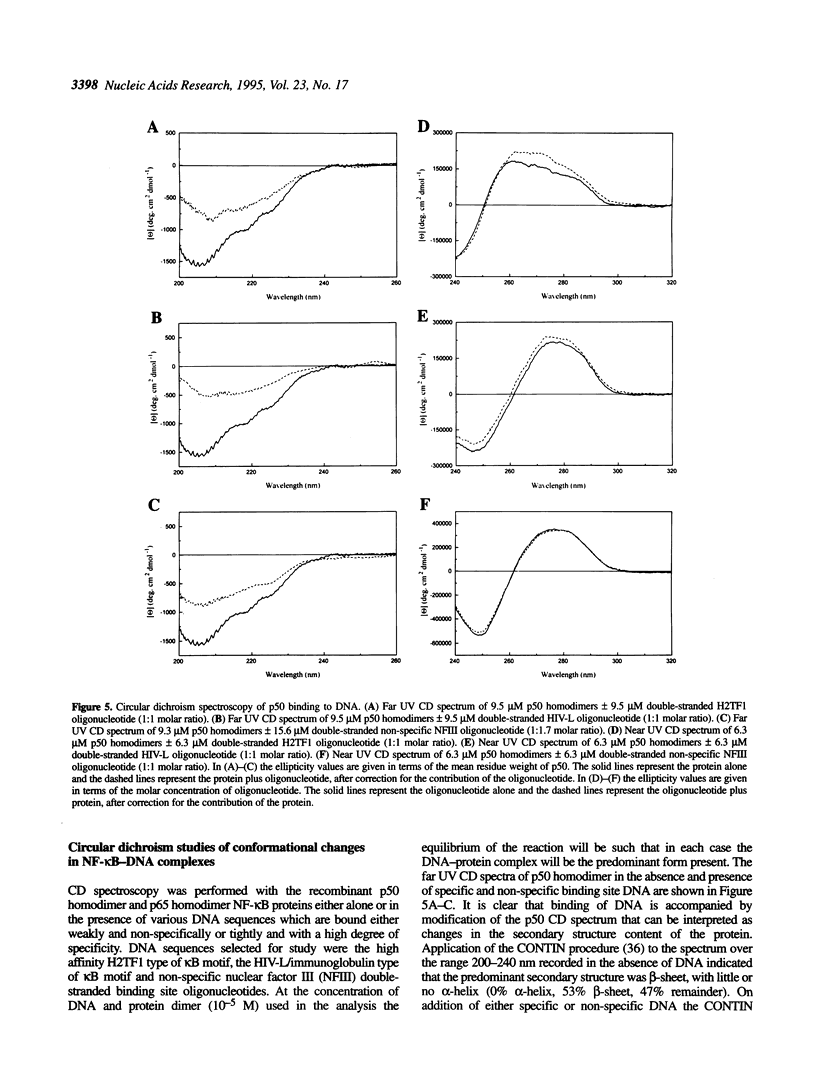
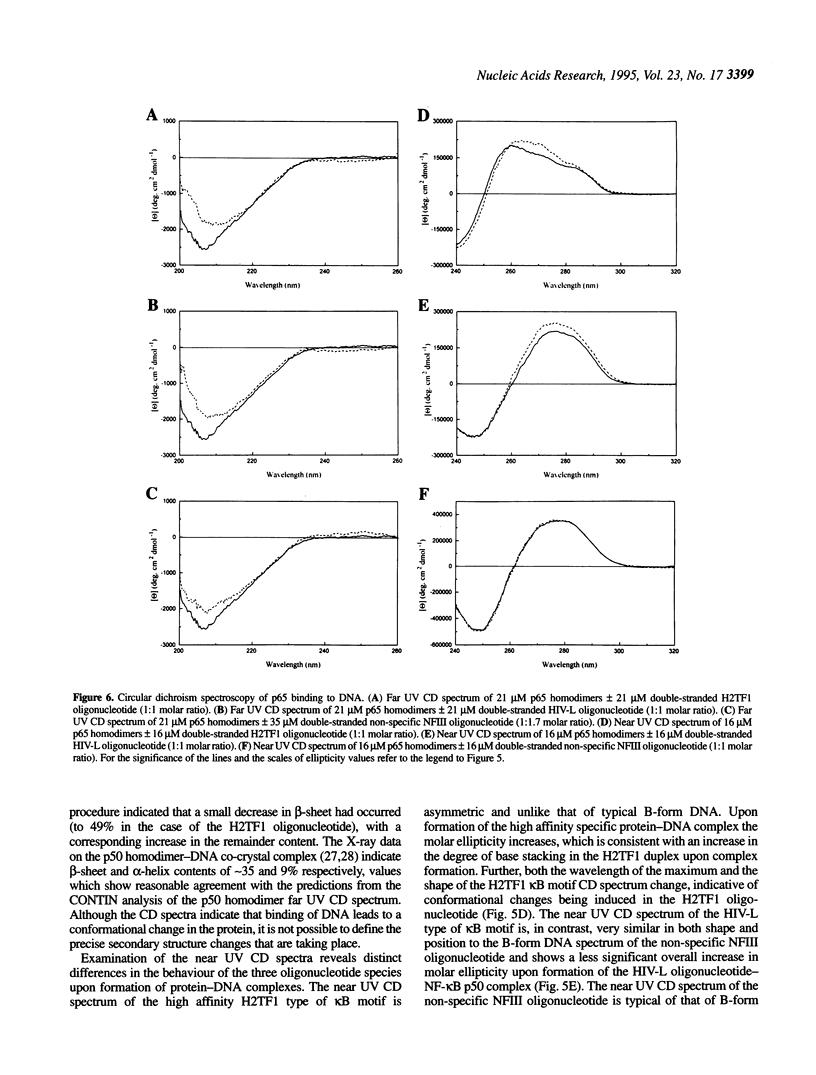
The transcription factor NF-kappa B makes extensive contacts with its recognition site over one complete turn of the double helix. Structural transitions, in both protein and DNA, that accompany formation of the DNA-protein complex were analysed by proteinase sensitivity and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. In the absence of DNA chymotrypsin cleaved p50 after residues Y60 and N78, while proteinase K cleaved p50 after residues S74 and Q180. Previous experiments had indicated that trypsin cleaved p50 after K77. Cleavages after Y60, S74, K77 and N78 were blocked in the presence of bound DNA, whereas cleavage after Q180 was enhanced. Y60, S74, K77 and N78 are all located in the p50 N-terminal domain AB loop, whereas Q180 is located in the mainly alpha-helical region between p50 N-terminal domain beta-strands G' and H. As only Y60 makes direct contact with the DNA it is likely that the AB loop is highly unstructured in the absence of DNA, but is held in a rigid, proteinase-resistant structure by bound DNA. These conclusions were supported by CD spectroscopic studies of recombinant p50 and p65 homodimers, which indicated that both species changed conformation when binding DNA. Examination of the near UV CD spectra revealed that with some DNA sequences the bound and free forms of the DNA assumed different conformations. While this was evident for a fully symmetrical, high affinity recognition site DNA, it was not apparent with less tightly bound DNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Burd P. R., Brown K., Villalobos J., Park S., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. A novel mitogen-inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappa B participates in transactivation through a kappa B site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):685–695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mittereder N., Rice N. R. A human rel proto-oncogene cDNA containing an Alu fragment as a potential coding exon. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Hay R. T. Sequence requirement for specific interaction of an enhancer binding protein (EBP1) with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):499–516. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Matthews J. R., Hay R. T. Interaction of enhancer-binding protein EBP1 (NF-kappa B) with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1335–1344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1335-1344.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Nicholson J., Hay R. T. Enhancer binding protein (EBP1) makes base and backbone contacts over one complete turn of the DNA double helix. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90570-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. A., Kunsch C., Maher M., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Acquisition of NFKB1-selective DNA binding by substitution of four amino acid residues from NFKB1 into RelA. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Independent modes of transcriptional activation by the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):775–787. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh G., van Duyne G., Ghosh S., Sigler P. B. Structure of NF-kappa B p50 homodimer bound to a kappa B site. Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):303–310. doi: 10.1038/373303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm S., Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B: structure-function relationship of its protein subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):297–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2900297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., Nicholson J. DNA binding alters the protease susceptibility of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4592–4598. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Ueno Y., Okamoto T. Oxidoreductive regulation of nuclear factor kappa B. Involvement of a cellular reducing catalyst thioredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11380–11388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornby D. P., Whitmarsh A., Pinarbasi H., Kelly S. M., Price N. C., Shore P., Baldwin G. S., Waltho J. The DNA recognition subunit of a DNA methyltransferase is predominantly a molten globule in the absence of DNA. FEBS Lett. 1994 Nov 21;355(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Reach M., Engstrom Y., Kadalayil L., Cai H., González-Crespo S., Tatei K., Levine M. Dif, a dorsal-related gene that mediates an immune response in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90495-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. The RxxRxRxxC motif conserved in all Rel/kappa B proteins is essential for the DNA-binding activity and redox regulation of the v-Rel oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3094–3106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuprash D. V., Rice N. R., Nedospasov S. A. Homodimer of p50 (NF kappa B1) does not introduce a substantial directed bend into DNA according to three different experimental assays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):427–433. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Sodeoka M., Lane W. S., Verdine G. L. Evidence for a non-alpha-helical DNA-binding motif in the Rel homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):908–912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. R., Kaszubska W., Turcatti G., Wells T. N., Hay R. T. Role of cysteine62 in DNA recognition by the P50 subunit of NF-kappa B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1727–1734. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. R., Wakasugi N., Virelizier J. L., Yodoi J., Hay R. T. Thioredoxin regulates the DNA binding activity of NF-kappa B by reduction of a disulphide bond involving cysteine 62. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3821–3830. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. R., Watson E., Buckley S., Hay R. T. Interaction of the C-terminal region of p105 with the nuclear localisation signal of p50 is required for inhibition of NF-kappa B DNA binding activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 25;21(19):4516–4523. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.19.4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C. W., Rey F. A., Sodeoka M., Verdine G. L., Harrison S. C. Structure of the NF-kappa B p50 homodimer bound to DNA. Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):311–317. doi: 10.1038/373311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nekludova L., Pabo C. O. Distinctive DNA conformation with enlarged major groove is found in Zn-finger-DNA and other protein-DNA complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6948–6952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. The inhibitory ankyrin and activator Rel proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W., Glöckner J. Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):33–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Klement J. F., Coleman T. A., Maher M., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. I-Rel: a novel rel-related protein that inhibits NF-kappa B transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):745–760. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Ghosh D., Trinh F., Leonard W. J. N-terminal DNA-binding domains contribute to differential DNA-binding specificities of NF-kappa B p50 and p65. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):852–860. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Modulation of transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4328–4332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Ellenberger T., Wobbe C. R., Lee J. P., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Folding transition in the DNA-binding domain of GCN4 on specific binding to DNA. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):575–578. doi: 10.1038/347575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]