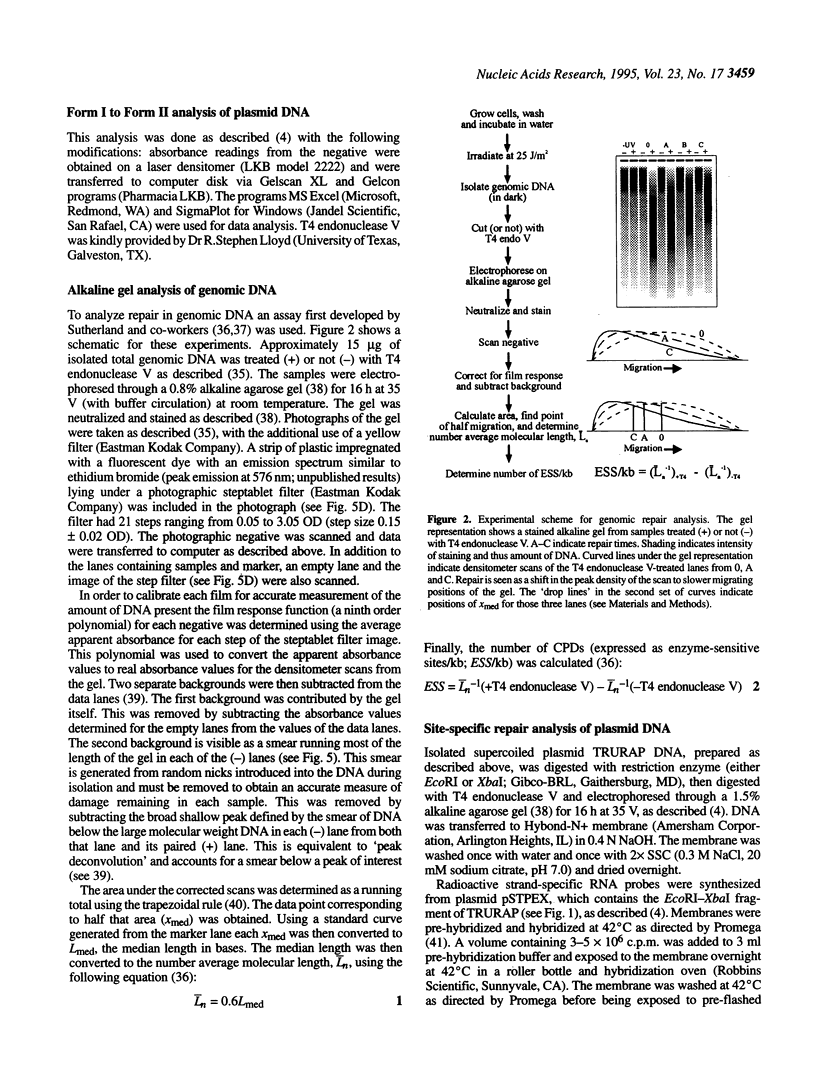
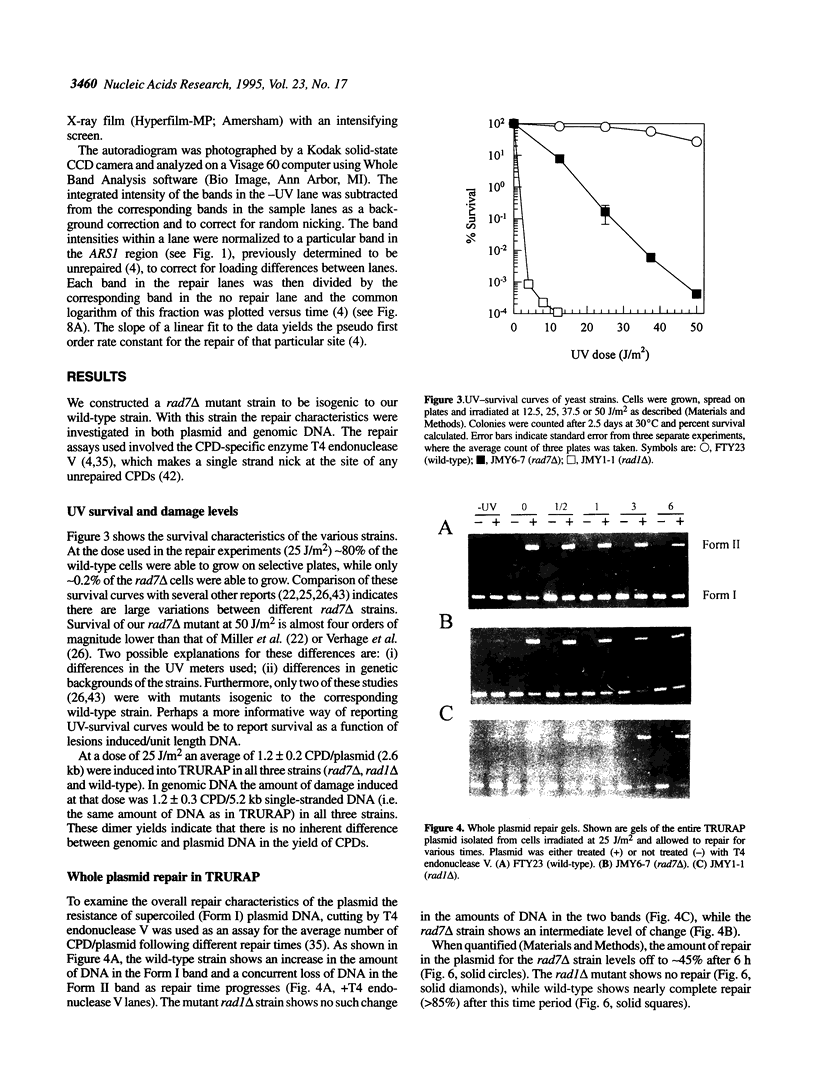
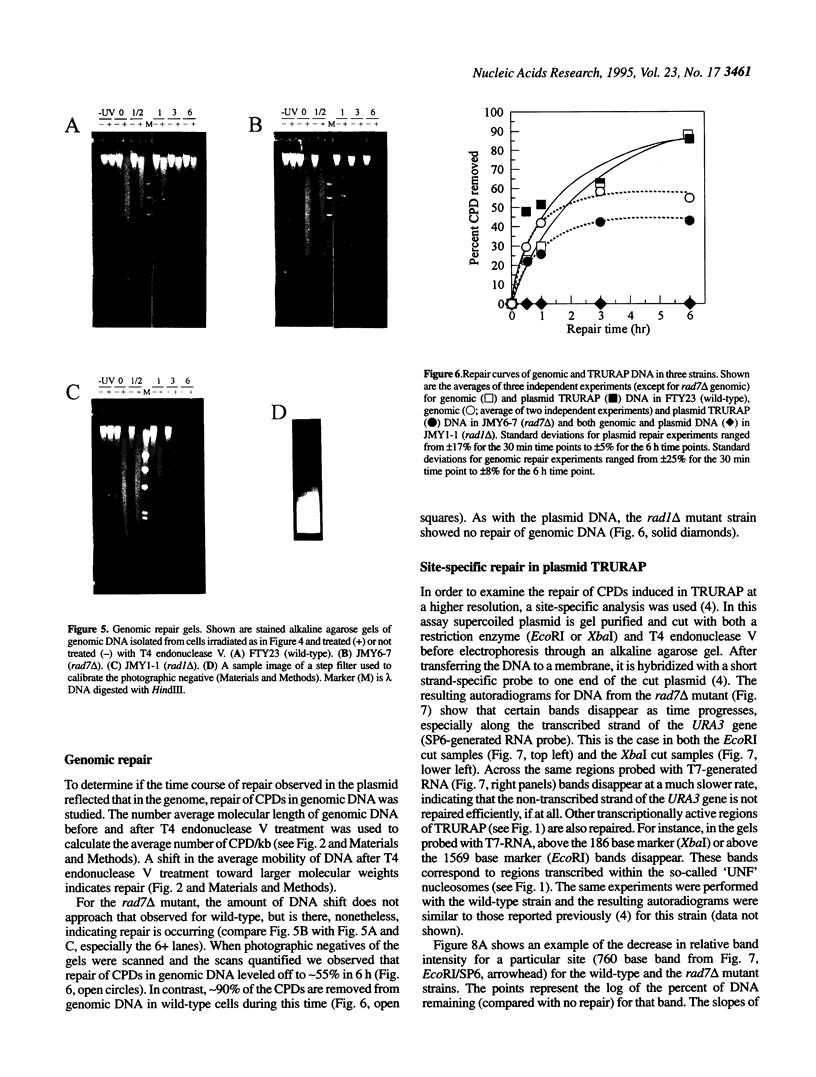
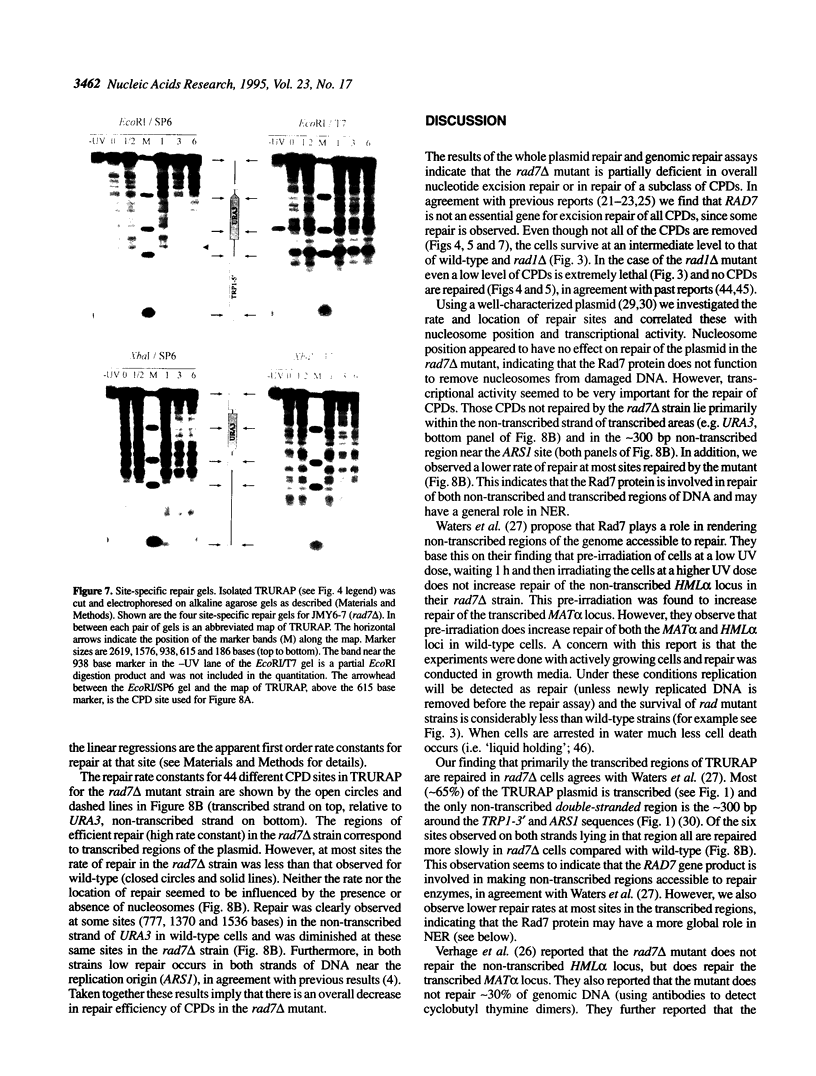
Abstract
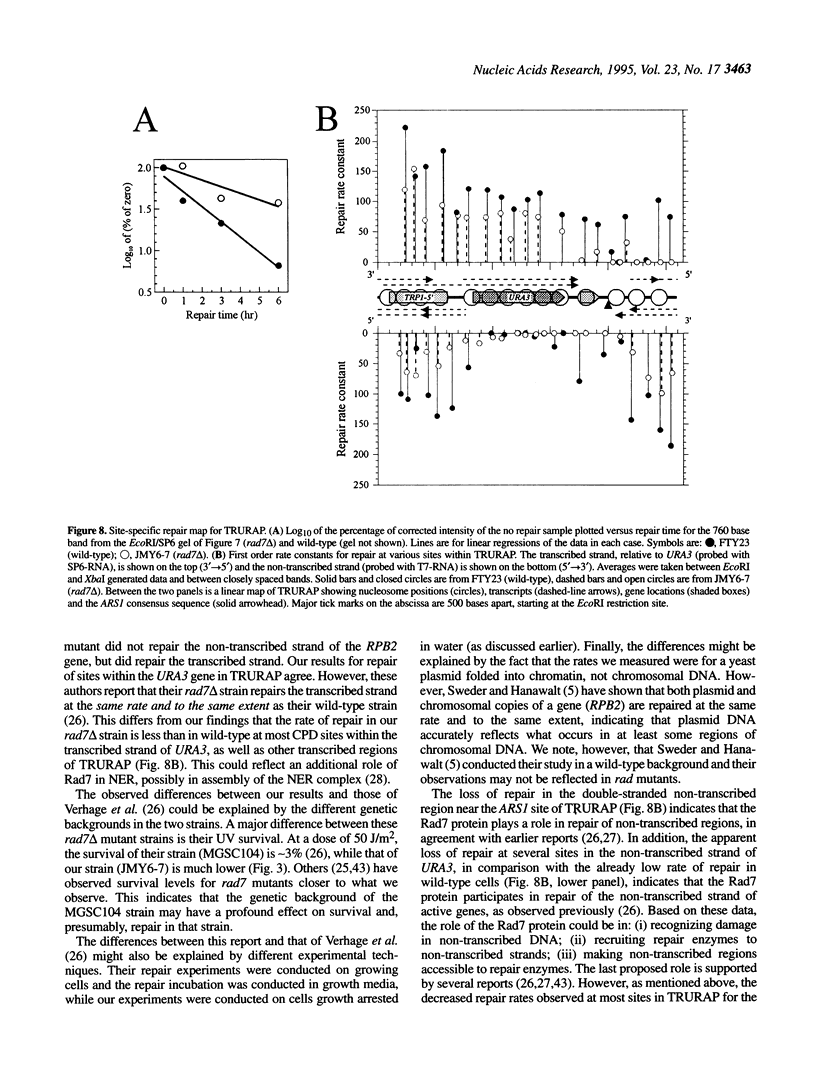
Repair of UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) was examined in a yeast plasmid of known chromatin structure and in genomic DNA in a radiation-sensitive deletion mutant of yeast, rad7 delta, and its isogenic wild-type strain. A whole plasmid repair assay revealed that only approximately 50% of the CPDs in plasmid DNA are repaired after 6 h in this mutant, compared with almost 90% repaired in wild-type. Using a site-specific repair assay on 44 individual CPD sites within the plasmid we found that repair in the rad7 delta mutant occurred primarily in the transcribed regions of each strand of the plasmid, however, the rate of repair at nearly all sites measured was less than in the wild-type. There was no apparent correlation between repair rate and nucleosome position. In addition, approximately 55% of the CPDs in genomic DNA of the mutant are repaired during the 6 h period, compared with > 80% in the wild-type.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly V., Sommers C. H., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Specific complex formation between proteins encoded by the yeast DNA repair and recombination genes RAD1 and RAD10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8273–8277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa W., Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Yeast regulatory gene GAL3: carbon regulation; UASGal elements in common with GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, GAL80, and MEL1; encoded protein strikingly similar to yeast and Escherichia coli galactokinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3439–3447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell A. J., Bardwell L., Johnson D. K., Friedberg E. C. Yeast DNA recombination and repair proteins Rad1 and Rad10 constitute a complex in vivo mediated by localized hydrophobic domains. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1177–1188. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedoyan J., Gupta R., Thoma F., Smerdon M. J. Transcription, nucleosome stability, and DNA repair in a yeast minichromosome. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5996–6005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. L., Schrock R. D., 3rd, Lloyd R. S. Evidence for an imino intermediate in the T4 endonuclease V reaction. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8284–8290. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Svejstrup J. Q., Bardwell L., Bardwell A. J., Buratowski S., Gulyas K. D., Donahue T. F., Friedberg E. C., Kornberg R. D. Dual roles of a multiprotein complex from S. cerevisiae in transcription and DNA repair. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1379–1387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90624-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S. E., Blackett A. D., Monteleone D. C., Setlow R. B., Sutherland B. M., Sutherland J. C. Quantitation of radiation-, chemical-, or enzyme-induced single strand breaks in nonradioactive DNA by alkaline gel electrophoresis: application to pyrimidine dimers. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90599-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Schiestl R. H. Applications of high efficiency lithium acetate transformation of intact yeast cells using single-stranded nucleic acids as carrier. Yeast. 1991 Apr;7(3):253–263. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Sung P., Bailly V., Prakash L., Prakash S. RAD25 is a DNA helicase required for DNA repair and RNA polymerase II transcription. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):578–581. doi: 10.1038/369578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Yeast DNA-repair gene RAD14 encodes a zinc metalloprotein with affinity for ultraviolet-damaged DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5433–5437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habraken Y., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Yeast excision repair gene RAD2 encodes a single-stranded DNA endonuclease. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):365–368. doi: 10.1038/366365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. S., Prakash L., Prakash S. Regulated expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA repair gene RAD7 in response to DNA damage and during sporulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3281–3285. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Hanawalt P. C. Induction of the Escherichia coli lactose operon selectively increases repair of its transcribed DNA strand. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):95–98. doi: 10.1038/342095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Spivak G., Hanawalt P. C. Selective removal of transcription-blocking DNA damage from the transcribed strand of the mammalian DHFR gene. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Defective excision of pyrimidine dimers and interstrand DNA crosslinks in rad7 and rad23 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):235–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00332681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. Mismatch repair, genetic stability, and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1959–1960. doi: 10.1126/science.7801122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naegeli H., Bardwell L., Friedberg E. C. Inhibition of Rad3 DNA helicase activity by DNA adducts and abasic sites: implications for the role of a DNA helicase in damage-specific incision of DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):613–621. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naegeli H., Bardwell L., Friedberg E. C. The DNA helicase and adenosine triphosphatase activities of yeast Rad3 protein are inhibited by DNA damage. A potential mechanism for damage-specific recognition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):392–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetkau D. W., Riese J. A., MacMorran W. S., Woods R. A., Gietz R. D. Interaction of the yeast RAD7 and SIR3 proteins: implications for DNA repair and chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 1;8(17):2035–2045. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.17.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozzi G., Prakash S. RAD7 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: transcripts, nucleotide sequence analysis, and functional relationship between the RAD7 and RAD23 gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1497–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L., Prakash S. Three additional genes involved in pyrimidine dimer removal in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: RAD7, RAD14 and MMS19. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Nov;176(3):351–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00333097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Sung P., Prakash L. DNA repair genes and proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:33–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. J., Friedberg E. C. Molecular mechanisms of pyrimidine dimer excision in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: incision of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):692–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.692-704.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A. Mechanisms of DNA excision repair. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1954–1956. doi: 10.1126/science.7801120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Molecular mechanism of transcription-repair coupling. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8465200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Bedoyan J., Thoma F. DNA repair in a small yeast plasmid folded into chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2045–2051. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Thoma F. Site-specific DNA repair at the nucleosome level in a yeast minichromosome. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90479-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Matson S. W., Prakash S. RAD3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8951–8955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Weber S., Prakash S. The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA-dependent ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Reynolds P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Purification and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD1/RAD10 endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26391–26399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Watkins J. F., Prakash L., Prakash S. Negative superhelicity promotes ATP-dependent binding of yeast RAD3 protein to ultraviolet-damaged DNA. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8303–8308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland B. M., Shih A. G. Quantitation of pyrimidine dimer contents of nonradioactive deoxyribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in alkaline agarose gels. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):745–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweder K. S., Hanawalt P. C. Preferential repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in the transcribed strand of a gene in yeast chromosomes and plasmids is dependent on transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10696–10700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Protein-DNA interactions and nuclease-sensitive regions determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmid chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhage R., Zeeman A. M., de Groot N., Gleig F., Bang D. D., van de Putte P., Brouwer J. The RAD7 and RAD16 genes, which are essential for pyrimidine dimer removal from the silent mating type loci, are also required for repair of the nontranscribed strand of an active gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6135–6142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R., Zhang R., Jones N. J. Inducible removal of UV-induced pyrimidine dimers from transcriptionally active and inactive genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):28–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00281597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. I., Sedgwick S. G. The use of plasmid DNA to probe DNA repair functions in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(1):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00397993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. R., Prakash L. Incision and postincision steps of pyrimidine dimer removal in excision-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.618-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gool A. J., Verhage R., Swagemakers S. M., van de Putte P., Brouwer J., Troelstra C., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. RAD26, the functional S. cerevisiae homolog of the Cockayne syndrome B gene ERCC6. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5361–5369. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]