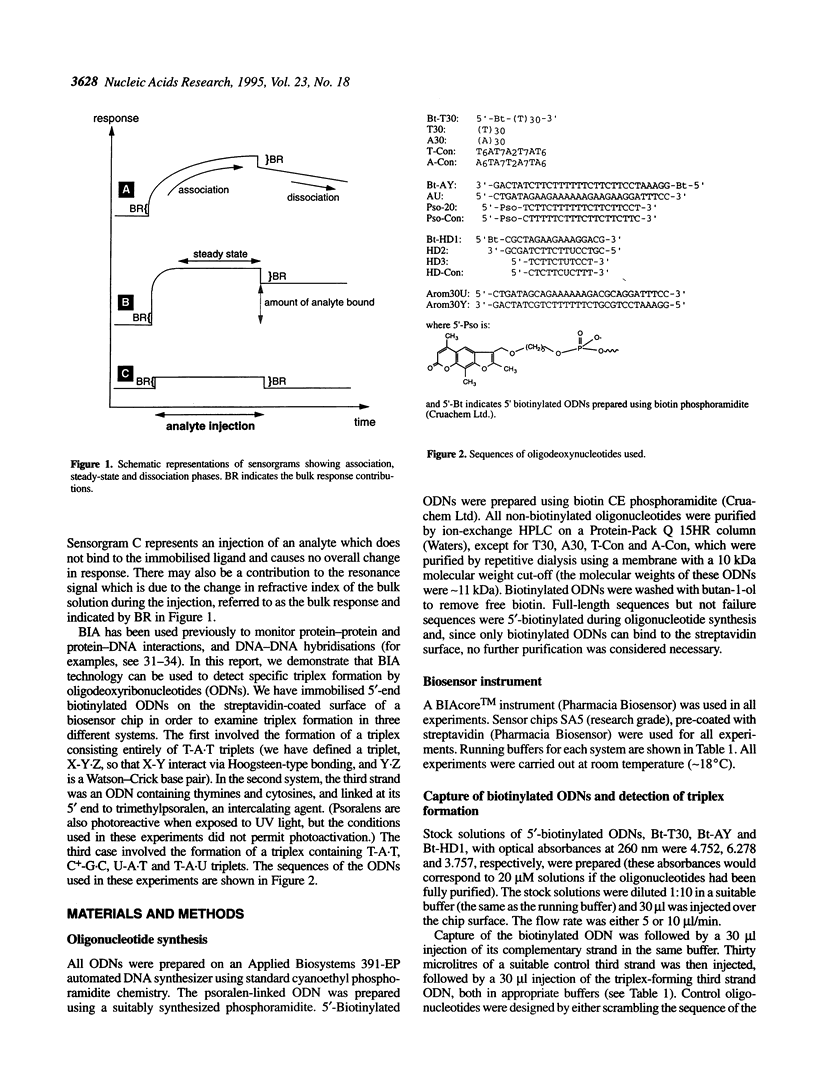
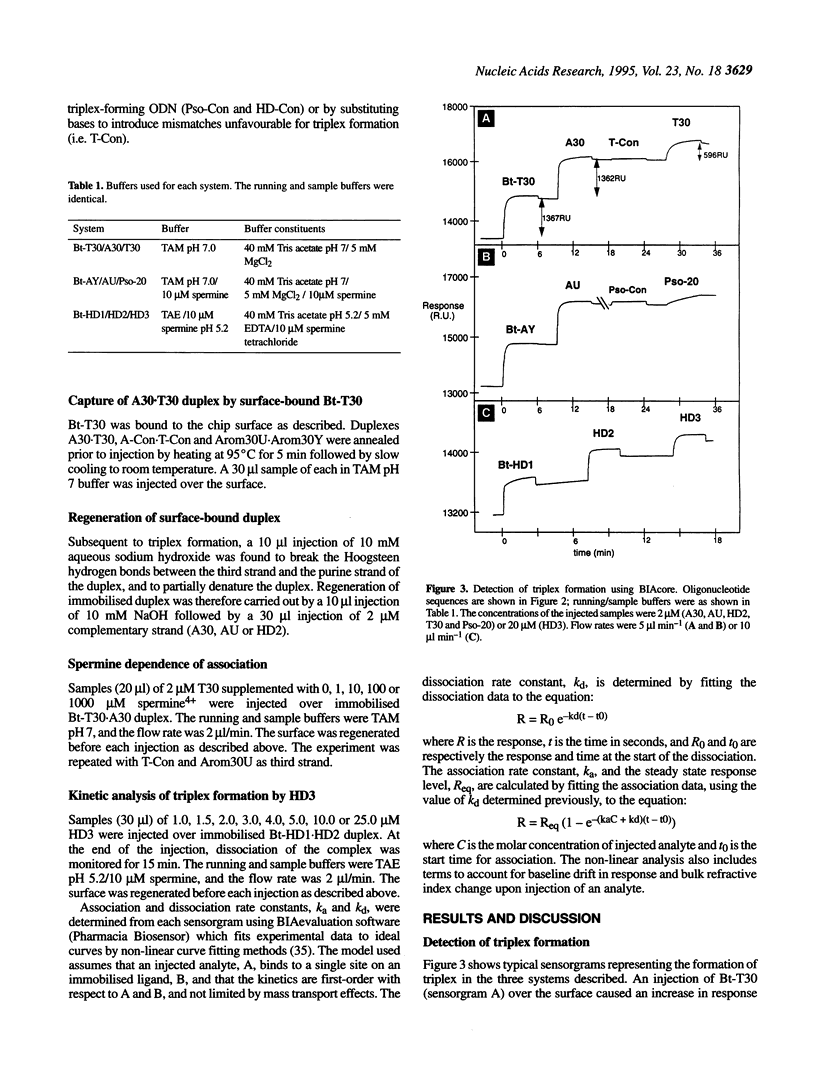
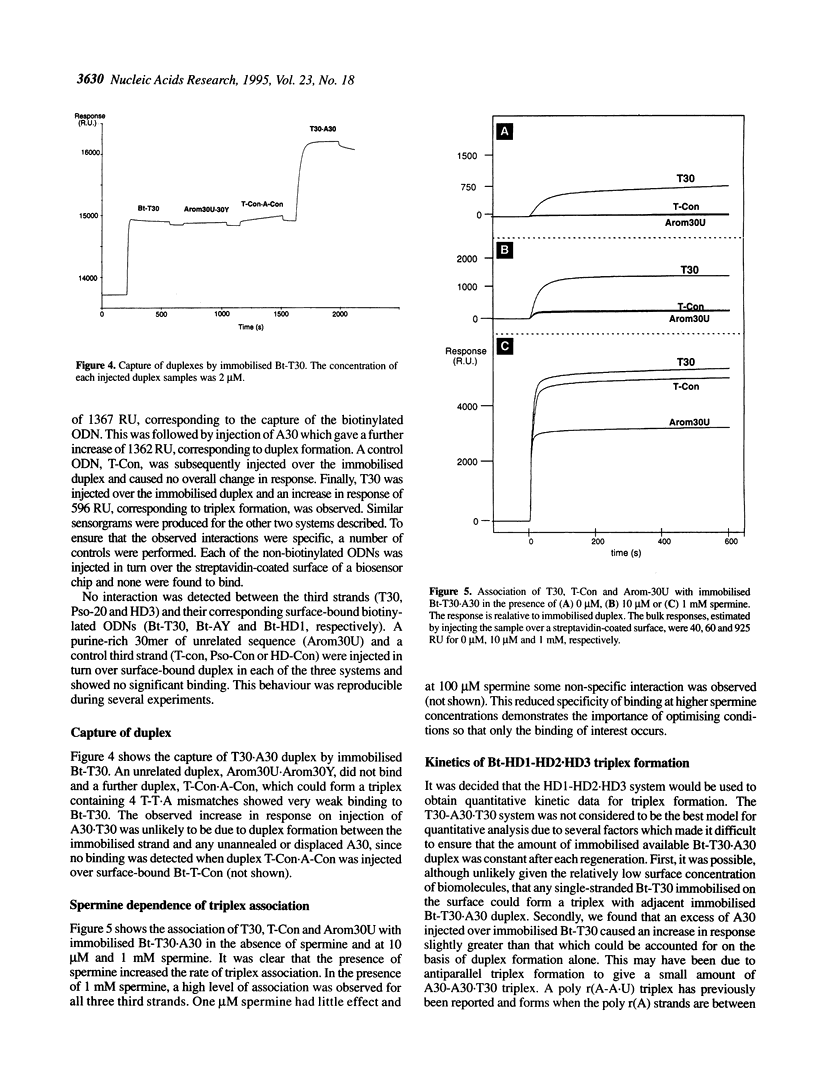
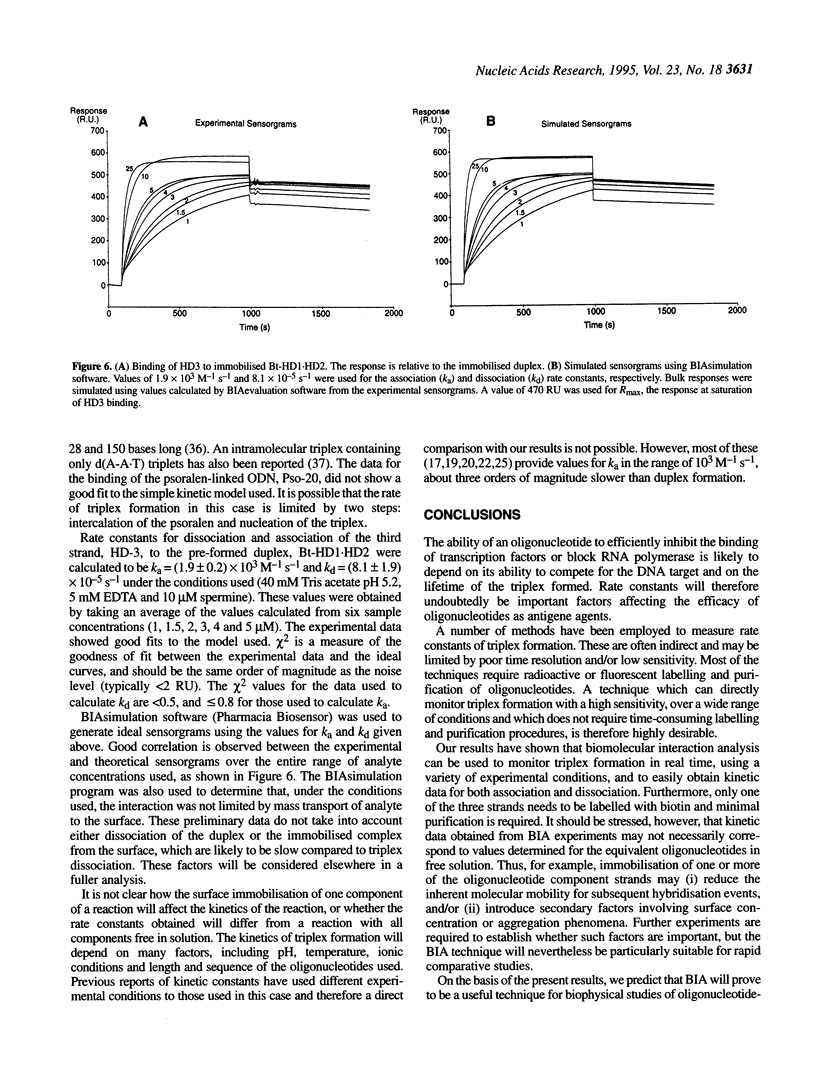
Abstract
Real-time biomolecular interaction analysis (BIA) has been applied to triplex formation between oligodeoxynucleotides. 5'-Biotinylated oligonucleotides were immobilised on the streptavidin-coated surface of a biosensor chip and subsequently hybridised to their complementary strand. Sequence-specific triplex formation was observed when a suitable third-strand oligopyrimidine was injected over the surface-bound duplex. In addition, a single-stranded oligonucleotide immobilised on the chip surface was able to capture a DNA duplex by triplex recognition. The presence of spermine increases the rate of association between the third strand and immobilised duplex, but at elevated spermine concentrations non-specific association is observed. A preliminary kinetic analysis of triplex formation at pH 5.2 by an 11mer third strand containing thymine, cytosine and uracil is reported. Values for the association and dissociation rate constants were determined to be (1.9 +/- 0.2) x 10(3) M-1 s-1 and (8.1 +/- 1.9) x 10(-5) s-1, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broitman S. L., Im D. D., Fresco J. R. Formation of the triple-stranded polynucleotide helix, poly(A.A.U). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. Comparison of a structural and a functional epitope. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):554–563. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Fivash M., Casas-Finet J., Erickson J. W., Kondoh A., Bladen S. V., Fisher C., Watson D. K., Papas T. Real-time DNA binding measurements of the ETS1 recombinant oncoproteins reveal significant kinetic differences between the p42 and p51 isoforms. Protein Sci. 1994 Feb;3(2):257–266. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R. Kinetic studies on the formation of acridine-linked DNA triple helices. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 9;357(3):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01387-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fägerstam L. G., Frostell-Karlsson A., Karlsson R., Persson B., Rönnberg I. Biospecific interaction analysis using surface plasmon resonance detection applied to kinetic, binding site and concentration analysis. J Chromatogr. 1992 Apr 24;597(1-2):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(92)80137-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Guieysse A. L., Robin P., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. Inhibition of gene expression by triple helix-directed DNA cross-linking at specific sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3501–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm C. W., Shrestha K., Thomas S., Shingleton H. M., Miller D. M. A unique c-myc-targeted triplex-forming oligonucleotide inhibits the growth of ovarian and cervical carcinomas in vitro. Gynecol Oncol. 1993 Jun;49(3):339–343. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1993.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs C. A., Yoon K. Differential regulation of gene expression in vivo by triple helix-forming oligonucleotides as detected by a reporter enzyme. Antisense Res Dev. 1994 Spring;4(1):1–8. doi: 10.1089/ard.1994.4.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüsler P. L., Klump H. H. Prediction of pH-dependent properties of DNA triple helices. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 Feb 20;317(1):46–56. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Kessler D. J., Murphy M., Jayaraman K., Zendegui J. G., Hogan M. E., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. In vivo transcription of a progesterone-responsive gene is specifically inhibited by a triplex-forming oligonucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2789–2796. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Sequence-specific DNA purification by triplex affinity capture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):495–498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson U., Fägerstam L., Ivarsson B., Johnsson B., Karlsson R., Lundh K., Löfås S., Persson B., Roos H., Rönnberg I. Real-time biospecific interaction analysis using surface plasmon resonance and a sensor chip technology. Biotechniques. 1991 Nov;11(5):620–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klysik J., Rippe K., Jovin T. M. Parallel-stranded DNA under topological stress: rearrangement of (dA)15.(dT)15 to a d(A.A.T)n triplex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec;19(25):7145–7154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.25.7145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist M. Biospecific interaction analysis using biosensor technology. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):186–187. doi: 10.1038/361186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marengere L. E., Songyang Z., Gish G. D., Schaller M. D., Parsons J. T., Stern M. J., Cantley L. C., Pawson T. SH2 domain specificity and activity modified by a single residue. Nature. 1994 Jun 9;369(6480):502–505. doi: 10.1038/369502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McShan W. M., Rossen R. D., Laughter A. H., Trial J., Kessler D. J., Zendegui J. G., Hogan M. E., Orson F. M. Inhibition of transcription of HIV-1 in infected human cells by oligodeoxynucleotides designed to form DNA triple helices. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5712–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Buchardt O. Peptide nucleic acid (PNA). A DNA mimic with a peptide backbone. Bioconjug Chem. 1994 Jan-Feb;5(1):3–7. doi: 10.1021/bc00025a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson P., Persson B., Uhlén M., Nygren P. A. Real-time monitoring of DNA manipulations using biosensor technology. Anal Biochem. 1995 Jan 1;224(1):400–408. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shannessy D. J., Brigham-Burke M., Peck K. Immobilization chemistries suitable for use in the BIAcore surface plasmon resonance detector. Anal Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;205(1):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90589-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shannessy D. J., Brigham-Burke M., Soneson K. K., Hensley P., Brooks I. Determination of rate and equilibrium binding constants for macromolecular interactions using surface plasmon resonance: use of nonlinear least squares analysis methods. Anal Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;212(2):457–468. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch D. S., Brousseau R., Shafer R. H. Thermodynamics of triple helix formation: spectrophotometric studies on the d(A)10.2d(T)10 and d(C+3T4C+3).d(G3A4G3).d(C3T4C3) triple helices. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5743–5750. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum G. E., Park Y. W., Singleton S. F., Dervan P. B., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamic characterization of the stability and the melting behavior of a DNA triplex: a spectroscopic and calorimetric study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougée M., Faucon B., Mergny J. L., Barcelo F., Giovannangeli C., Garestier T., Hélène C. Kinetics and thermodynamics of triple-helix formation: effects of ionic strength and mismatches. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9269–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. Inhibition of gene transcription by purine rich triplex forming oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2845–2852. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Sugiura S., Torigoe H., Shindo H. Thermodynamic and kinetic analyses of DNA triplex formation: application of filter-binding assay. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1993 Oct;11(2):245–252. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1993.10508724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Torigoe H., Sarai A. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of DNA triplex formation of an oligohomopyrimidine and a matched duplex by filter binding assay. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 31;32(34):8963–8969. doi: 10.1021/bi00085a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xodo L. E. Kinetic analysis of triple-helix formation by pyrimidine oligodeoxynucleotides and duplex DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Mar 15;228(3):918–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xodo L. E., Manzini G., Quadrifoglio F., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H. Effect of 5-methylcytosine on the stability of triple-stranded DNA--a thermodynamic study. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5625–5631. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Ghosh S. S., Millar D. P. Direct measurement of thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of DNA triple helix formation by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 27;33(51):15329–15337. doi: 10.1021/bi00255a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



