Abstract
On the basis of primary sequence comparisons and secondary structure predictions, picornavirus internal ribosome entry segments (IRESes) have been divided into three groups (entero- and rhinoviruses; cardio- and and aphthoviruses; and hepatitis A virus). Here, we describe a detailed comparison of the ability of IRESes from each group to direct internal initiation of translation in vitro using a single dicistronic mRNA (the only variable being the IRES inserted into the dicistronic region). We studied the influence of various parameters on the capacity of six different picornaviral IRESes, and the non-picornaviral hepatitis C virus IRES, to direct internal initiation of translation: salt concentration, the addition of HeLa cell proteins to rabbit reticulocyte lysate translation reactions, the presence of foot-and-mouth disease virus Lb or human rhinovirus 2A proteinase. On the basis of the characteristics of IRES-driven translation in vitro, the picornaviral IRESes can be classified in a similar manner to when sequence homologies are considered. IRESes from each of the three groups responded differently to all of the parameters tested, indicating that while all of these elements can direct internal ribosome entry, the functional requirements for efficient IRES activity vary dramatically. In the individual optimal conditions for translation initiation, the best IRESes were those from the cardio- and aphthoviruses, followed by those from the enteroviruses, which exhibited up to 70% of the efficiency of the EMCV element in directing internal initiation of translation.
Full text
PDF

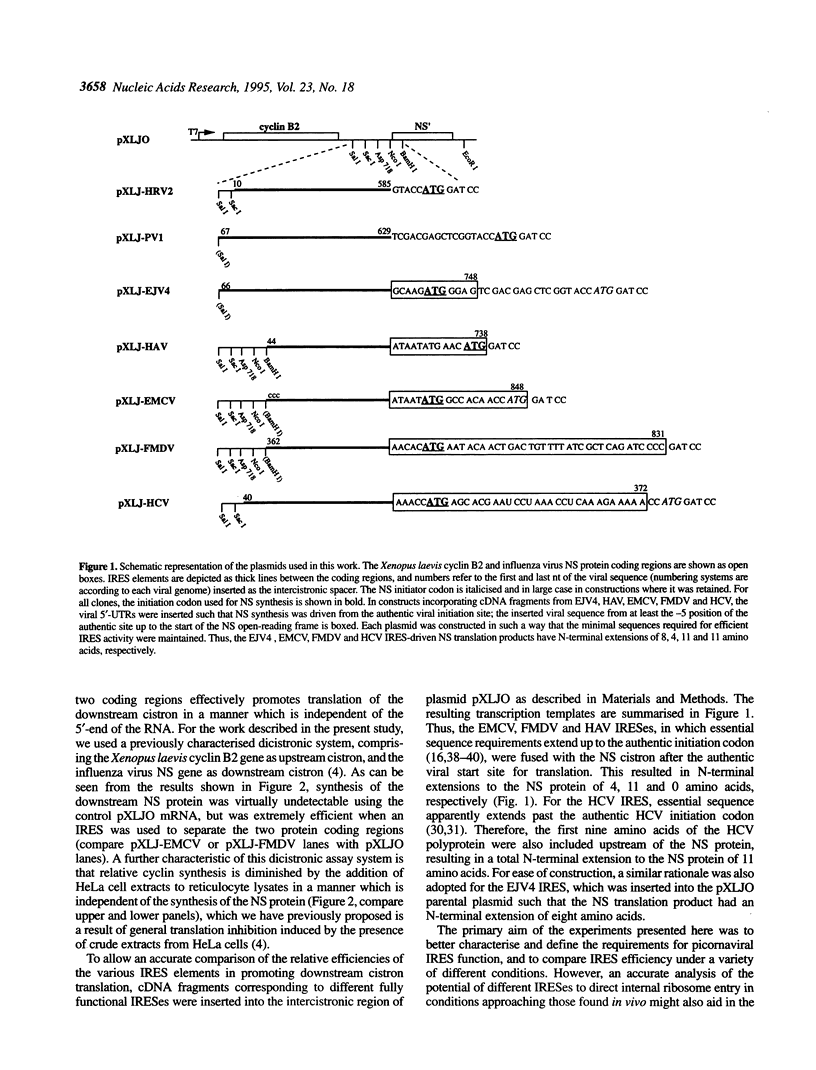





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam M. A., Ramesh N., Miller A. D., Osborne W. R. Internal initiation of translation in retroviral vectors carrying picornavirus 5' nontranslated regions. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4985–4990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4985-4990.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Brangwyn J. K. A region of the 5' noncoding region of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA directs efficient internal initiation of protein synthesis within cells: involvement with the role of L protease in translational control. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5389–5395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5389-5395.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlioz C., Darlix J. L. An internal ribosomal entry mechanism promotes translation of murine leukemia virus gag polyprotein precursors. J Virol. 1995 Apr;69(4):2214–2222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.4.2214-2222.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borman A. M., Deliat F. G., Kean K. M. Sequences within the poliovirus internal ribosome entry segment control viral RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3149–3157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borman A., Jackson R. J. Initiation of translation of human rhinovirus RNA: mapping the internal ribosome entry site. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90523-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Day S. P., Jansen R. W., Lemon S. M. The 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA: secondary structure and elements required for translation in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5828–5838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5828-5838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Zajac A. J., Lemon S. M. In vitro characterization of an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) present within the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA: comparison with the IRES of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1066–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1066-1074.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. H., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Cell type-specific proteins which interact with the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6716–6725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6716-6725.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. C., Jackson R. J. On the fidelity of mRNA translation in the nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysate system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3129–3144. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day S. P., Murphy P., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Mutations within the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA which enhance replication in BS-C-1 cells. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6533–6540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6533-6540.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghattas I. R., Sanes J. R., Majors J. E. The encephalomyocarditis virus internal ribosome entry site allows efficient coexpression of two genes from a recombinant provirus in cultured cells and in embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5848–5859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass M. J., Jia X. Y., Summers D. F. Identification of the hepatitis A virus internal ribosome entry site: in vivo and in vitro analysis of bicistronic RNAs containing the HAV 5' noncoding region. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):842–852. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. L., Kaminski A., Jackson R. J. The influence of viral coding sequences on the efficiency of internal initiation of translation of cardiovirus RNAs. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):801–807. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J. Potassium salts influence the fidelity of mRNA translation initiation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: unique features of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):345–358. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cell culture-adapted variant of hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus with restricted capacity for in vitro replication. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia X. Y., Scheper G., Brown D., Updike W., Harmon S., Richards O., Summers D., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of hepatitis A virus RNA in vitro: aberrant internal initiations influenced by 5' noncoding region. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):712–722. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90612-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Howell M. T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: the authentic initiation site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3753–3759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchweger R., Ziegler E., Lamphear B. J., Waters D., Liebig H. D., Sommergruber W., Sobrino F., Hohenadl C., Blaas D., Rhoads R. E. Foot-and-mouth disease virus leader proteinase: purification of the Lb form and determination of its cleavage site on eIF-4 gamma. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5677–5684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5677-5684.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Luz N., Beck E. Functional analysis of the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4625–4631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4625-4631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Racaniello V. R. Differences in replication of attenuated and neurovirulent polioviruses in human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2357–2360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2357-2360.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le S. Y., Chen J. H., Sonenberg N., Maizel J. V., Jr Conserved tertiary structural elements in the 5' nontranslated region of cardiovirus, aphthovirus and hepatitis A virus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2445–2451. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebig H. D., Ziegler E., Yan R., Hartmuth K., Klump H., Kowalski H., Blaas D., Sommergruber W., Frasel L., Lamphear B. Purification of two picornaviral 2A proteinases: interaction with eIF-4 gamma and influence on in vitro translation. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 27;32(29):7581–7588. doi: 10.1021/bi00080a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation mediated by the 5' leader of a cellular mRNA. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):90–94. doi: 10.1038/353090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan J. P., Singer M. F. Translation of the human LINE-1 element, L1Hs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11533–11537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Jang S. K., Paul A. V., Reuer Q., Wimmer E. Cardioviral internal ribosomal entry site is functional in a genetically engineered dicistronic poliovirus. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):255–257. doi: 10.1038/356255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. A., Couture L., Elroy-Stein O., Ragheb J., Moss B., Anderson W. F. Retroviral vectors containing putative internal ribosome entry sites: development of a polycistronic gene transfer system and applications to human gene therapy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1293–1299. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R., Pelletier J., Le S. Y., Sonenberg N. Structural and functional analysis of the ribosome landing pad of poliovirus type 2: in vivo translation studies. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5886–5894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5886-5894.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. K., Scott M. P., Sarnow P. Homeotic gene Antennapedia mRNA contains 5'-noncoding sequences that confer translational initiation by internal ribosome binding. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1643–1653. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlmann T., Rau M., Morley S. J., Pain V. M. Proteolytic cleavage of initiation factor eIF-4 gamma in the reticulocyte lysate inhibits translation of capped mRNAs but enhances that of uncapped mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):334–340. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Chernov B. K., Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V. I. Conservation of the secondary structure elements of the 5'-untranslated region of cardio- and aphthovirus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5701–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Romanova L. I., Sinyakov A. N., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Conserved structural domains in the 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes: an analysis of the segment controlling translation and neurovirulence. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Gmyl A. P., Maslova S. V., Svitkin Y. V., Sinyakov A. N., Agol V. I. Prokaryotic-like cis elements in the cap-independent internal initiation of translation on picornavirus RNA. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90211-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Pestova T. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Point mutations modify the response of poliovirus RNA to a translation initiation factor: a comparison of neurovirulent and attenuated strains. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesar M., Harmon S. A., Summers D. F., Ehrenfeld E. Hepatitis A virus polyprotein synthesis initiates from two alternative AUG codons. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90027-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama-Kohara K., Iizuka N., Kohara M., Nomoto A. Internal ribosome entry site within hepatitis C virus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1476–1483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1476-1483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetter L. E., Day S. P., Elroy-Stein O., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Low efficiency of the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA in directing cap-independent translation in permissive monkey kidney cells. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):5253–5263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5253-5263.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E., Borman A. M., Kirchweger R., Skern T., Kean K. M. Foot-and-mouth disease virus Lb proteinase can stimulate rhinovirus and enterovirus IRES-driven translation and cleave several proteins of cellular and viral origin. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3465–3474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3465-3474.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





