Abstract
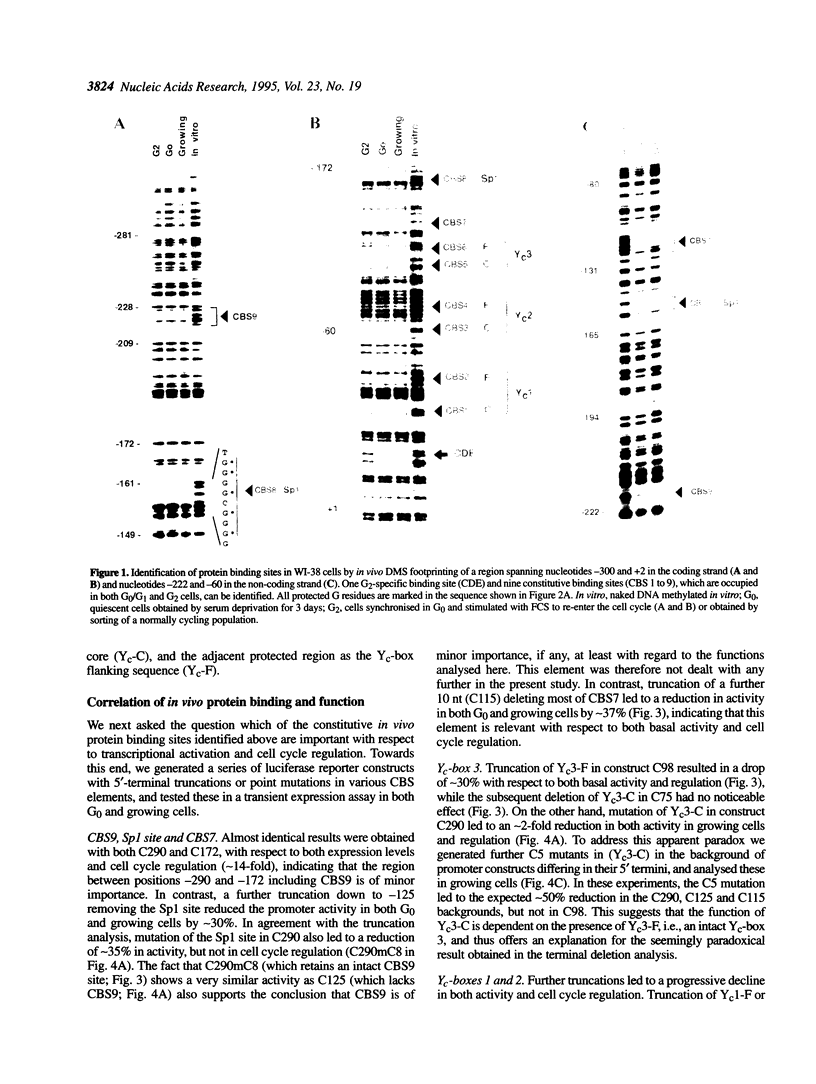
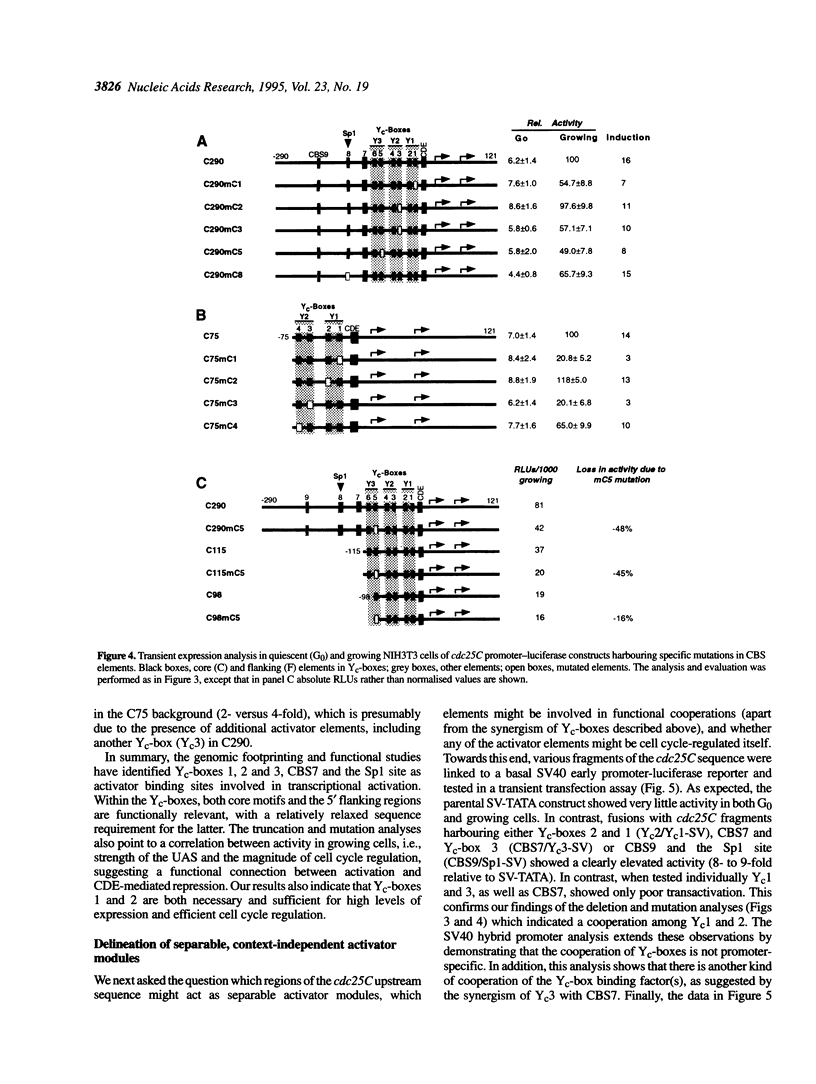
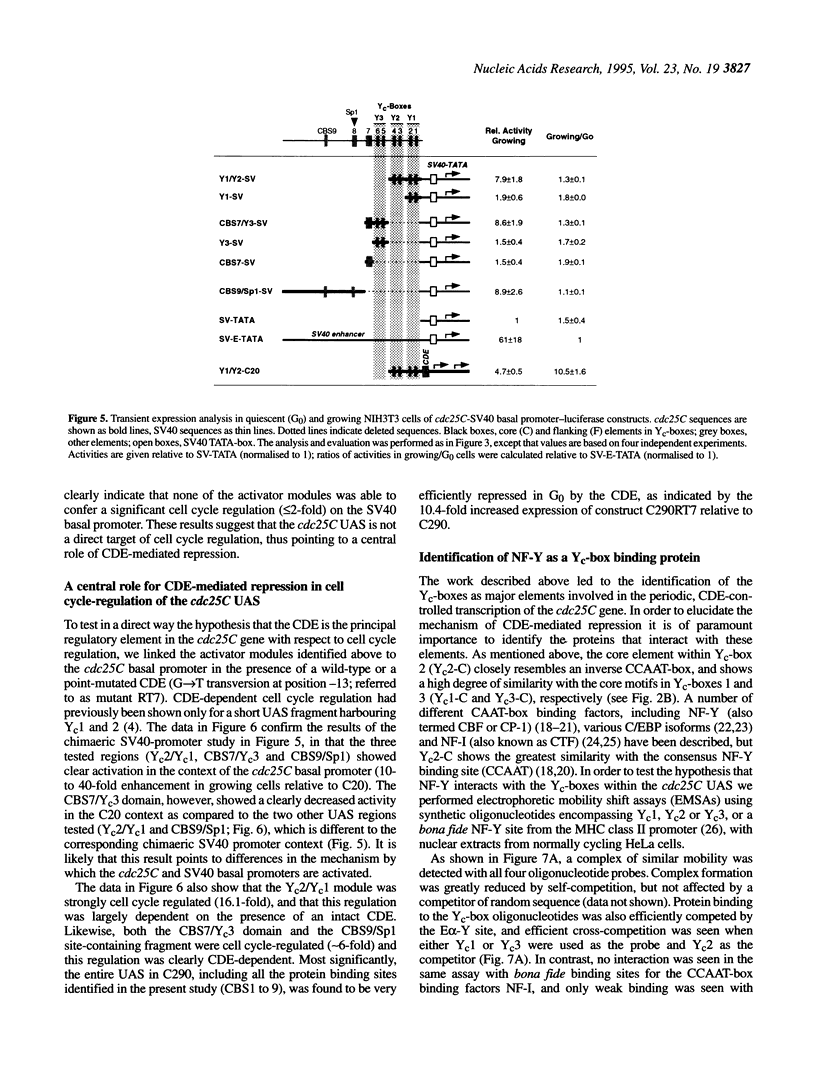
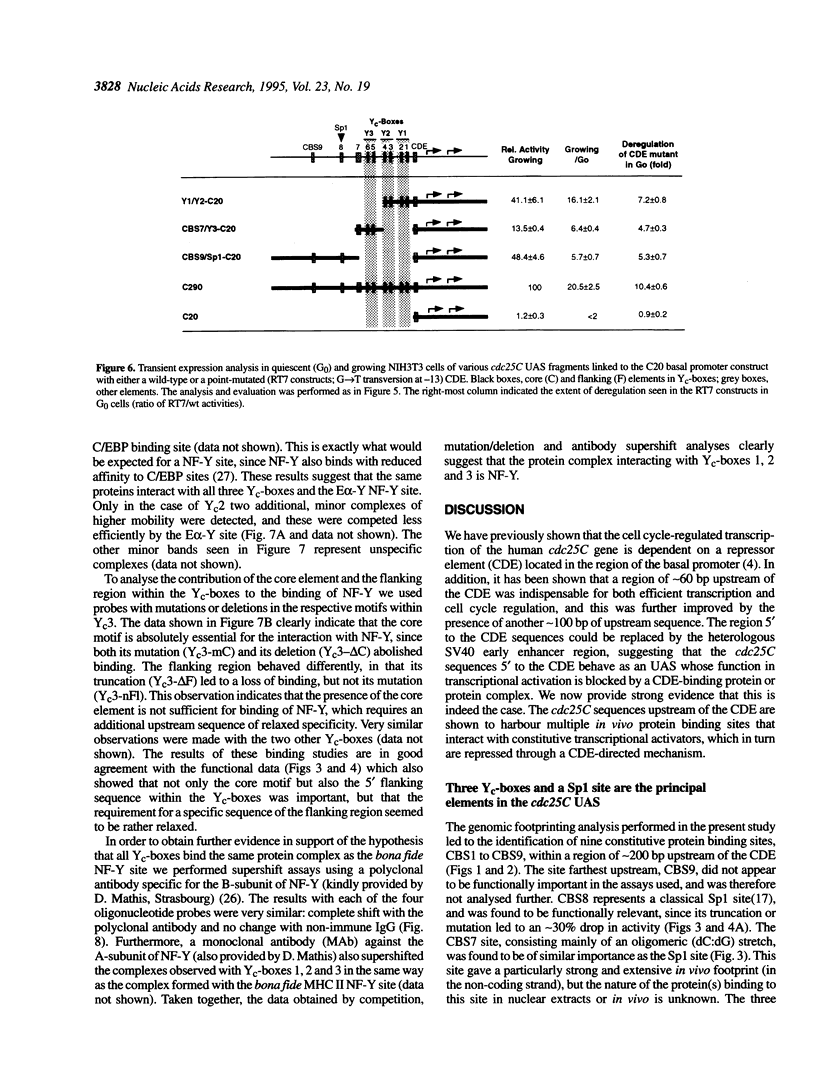
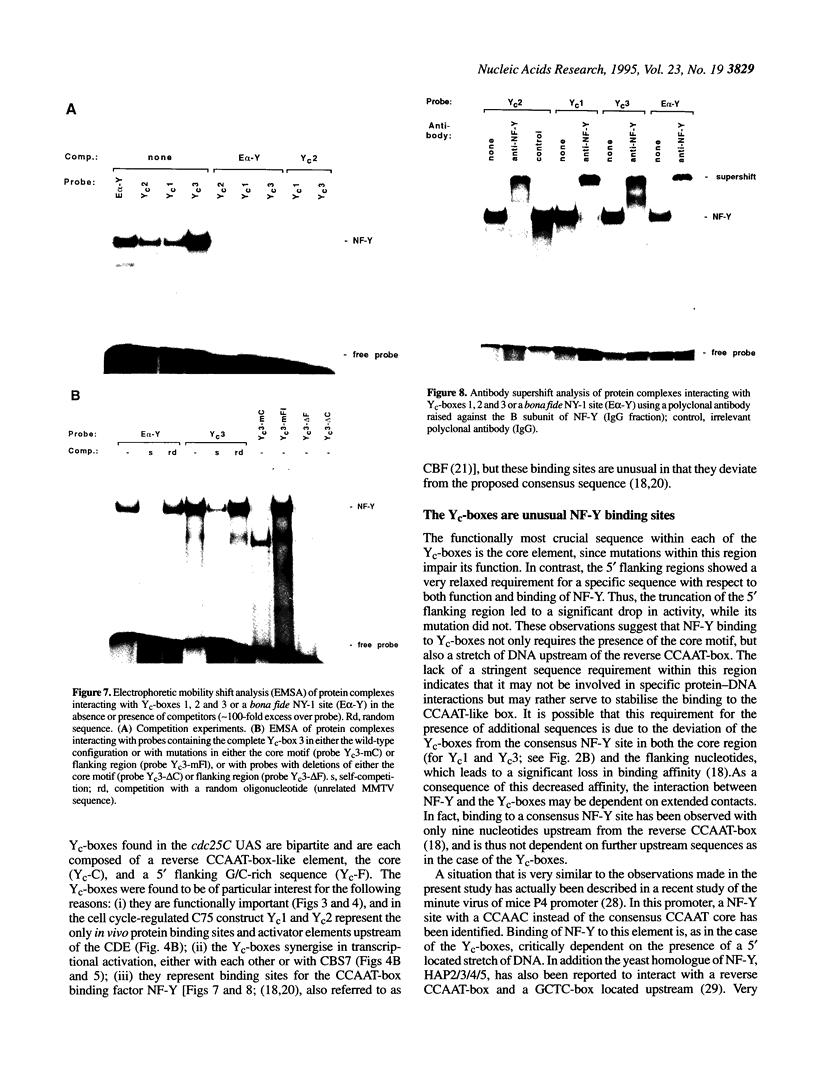
The late S/G2-specific transcription of the human cdc25C gene is dependent on an initiator-proximal repressor element (CDE) and an upstream activating sequence (UAS) of undefined nature. We now show that these upstream sequences harbour multiple in vivo protein binding sites that interact with transcriptional activators and form separable, context-independent functional modules. Major components of the UAS are a bona fide Sp1 site and three direct sequence repeats (Yc-boxes). The Yc-boxes interact with the CCAAT-box binding protein NF-Y and are critically dependent on synergistic interactions for efficient transcription activation. The NF-Y complexes, as well as Sp1, are constitutive activators, whose activation function is periodically repressed through the CDE. These observations indicate that the cell cycle regulation of cdc25C transcription is mainly due to the CDE-mediated repression of glutamine-rich activators.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coustry F., Maity S. N., de Crombrugghe B. Studies on transcription activation by the multimeric CCAAT-binding factor CBF. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 6;270(1):468–475. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.1.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good L., Nazar R. N. An improved thermal cycle for two-step PCR-based targeted mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4934–4934. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. TBP-TAF complexes: selectivity factors for eukaryotic transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Plaza S., Perros M., Cziepluch C., Rommelaere J., Cornelis J. J. NF-Y controls transcription of the minute virus of mice P4 promoter through interaction with an unusual binding site. J Virol. 1995 Jan;69(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.1.239-246.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. THE LIMITED IN VITRO LIFETIME OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELL STRAINS. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Mar;37:614–636. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henglein B., Chenivesse X., Wang J., Eick D., Bréchot C. Structure and cell cycle-regulated transcription of the human cyclin A gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5490–5494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herber B., Truss M., Beato M., Müller R. Inducible regulatory elements in the human cyclin D1 promoter. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1295–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Li X. Y., Black D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Co-evolution from yeast to mouse: cDNA cloning of the two NF-Y (CP-1/CBF) subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3119–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. M., McMahon S. L., Farnham P. J. Multiple DNA elements are required for the growth regulation of the mouse E2F1 promoter. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1526–1537. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Ohtani K., Nevins J. R. Autoregulatory control of E2F1 expression in response to positive and negative regulators of cell cycle progression. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1514–1525. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B. DP and E2F proteins: components of a heterodimeric transcription factor implicated in cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. Y., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Mantovani R., Benoist C., Mathis D. Intron-exon organization of the NF-Y genes. Tissue-specific splicing modifies an activation domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8984–8990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Truss M., Zwicker J., Ehlert F., Beato M., Müller R. Periodic cdc25C transcription is mediated by a novel cell cycle-regulated repressor element (CDE). EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):132–142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maity S. N., Sinha S., Ruteshouser E. C., de Crombrugghe B. Three different polypeptides are necessary for DNA binding of the mammalian heteromeric CCAAT binding factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16574–16580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani R., Pessara U., Tronche F., Li X. Y., Knapp A. M., Pasquali J. L., Benoist C., Mathis D. Monoclonal antibodies to NF-Y define its function in MHC class II and albumin gene transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3315–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Gander I., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L. A quantitative analysis of nuclear factor I/DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4419–4435. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., Russell P. The cdc25 M-phase inducer: an unconventional protein phosphatase. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90177-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mink S., Härtig E., Jennewein P., Doppler W., Cato A. C. A mammary cell-specific enhancer in mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is composed of multiple regulatory elements including binding sites for CTF/NFI and a novel transcription factor, mammary cell-activating factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4906–4918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. Transcriptional regulation during the mammalian cell cycle. Trends Genet. 1995 May;11(5):173–178. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(00)89039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu K., Reed S. I., Richardson H., Russell P. Human homolog of fission yeast cdc25 mitotic inducer is predominantly expressed in G2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5139–5143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha S., Maity S. N., Lu J., de Crombrugghe B. Recombinant rat CBF-C, the third subunit of CBF/NFY, allows formation of a protein-DNA complex with CBF-A and CBF-B and with yeast HAP2 and HAP3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J., Mueller C., Schibler U. A ubiquitous CCAAT factor is required for efficient in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):865–874. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90341-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker J., Lucibello F. C., Wolfraim L. A., Gross C., Truss M., Engeland K., Müller R. Cell cycle regulation of the cyclin A, cdc25C and cdc2 genes is based on a common mechanism of transcriptional repression. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 15;14(18):4514–4522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]