Abstract
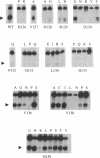
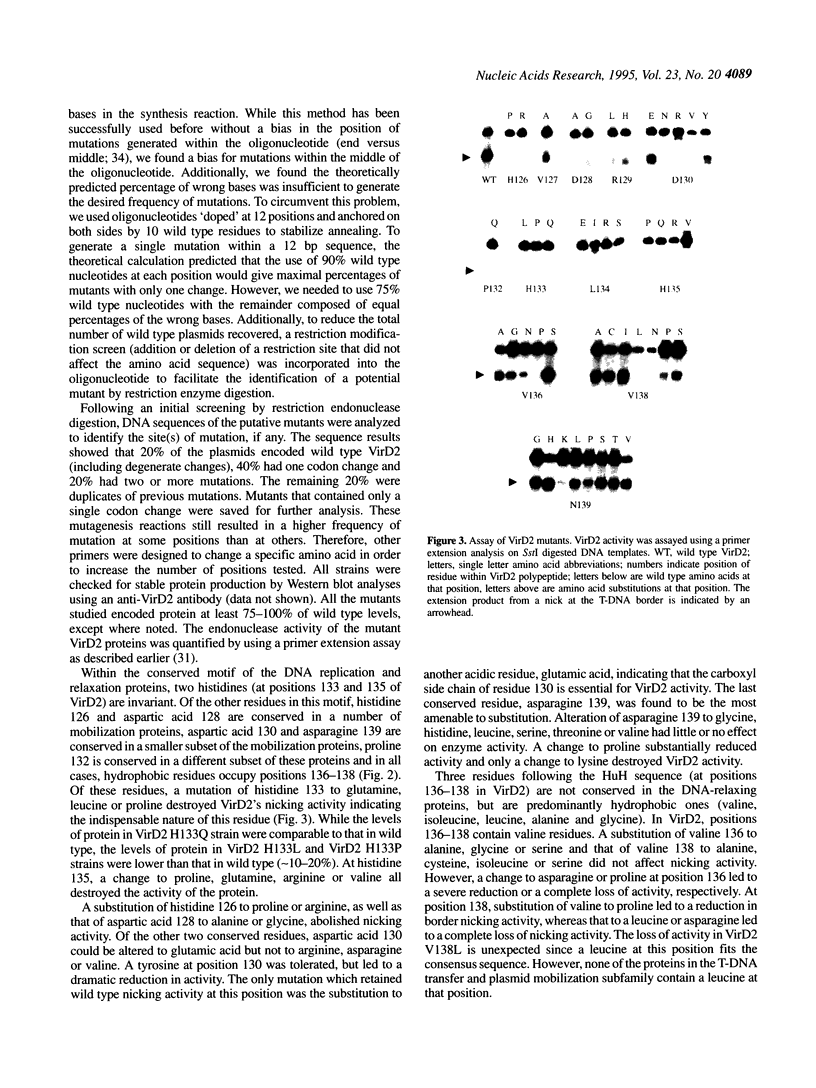
The VirD2 polypeptide from Agrobacterium tumefaciens, in the presence of VirD1, introduces a site- and strand-specific nick at the T-DNA borders. A similar reaction at the origin of transfer (oriT) of plasmids is essential for plasmid transfer by bacterial conjugation. A comparison of protein sequences of VirD2 and its functional homologs in bacterial conjugation and in rolling circle replication revealed that they share a conserved 14 residue segment, HxDxxx(P/u)HuHuuux [residues 126-139 of VirD2; Ilyina, T.V. and Koonin, E.V. (1992) Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 3279-3285]. A mutational approach was used to test the role of these residues in the endonuclease activity of VirD2. The results demonstrated that the two invariant histidine residues (H133 and H135) are essential for activity. Mutations at three sites, histidine 126, aspartic acid 128 and aspartic acid 130, that are conserved in a subfamily of the plasmid mobilization proteins, led to the loss of VirD2 activity. Aspartic acid at position 130, could be substituted with glutamic acid and to a much lesser extent, with tyrosine. In contrast, another conserved residue, asparagine 139, tolerated many different amino acid substitutions. The non-conserved residues, arginine 129, proline 132 and leucine 134, were also found to be important for function. Isolation of null mutations that map throughout this conserved domain confirm the hypothesis that this region is essential for function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. A sequence motif in many polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9909–9916. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijersbergen A., Dulk-Ras A. D., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Conjugative Transfer by the Virulence System of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1324–1327. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5061.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti P. Geometry of interaction of metal ions with histidine residues in protein structures. Protein Eng. 1990 Oct;4(1):57–63. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang L. W., Kovari I., Howe M. M. Mutagenic oligonucleotide-directed PCR amplification (Mod-PCR): an efficient method for generating random base substitution mutations in a DNA sequence element. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 Feb;2(3):210–217. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citovsky V., Wong M. L., Zambryski P. Cooperative interaction of Agrobacterium VirE2 protein with single-stranded DNA: implications for the T-DNA transfer process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Ziegelin G., Kröger M., Lanka E. Conjugative transfer of promiscuous IncP plasmids: interaction of plasmid-encoded products with the transfer origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1771–1775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghai J., Das A. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid encodes a DNA-relaxing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3109–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. S., Martin A. C., Cheetham J. C., Rees A. R. The prediction and characterization of metal binding sites in proteins. Protein Eng. 1993 Jan;6(1):29–35. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermes J. D., Parekh S. M., Blacklow S. C., Köster H., Knowles J. R. A reliable method for random mutagenesis: the generation of mutant libraries using spiked oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers. Gene. 1989 Dec 7;84(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella A., Chen Z. M., Van Montagu M., Wang K. VirD proteins of Agrobacterium tumefaciens are required for the formation of a covalent DNA--protein complex at the 5' terminus of T-strand molecules. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4055–4062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., Schilperoort R. A. Agrobacterium and plant genetic engineering. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):15–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00015604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyina T. V., Koonin E. V. Conserved sequence motifs in the initiator proteins for rolling circle DNA replication encoded by diverse replicons from eubacteria, eucaryotes and archaebacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3279–3285. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper F., Koncz C., Schell J., Steinbiss H. H. Agrobacterium T-strand production in vitro: sequence-specific cleavage and 5' protection of single-stranded DNA templates by purified VirD2 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaswal R. K., Veluthambi K., Gelvin S. B., Slightom J. L. Double-stranded cleavage of T-DNA and generation of single-stranded T-DNA molecules in Escherichia coli by a virD-encoded border-specific endonuclease from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5035–5045. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5035-5045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koukolíková-Nicola Z., Raineri D., Stephens K., Ramos C., Tinland B., Nester E. W., Hohn B. Genetic analysis of the virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a search for functions involved in transport of T-DNA into the plant cell nucleus and in T-DNA integration. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):723–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.723-731.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Relationship of DNA-transfer-systems: essential transfer factors of plasmids RP4, Ti and F share common sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):6099–6100. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.6099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Kado C. I. The virD4 gene is required for virulence while virD3 and orf5 are not required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):803–812. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Balzer D., Kruft V., Lurz R., Lanka E. In vitro assembly of relaxosomes at the transfer origin of plasmid RP4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6555–6559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Common sequence motifs in DNA relaxases and nick regions from a variety of DNA transfer systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3455–3455. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Schröder W., Lanka E. Concerted action of three distinct domains in the DNA cleaving-joining reaction catalyzed by relaxase (TraI) of conjugative plasmid RP4. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2782–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansegrau W., Schröder W., Lanka E. Relaxase (TraI) of IncP alpha plasmid RP4 catalyzes a site-specific cleaving-joining reaction of single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2925–2929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S. G., Yanofsky M. F., Nester E. W. Molecular characterization of the virD operon from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7503–7517. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheiffele P., Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Initiation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens T-DNA processing. Purified proteins VirD1 and VirD2 catalyze site- and strand-specific cleavage of superhelical T-border DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):1269–1276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen P., Pazour G. J., Anderson D., Das A. Cooperative binding of Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirE2 protein to single-stranded DNA. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2573–2580. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2573-2580.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., Zambryski P. Activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression generates multiple single-stranded T-strand molecules from the pTiA6 T-region: requirement for 5' virD gene products. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):857–863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A. M., Das A. Mutational analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens pTiA6 virD1: identification of functionally important residues. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jun;12(5):811–817. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A. M., Das A. Mutational analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virD2: tyrosine 29 is essential for endonuclease activity. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):303–308. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.303-308.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A. M., Das A. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virD3 gene is not essential for tumorigenicity on plants. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5161–5164. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5161-5164.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters V. L., Guiney D. G. Processes at the nick region link conjugation, T-DNA transfer and rolling circle replication. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1123–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters V. L., Hirata K. H., Pansegrau W., Lanka E., Guiney D. G. Sequence identity in the nick regions of IncP plasmid transfer origins and T-DNA borders of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1456–1460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav N. S., Vanderleyden J., Bennett D. R., Barnes W. M., Chilton M. D. Short direct repeats flank the T-DNA on a nopaline Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Porter S. G., Young C., Albright L. M., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes a site-specific endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90604-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Nester E. W. Association of the virD2 protein with the 5' end of T strands in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3367–3374. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3367-3374.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P. Basic processes underlying Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer to plant cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]