Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States. CRC is initiated by mutations of the tumor suppressor gene, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) or β-catenin gene. These mutations stabilize β-catenin and constitutively activate Wnt/β-catenin target genes, such as c-Myc and Cyclin D1, ultimately leading to cancer. Naturally occurring stilbene derivatives, resveratrol and pterostilbene, inhibit Wnt signaling and repress CRC cell proliferation but are ineffective at concentrations lower than 10 µM. To understand the structure/activity relationship within these stilbene derivatives and to develop more efficacious Wnt inhibitors than these natural products, we synthesized and evaluated a panel of fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes. Among this panel, (E)-4-(2,6-difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4r) inhibits Wnt signaling at nanomolar levels and inhibits the growth of human CRC cell xenografts in athymic nude mice at a dosage of 20mg/kg. These fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes appear to inhibit Wnt signaling downstream of β-catenin, probably at the transcriptional level.
Keywords: resveratrol; pterostilbene; N,N-dialkylaminostyrene; Wnt signaling; beta-catenin; colorectal cancer
Introduction
Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays an important role in development and tumorigenesis1, 2, and the deregulation of Wnt signaling results in the formation of tumors. More than 90% of CRCs contain a mutation in APC or β-catenin3–5, and these mutations stabilize β-catenin and activate Wnt signaling. Cells containing these mutations constitutively activate Wnt signaling and undergo strong proliferation that ultimately leads to cancer3. Intercepting and blocking the Wnt pathway at various points in the signaling cascade is an attractive approach for CRC chemoprevention and therapeutics.
In normal cells, β-catenin degradation is under the control of Wnt signaling. In the absence of Wnt stimulation, the Axin complex, consisting of GSK-3, CKIα, and the tumor suppressor proteins Axin and APC, phosphorylates β-catenin. Recognition of the phosphorylated β-catenin by the ubiquitin ligase β-Trcp triggers degradation by the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway 6, 7. Without β-catenin, the TCF/LEF-family of transcription factors recruits the co-repressors Groucho and CtBP, repressing the expression of Wnt target genes1. When Wnt protein binds its receptor Frizzled and co-receptor LRP5/6, Wnt stimulates LRP5/6 phosphorylation in part through the recruitment of the cytoplasmic protein Disheveled8. Phosphorylated LRP5/6 then recruits Axin to the cell membrane, disrupts the Axin complex, and thus stabilizes β-catenin8, 9. Accumulated β-catenin subsequently enters the nucleus, binds TCF/LEF, and recruits transcriptional co-activators such as Bcl9, Pygopus and CBP/p300 in order to activate downstream target genes, such as Cyclin D1, c-Myc, survivin and Axin21, 3.
In CRCs, β-catenin is stabilized by mutations of APC or β-catenin. APC truncations inhibit β-catenin phosphorylation, ubiquitination and degradation 4, 5, 10. β-catenin mutations at N-terminal serine/threonine residues prevent β-catenin phosphorylation, and thus prevent its ubiquitination and degradation7. These mutations decouple the regulation of β-catenin levels from upstream signaling events, and upstream inhibitors cannot efficiently inhibit Wnt signaling in CRCs. Thus, useful agents for CRC prevention and treatment must block the function of β-catenin in the nucleus through one of several mechanisms including blockade of nuclear translocation of β-catenin, assembly of the transcription complex and/or promoter-specific histone modification.
Recently, several Wnt inhibitors were identified in high-throughput screening11, 12 that target the upstream signaling of β-catenin in order to promote β-catenin degradation. Although these agents efficiently inhibit Wnt signaling in normal cells and some APC-mutated CRC cells, they may not be effective in CRC cells containing β-catenin mutations13. Several other Wnt inhibitors have also been reported; however, side effects limit their potential utility in humans 14, 15. Natural products found in foods are potentially ideal chemopreventive and therapeutic agents for CRCs if they possess sufficient potency and minimal toxicity, and at the very least, natural products are a time-honored starting point for the synthesis of new pharmaceutical agents.
Resveratrol (trans- or (E)-3, 5, 4’-trihydroxystilbene) is a phytoalexin produced in plants and popularized as a beneficial ingredient in red wine16. Resveratrol and other stilbene derivatives, including pterostilbene, a resveratrol analog found in blueberries, exhibit anti-cancer activity17, 18. Several studies have indicated that 10–100µM resveratrol inhibit Wnt signaling19–21, which suggests that inhibition of Wnt signaling may be important in mediating the chemopreventive function of these naturally occurring stilbenes. In this study, we designed and synthesized a panel of novel resveratrol analogs in order to identify more potent agents for Wnt pathway inhibition and CRC repression.
Results
Natural stilbene analogs resveratrol and pterostilbene inhibit Wnt signaling
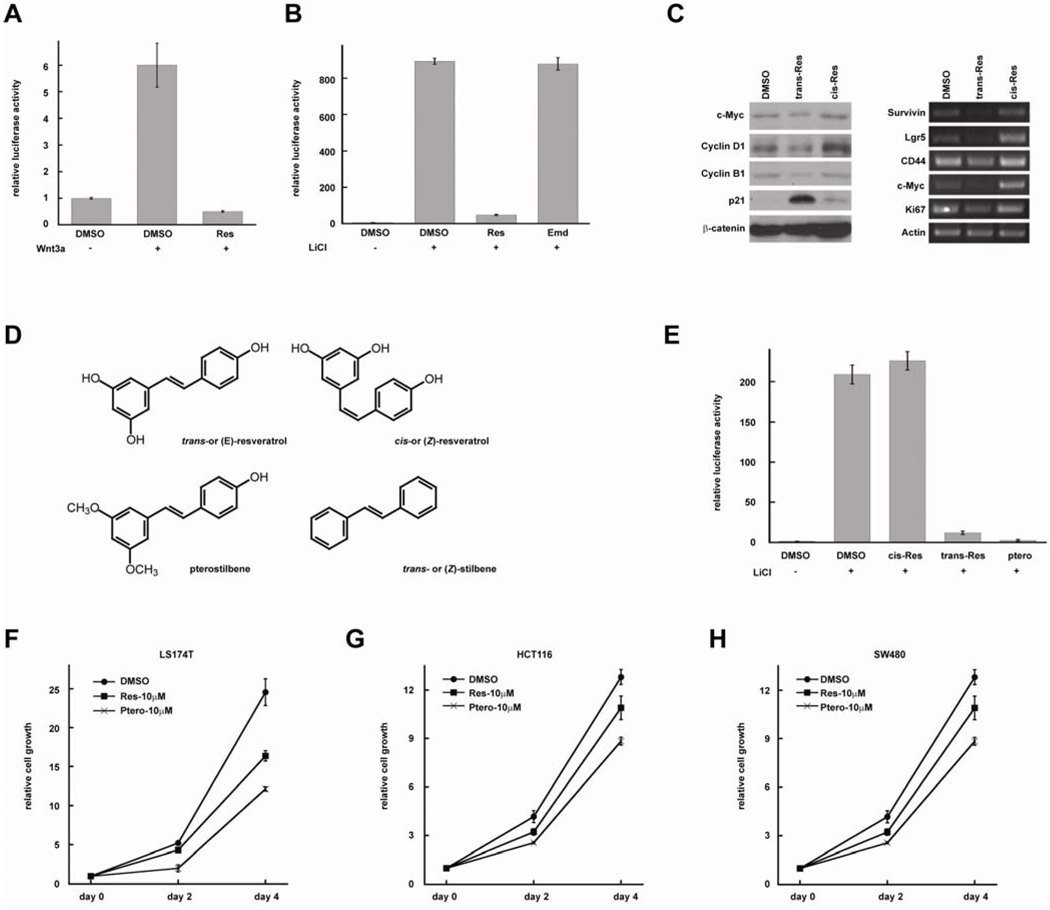
To identify Wnt pathway inhibitors for CRC prevention and treatment, we screened a number of anti-cancer agents from plants using TopFlash reporter assay. The TopFlash reporter was transfected into HEK293T cells, and the cells were treated with Wnt3A-conditioned medium in order to activate the luciferase reporter (Figure 1A). Resveratrol (100 µM) significantly inhibited Wnt-induced luciferase activity. To determine if resveratrol regulates β-catenin degradation, we treated the cells with 25mM LiCl which inhibits GSK-3 and stabilizes β-catenin. In this assay, LiCl activated the reporter more strongly than Wnt3A conditioned medium (Figure 1B). We found that resveratrol strongly inhibited LiCl-induced Wnt signaling, suggesting that resveratrol inhibits Wnt signaling by regulating β-catenin activity but not its degradation. Emodin is an anti-cancer agent from plants22; it exists in many unpurified resveratrol products. We found that Emodin had no effect on Wnt signaling (Figure 1B).
Figure 1. Resveratrol and pterostilbene inhibit Wnt signaling and repress proliferation of CRC cells.
(A) Resveratrol (100µM) inhibits Wnt-induced TopFlash reporter activity. (B) Resveratrol (100µM) inhibits LiCl-induced TopFlash reporter activity. (C) Resveratrol (100µM) inhibits the expression of endogenous Wnt targets in CRC cells. Left panel: protein levels. Right panel: mRNA levels. (D) Structures of trans-resveratrol, cis-resveratrol, pterostilbene and stilbene. (E) Trans-resveratrol and pterostilbene, but not cis-resveratrol inhibits Wnt signaling at 100µM. (F, G, H) Resveratrol and Pterostilbene inhibit the proliferation of CRC cell lines LS174, HCT116 and SW480.
To confirm these results, we analyzed β-catenin target genes in LS174 CRC cells by Western blot and RT-PCR (Figure 1C). We found that the protein levels of c-Myc and Cyclin D1, which are β-catenin targets, are reduced by resveratrol but not its isomer, cis- or (Z)-resveratrol (Figure 1C). Cyclin B1 levels were decreased, whereas p21WAF1/CIP1 levels increased, consistent with the fact that p21WAF1/CIP1 expression is repressed by c-Myc. β-catenin levels were not affected by resveratrol. Next, we analyzed the mRNA levels of β-catenin target genes using RT-PCR. Expression of survivin, Lgr5, CD44, and c-Myc were decreased in resveratrol-treated cells. The cell proliferation marker, Ki67, also decreased. These results confirmed that resveratrol inhibits endogenous Wnt target genes in CRC cells.
Many stilbene derivatives also exhibit anti-cancer activity. To understand the structure/activity relationship of these compounds, we tested several resveratrol analogs (Figure 1D). We found that pterostilbene also inhibits Wnt signaling (Figure 1E). To study the effects of resveratrol and pterostilbene on cell growth, we treated LS174 CRC cells with resveratrol and pterostilbene for 2d and 4d. We found that both compounds inhibited cell proliferation (Figure 1F). Similar results were observed with other CRC lines (Figure 1G, H). Pterostilbene was more active than resveratrol in these assays, suggesting that it is possible to identify better resveratrol analogs for Wnt inhibition and CRC repression
Fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes are potent Wnt inhibitors
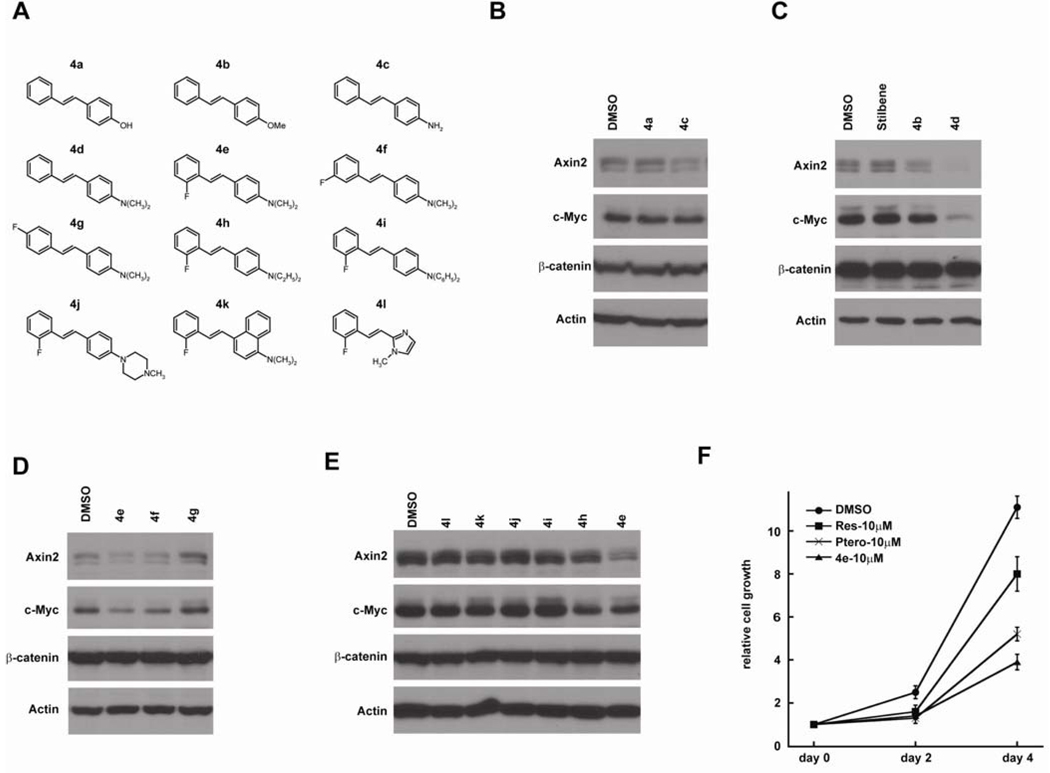
Using resveratrol and pterostilbene as lead structures, we designed and synthesized a panel of stilbene analogs (Figures 2, 3A and 4A). We first explored various monosubstituted hydroxyl, alkoxy, amino and N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes using Western blot assay (Figure 3B, 3C), and of these substituents, (E)-4-styryl-N,N-dimethylaniline (4d) at 30 µM with an N,N-dimethylamino substituent strongly repressed Wnt target genes, Axin2 and c-Myc, in CRC cells (Figure 3C). However, the solubility of 4d was poor and it was not effective below 10 µM concentrations (data not shown). To improve its solubility and activity, we modified 4d with 2’-fluoro 4e, 3’-fluoro 4f and 4’-fluoro 4g substituents (Figure 3D). Although both 4e and 4f had promising activity at 10 µM, (E)-4-(2-fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4e) was best among all of the monofluoro-substituted compounds. We next examined modifications of the N,N-dimethylamino group within 4e, and found that the N,N-diethylamino group in (E)-4-(2-fluorostyryl)-N,N-diethylaniline (4h) is also active at 10µM but not as potent as 4e) and the N,N-diphenylamino group in 4i was inactive (Figure 3E). These analogs had no effects on β-catenin levels, further indicating that they affect β-catenin activity but not stability. We compared the effects of 4e, resveratrol, and pterostilbene on CRC cell growth, and found that 4e is a much better inhibitor in the cell proliferation assay (Figure 3F).
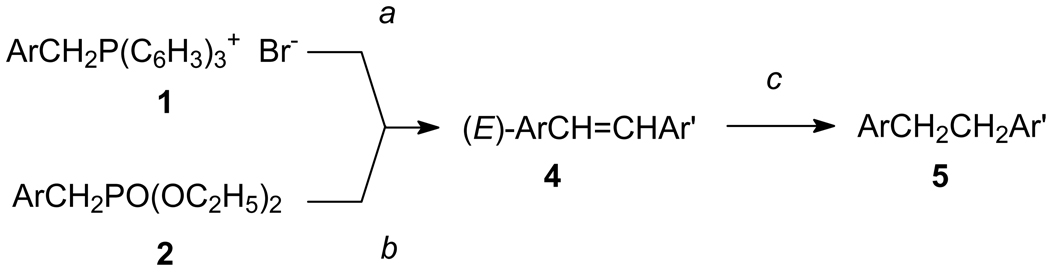
Figure 2. Synthesis of fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes.
Reagents: a, (1) n-BuLi, THF; (2) ArCHO 3; b, (1) NaH, DMF; (2) ArCHO 3; c, H2, Pd-C, THF. Either Wittig or Wadsworth-Emmons reactions using phosphonium salts 1 or diethyl phosphonates 2, respectively, with aldehydes 3 provided the (E)-stilbenes 4 in good yield. The phosphonium salts 1 were prepared from commercial samples of the corresponding benzyl bromides and triphenylphosphine, and the diethyl phosphonates 2 were prepared from the corresponding benzyl bromides and triethyl phosphite using the Arbuzov reaction according to standard literature procedures. The hydrogenation of 4n using 10% Pd-C provided 4-(2,6-difluorophenethyl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (5r). Compounds were characterized fully and purity (> 95% established through combustion analyses.
Figure 3. Fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes inhibit Wnt signaling in CRC cells.
(A) Chemical structure of synthesized resveratrol analogs. (B) 4-amino-stilbene (4c) represses Wnt target genes at 30µM. (C) 4-Styryl-N,N-dimethylaniline (4d) is more active than 4-Methoxystilbene (4b) at 30µM. (D) 4-(2-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4e) and 4-(3-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4f) represses Wnt target genes at 10µM. (E) The dimethylaminophenyl group within 4e is critical for its activity. (F) 4e is more potent than resveratrol and pterostilbene in inhibiting the proliferation of CRC cells.
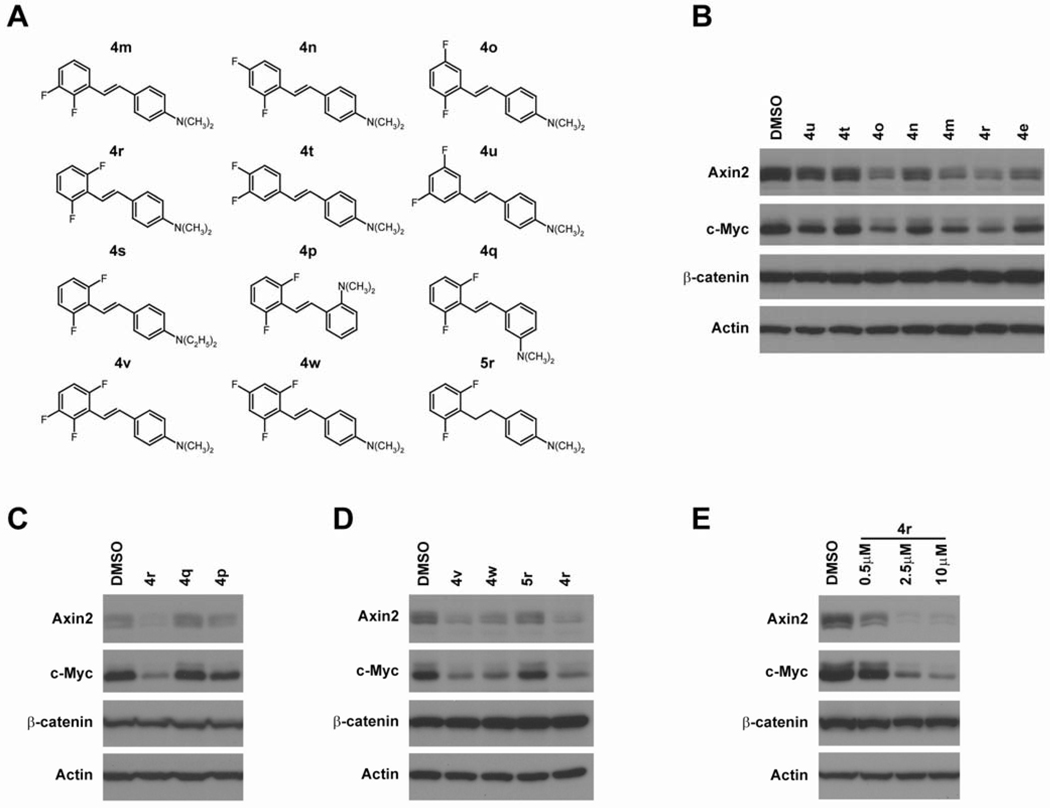
Figure 4. 4-(2,6-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4r) is a potent Wnt inhibitor.
(A) Chemical structures of difluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes. (B) Difluorinated N,N-dimethylaminostilbenes, 4o, 4m and 4r, repress Wnt target genes at 10 µM. (C) The ortho- and meta-isomers of N,N-dimethylamino analogs (4p and 4q) are not as active as the para-isomer (4r). (D) Trifluorinated N,N-dimethylaminostilbenes (4v and 4w) are active Wnt inhibitors but have no particular advantage over 4r. The carbon-carbon double bond in 4r is necessary for its activity. (E) 4r represses Wnt target genes at 0.5 µM.
Based on the improved activity seen in 4e relative to 4d, we synthesized difluorinated N,N-dimethylaminostilbenes in which at least one of the fluorine substituents is in the 2’- or 3’-position (Figure 4A). We found that the compounds with a 2’-fluoro and another fluoro ortho or meta to the double bond (4m, 4o and 4r) are more active than 4e (Figure 4B). The (E)-4-(2,6-difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4r) had the best activity. The ortho- and meta-N,N-dimethylamino analogs of 4r (i.e., 4p and 4q) are not as active as 4r, indicating that the para-dimethylamino in 4r is important for its activity (Figure 4C). Based on the structure of 4r, we also made two trifluorinated dimethylaminostilbenes 4v and 4w in which two of the fluorine substituents are in the 2’- and 6’-positions (Figure 4D). Although 4v and 4w were active at 10 µM, they showed no significant improvements over 4r. When the stilbene carbon-carbon double bond in 4r was reduced to a saturated, single bond in the 1,2-diarylethane 5r, the activity was lost, suggesting that the double bond was necessary for biological activity (Figure 4D). We treated LS174 CRC cells with different dosages of 4r and found that 4r significantly inhibited Wnt target genes at 2.5 µM and is even active at 0.5 µM (Figure 4E).
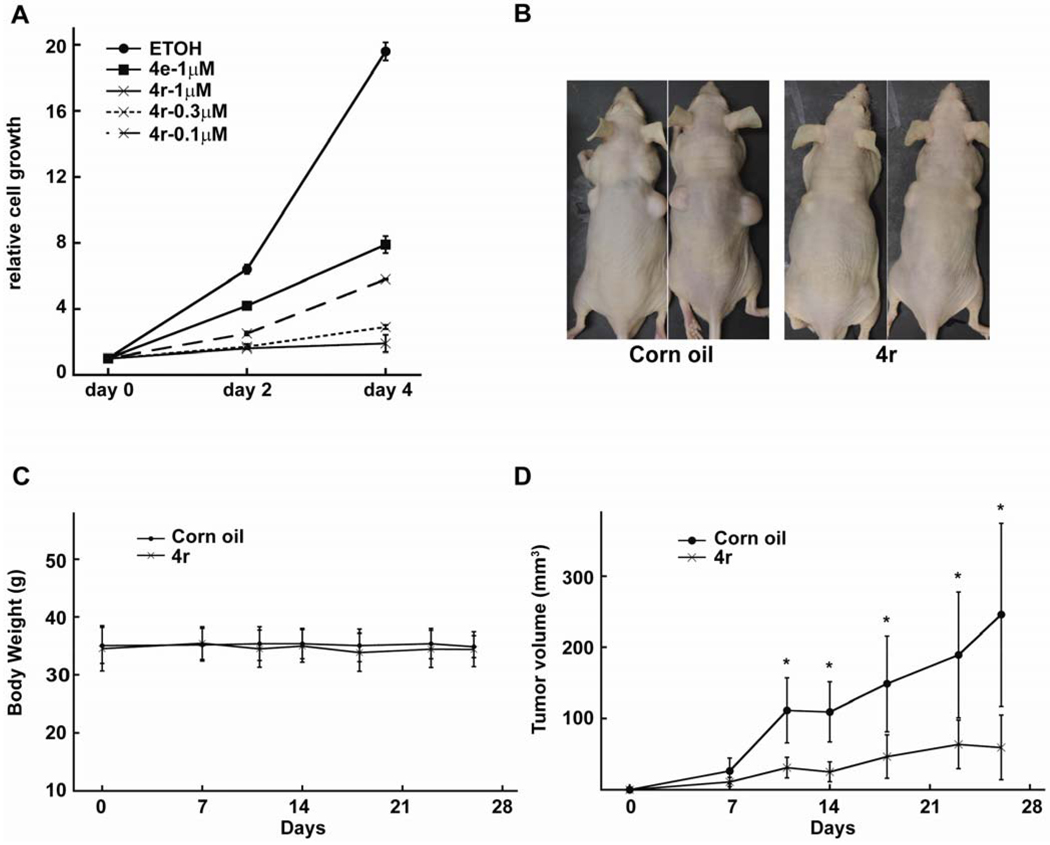
Fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes inhibit CRC in vitro and in vivo. We analyzed the effects of these novel agents on CRC cells growth. Consistent with the Western blot results, stilbene 4r was more potent than 4e in cell proliferation assay; it inhibited LS174 cell proliferation at nanomolar concentrations (Figure 5A). To test the effects of 4r on tumor growth in vivo, we injected LS174 cells subcutaneously into the flanks of athymic nude mice. The mice were randomized into two groups. One group of mice were treated with 4r (20mg/kg/day) dissolved in corn oil by intraperitoneal (ip) injection. The control mice were treated with same volume of corn oil (50 µL) by ip injection. The mice were weighted and tumors measured twice weekly. The 4r treated mice and control mice have no significant difference in body weight within one month (Figure 5B and 5C), suggesting that 4r has no significant toxic effect at this dosage. However, the growth of tumor xenografts were significantly inhibited by 4r treatment (Figure 5D).
Figure 5. Effects of fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes on CRC cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo.
(A) 4r inhibits CRC cell proliferation at 0.1 µM. (B) LS174 CRC cells (2×106) were injected subcutaneously into both flanks of athymic nude mice. (B) Representative nude mice treated with 4r or corn oil. (C) Body weights of nude mice treated with 4r and corn oil. (D) The tumor sizes were measured twice a week. The tumor volumes were calculated using the formula: V=1/2LW2 (mm3). The xenograft tumors treated with 4r grew to a lesser extent than the xenograft tumors treated with just corn oil. Statistical significance was calculated by the student’s t test (*p<0.05).
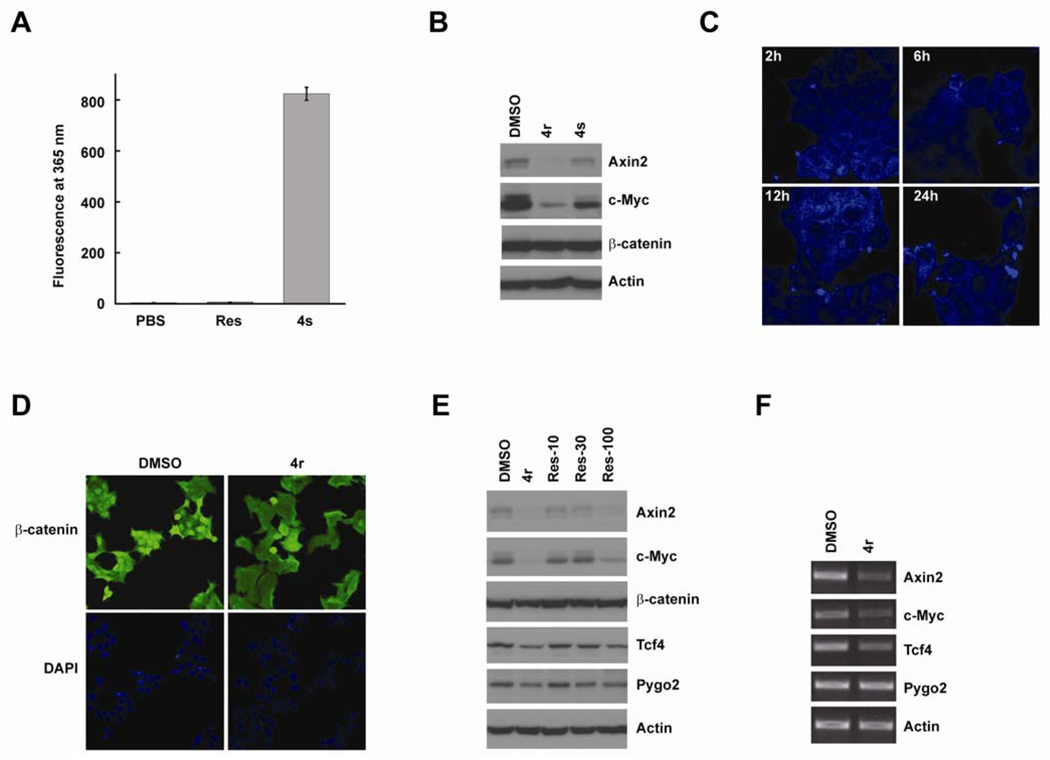
Fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes inhibit Wnt signaling in the nucleus. The stilbene analogs and in particular, (E)-4-(2,6-difluorostyryl)-N,N-diethylaniline (4s) (Figure 4A) exhibit strong fluorescence at 365 nm (Figures 6A), albeit 4s is slightly less active than 4r (Figure B). Nevertheless, 4s lends itself well to a mechanistic study of the site of action of these compounds. We treated LS174 cells with 10 µM of 4s for 2h, 6h, 12h, and 24h. The cells were fixed and analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. We found that 4s was localized throughout the nucleus and cytoplasm at 2h. After 12h, the nuclear levels of 4s were decreased (Figure 6C). To study the effects of these compounds on β-catenin localization, we treated LS174 cells with 10 µM of 4r for 24h. The cells were fixed and β-catenin localization analyzed by immunofluorescence (Figure 6D). The nuclear β-catenin levels were decreased in 4r treated cells compared with the DMSO-treated cells. However, significant levels of nuclear β-catenin can still be detected in the nucleus of 4r treated cells, suggesting that 4r may also inhibit Wnt signaling though mechanisms other than regulating β-catenin level and localization. We analyzed the downstream factors of β-catenin, and found that the protein levels of TCF4 and pygopus2 were reduced by 4r and resveratrol in CRC cells (Figure 6E). RT-PCR assay suggested that 4r strongly inhibited the transcription of Wnt target genes. It also inhibited TCF4 genes but had no significant effects on pygopus2 genes, which suggested that these new fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes inhibited Wnt/mediated transcription at multiple levels (Figure 6E).
Figure 6. Potential mechanisms of fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes in Wnt inhibition.
(A) 4s has strong fluorescence at 365 nM (detected by Promega GloMax® Luminometer). (B) 4s is an active Wnt inhibitor. (C) 4s was incubated with LS174 CRC cells for 2h, 6h, 12h, and 24h. The localization of 4s was analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of β-catenin in LS174 cells treated with DMSO or 4r. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. (F) 4r (10 µM) and resveratrol (100 µM) reduced the protein levels of Wnt/ β-catenin targets in LS174 cells. 4r and resveratrol also reduced the protein levels of TCF4 and Pygopus2 but not β-catenin. (G) 4r repressed the transcription of Wnt target genes.
Discussion
The Wnt pathway is an important drug target for human cancers, particularly CRC. β-catenin levels are significantly increased in CRC cells because of the mutation of APC or β-catenin. Several small molecular inhibitors are reported to promote β-catenin degradation by inhibiting tankyrase11, 12. Although these inhibitors are useful in studying Wnt signaling in normal cells, they are less effective in CRC cells contain β-catenin mutations. Moreover, these inhibitors have not been tested in tumor models in vivo. Their potential toxicity remains an indeterminate concern if these compounds were used in clinical applications. For example, tankyrase is essential for embryonic development, and deficiency in both tankyrase 1 and 2 resulted in embryonic lethality by day 1023. The tankyrase inhibitors induced damage to intestinal tract, although this side effect is reversible, probably depend on the dosage15. Many anti-cancer agents derived from plants, including resveratrol, have been suggested to inhibit Wnt signaling, but the mechanisms are not clear21, 24–27. Resveratrol has been suggested to induce β-catenin degradation and inhibits its nuclear localization in CRC cells21, but increase β-catenin stability and nuclear accumulation in multipotent mesenchymal cells28. It has been suggested that resveratrol inhibits GSK-3 at low concentration and activates GSK-3 at high concentration in endothelial cells, it is possible that resveratrol regulates Wnt pathway depend on cell context29. In this study, we found that resveratrol and the more potent pterostilbene inhibited Wnt signaling downstream of β-catenin and inhibited the proliferation of CRC cells (Figure 1), but both agents are only active at 10–100 µM concentrations. We have synthesized and screened many analogs and identified several fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes as new and potent Wnt inhibitors.
Initial findings that resveratrol and other hydroxyl- or methoxy-substituted stilbenes produced greater than 50% Wnt inhibition at concentrations of 10–100 µM (data not shown) using a luciferase-based assay led to a search for modified stilbenes with improved potency. Because the luciferase-based assay was prone to false positives, an unambiguous but more laborious assay involving Western blots to measure Wnt target protein levels was employed. With this assay system, a broad spectrum of stilbenes were screened and the fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes 4 proved most promising. Efforts to replace one of the aryl rings with various heterocyclic and polyaromatic systems or to modify the N,N-dimethylamino substituent with other alkyl or aryl groups led to a loss of activity. The inclusion of fluorine substituents, particularly a fluorine ortho to the stilbene double bond, improved not only the solubility of the stilbenes but also led finally to (E)-4-(2,6-difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4r) as the most active compound in this series.
The stilbene 4r was 10- to 100-fold more potent that resveratrol and pterostilbene in Western blot and cell proliferation assays (Figure 4). Stilbene 4r also repressed the growth of LS174 tumor xenografts, suggesting that this agent inhibits Wnt signaling in vivo (Figure 5). LS174 and HCT116 cells contain a β-catenin mutation (Serine 45 deletion), and this mutation prevents β-catenin phosphorylation by CKIα and GSK-3, thus preventing β-catenin degradation. Upstream signals in Wnt signaling can no longer regulate β-catenin levels in these cells and agents targeting upstream of signaling events are ineffective (data not show). Since these new analogs inhibits Wnt signaling in LS174 and HCT116 cells, they must inhibit Wnt signaling downstream of β-catenin. This is consistent with the fact that these agents did not not reduce β-catenin levels, and that they inhibited both Wnt-induced and LiCl-induced reporter activities. Since Lgr5 and several other Wnt targets are markers for intestinal stem cell and CRC stem cells 30; it is possible that these agents inhibit cancer stem cells. Other than CRCs, Wnt signaling is required for tumorigeneis of many other types of cancer. For example, β-catenin mutations are frequent in hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatoblastoma3, 5. These fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes 4 that inhibit Wnt targets in CRC may also inhibit other human cancers.
Using fluorescence techniques, aided by the fact that these fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes themselves were fluorescent, we found that these agents are cell permeable and localize in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. After 12h, the nuclear levels of these agents are decreased (Figure 6), probably by a drug-exporting mechanism31. After 4r treatment, the β-catenin levels in the cytoplasmic and member factions were slightly increased, but significant amount of β-catenin were still localized in the nucleus. The strong inhibition displayed by these agents on β-catenin targets led to the hypothesis that these agents may inhibit Wnt signaling other than at β-catenin levels and localization. We analyzed the nuclear factors of the Wnt pathway and found that the protein levels of TCF4 and pygopus2 were decreased. Both TCF4 and pygopus2 are required for Wnt-mediated transcription 32, indicating that these agents inhibit the transcriptional initiation complex in the Wnt signaling. The mRNA levels of Wnt target genes, Axin2 and c-Myc, were significantly decreased (Figure 6E). TCF4 is a potential Wnt target gene 33. The transcription of TCF4 but not pygopus2 was inhibited by 4r, suggesting that these fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes 4 may regulate β-catenin activity through multiple mechanisms. Studies are underway to determine the direct target or targets of these promising new agents. In summary, we have identified fluorinated N,N-dialkylaminostilbenes as a family of new and potent stilbene analogs that inhibit Wnt pathway and CRC. This work will lead to further exploration of potential novel mechanisms and novel applications of these agents in human diseases.
Experimental Procedures
Chemistry
Chemicals were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, MP Biomedical (4c) or TCI (4d) or were synthesized according to literature procedures. Solvents were used from commercial vendors without further purification unless otherwise noted. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra were determined in acetone-d6 using a Varian instrument (1H, 400 MHz; 13C, 100 MHz unless otherwise noted). LRMS electron-impact (EI) ionization mass spectra were recorded at 70eV on a ThermoFinnigan PolarisQ (ion trap mass spectrometer). Samples were introduced via a heatable direct probe inlet. Purity of compounds was > 95% as established by combustion analyses. Elemental analyses were determined by Atlantic Microlabs, Inc., Norcross, GA. Compounds were chromatographed on preparative layer Merck silica gel F254 unless otherwise indicated.
General Procedure A
To 1.5 mmol of triphenylphosphonium bromide 1 suspended in 4 mL of anhydrous THF at −78°C was added 2.25 mmol (1.5 eq) of n-BuLi (1.6M in hexane). The mixture was allowed to warm to 25°C for 30 min, and 2.25 mmol of aldehyde 3 in 1 mL of anhydrous THF was added. The mixture was stirred for 24 h, diluted with CH2Cl2, washed with saturated NH4Cl solution, and dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The product was purified by chromatography and/or recrystallization as noted for individual stilbenes 4 listed below.
General Procedure B
To a solution of 1.5 mmol of diethyl phosphonate 2 in 4 mL of anhydrous DMF at 0°C was added 2.25 mmol (1.5 eq) of NaH (washed with hexanes to remove oil). The mixture was stirred for 20 min, and 1.5 mmol of aldehyde 3 in 1 mL of anhydrous DMF was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred 24 h at 25°C, quenched with ice, extracted with CH2Cl2, and dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The product was purified by chromatography and/or recrystallization as noted for individual stilbenes 4 listed below.
(E)-4-Hydroxystilbene (4a)
To 210 mg (1 mmol) of (E)-4-methoxystilbene (4b) in 7 mL of CH2Cl2 was added 1.28 mL of 1M BBr3 (1.3 mmol) in dichloromethane at −10 °C. The mixture was stirred for 4 h at −5°C and quenched by pouring into cold water. The product was extracted with CH2Cl2, dried over anhydrous MgSO4 and chromatographed using 1:10 CH3OH:CH2Cl2 to afford 85 mg (43%) of 4a. Mp 184–185°C. (lit.34 186 °C).
(E)-4-Methoxystilbene (4b)
Procedure B. Yield 87%. Colorless crystals: mp 136–137°C. (lit.34 136–138 °C).
(E)-4-(2-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4e)
Procedure B. Yield 84%. Light yellow crystals from acetonitrile. Mp 124–126°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.73-7.68 (m, 1H), 7.46 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.26-7.08 (m, 3H), 7.22 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.09 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 6.75 (d, 2H, J=9.2Hz), 2.98 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 160.18 (d, J=245.9Hz), 150.85, 131.67 (d, J=4.6Hz), 128.08 (d, J=8.4Hz), 127.93, 126.8 (d, J=4.5Hz), 126.14 (d, J=12.1Hz), 125.46, 124.59 (d, J=3.1Hz), 115.64 (d, J=22.0Hz), 115.49 (d, J=4.6Hz), 112.44, 39.69. MS: m/z (%) 241 (100), 240 (74), 225 (32), 197 (20), 196 (20), 177 (18), 176 (13). Anal. Calcd for C16H16FN: C, 79.64; H, 6.68. Found: C, 79.77; H, 6.80.
(E)-4-(3-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4f)
Procedure B. Yield 65%. Light yellow crystals from acetonitrile. Mp 147–148°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.42 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 7.35-7.25 (m, 3H), 7.17 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 6.96 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 6.93-6.88 (m, 1H), 6.72 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 2.95 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 163.47 (d, J=241.4Hz), 150.82, 141.36 (d, J=7.6Hz), 130.66, 130.42 (d, J=8.4Hz), 127.97, 125.22, 122.63 (d, J=2.2Hz), 122.24 (d, J=2.2Hz), 113.12 (d, J=21.3Hz), 112.43, 111.96 (d, J=22.0Hz), 39.69. MS: m/z (%) 241 (100), 240 (69), 225 (25), 197 (20), 196 (18), 177 (16), 176 (10). Anal. Calcd for C16H16FN: C, 79.64; H, 6.68. Found: C, 79.86; H, 6.67.
(E)-4-(4-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4g)
Procedure B. Yield 64%. Light yellow crystals from acetonitrile. Mp 197–198°C. [lit.35 194–195°C]. Anal. Calcd for C16H16FN: C, 79.64; H, 6.68. Found: C, 79.85; H, 6.64.
(E)-4-(2-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-diethylaniline (4h)
Procedure B. Yield 51%. Light yellow crystals from hexane. Mp 78–79°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.69-7.65 (m, 1H), 7.40 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.24-7.07 (m, 3H), 7.20 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.04 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 6.71 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 3.42 (q, 4H, J=7.2Hz), 1.16 (t, 6H, J=7.2Hz). 13C NMR: δ 160.13 (d, J=242.2Hz), 148.04, 131.73 (d, J=4.5Hz), 128.24, 127.91 (d, J=7.6Hz), 126.70 (d, J=4.5Hz), 126.27 (d, J=11.4Hz), 124.57 (d, J=3.8Hz), 124.49, 115.62 (d, J=22.0Hz), 114.82 (d, J=3.8Hz), 111.76, 44.19, 12.21. MS: m/z (%) 269 (34), 255 (19), 254 (100), 226 (22), 225 (20), 197 (16), 196 (17). Anal. Calcd for C18H20FN: C, 80.26; H, 7.48. Found: C, 80.07; H, 7.61.
(E)-4-(2-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-diphenylaniline (4i)
Procedure B. Yield 60%. Light yellow crystals from hexane. Mp 114–115°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.77-7.73 (m, 1H), 7.54 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 7.34-7.06 (m, 15H), 7.02 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz). 13C NMR: δ 160.39 (d, J=245.9Hz), 148.00, 147.73, 131.58, 130.87 (d, J=4.5Hz), 129.63, 128.90 (d, J=8.3Hz), 127.88, 127.23 (d, J=3.8Hz), 125.58 (d, J=12.0Hz), 124.75, 124.71, 123.53, 123.25, 118.78 (d, J=3.8Hz), 115.76 (d, J=22.0Hz). MS: m/z (%) 365 (100), 364 (12), 254 (13). Anal. Calcd for C26H20FN: C, 85.45; H, 5.52. Found: C, 85.59; H, 5.69.
(E)-1-(4-(2-Fluorostyryl)phenyl)-4-methylpiperazine (4j)
Procedure B. Yield 65%. Light yellow crystals from acetonitrile. Mp 142–144°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.72-7.69 (m, 1H), 7.48 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.28-7.09 (m, 3H), 7.24 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.13 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 6.96 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 3.22 (t, 4H, J=5.2Hz), 2.48 (t, 4H, J=5.2Hz), 2.54 (s, 3H). 13C NMR: δ 160.27 (d, J=245.2Hz), 151.59, 131.34 (d, J=5.3Hz), 128.42 (d, J=8.4Hz), 127.97, 127.81, 126.98 (d, J=3.8Hz), 125.90 (d, J=12.1Hz), 126.62 (d, J=3.8Hz), 116.85 (d, J=3.8Hz), 115.69 (d, J=22.0Hz), 115.46, 55.09, 48.34, 45.70. MS: m/z (%) 296 (100), 281 (42), 226 (24), 211 (46), 197 (28), 196 (42), 177 (28). Anal. Calcd for C19H21FN2: C, 77.00; H, 7.14. Found: C, 77.22; H, 7.49.
(E)-4-(2-Fluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylnaphthalen-1-amine (4k)
Procedure B. Yield 18%. Yellow crystals from hexane:Et2O. Mp 56–58°C. 1H NMR: δ 8.33-8.27 (m, 2H), 8.09 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.95-7.91 (m, 1H), 7.80 (d, 1H, J=8.0Hz), 7.58-7.52 (m, 2H), 7.36-7.15 (m, 4H), 7.28 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 2.90 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 160.49 (d, J=246.7Hz), 151.66, 132.85, 129.41, 129.10 (d, J=8.4Hz), 128.92, 128.38 (d, J=4.6Hz), 127.67 (d, J=3.8Hz), 126.27, 125.78 (d, J=12.2Hz), 125.17, 124.92, 124.74 (d, J=3.0Hz), 124.25, 124.03, 121.75 (d, J=3.8Hz), 115.78 (d, J=22.0Hz), 114.19, 44.62. MS: m/z (%) 291 (100), 290 (28), 276 (70), 261 (40), 247 (22), 246 (15). Anal. Calcd for C20H18FN: C, 82.45; H, 6.23. Found: C, 82.42; H, 6.22.
(E)-2-(4-(2-Fluorostyryl)phenyl)-1-methyl-1H-imidazole (4l)
Procedure B. Yield 47%. Colorless crystals from hexane. Mp 60–61°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.82-7.78 (m, 1H), 7.65 (d, 1H, J=16.0Hz), 7.35-7.29 (m, 1H), 7.26 (d, 1H, J=16.0Hz), 7.22-7.13 (m, 2H), 7.08 (d, 1H, J=1.2Hz), 6.96 (d, 1H, J=0.8Hz), 3.81 (s, 3H). 13C NMR: δ 160.65 (d, J=246.7Hz), 145.39, 129.53 (d, J=8.3Hz), 128.89, 127.66 (d, J=3.0Hz), 124.98 (d, J=11.4Hz), 124.71 (d, J=3.8Hz), 122.73 (d, J=3.8Hz), 122.18, 116.99 (d, J=5.3Hz), 115.83 (d, J=22.0Hz), 32.04. MS: m/z (%) 202 (17), 201 (59), 186 (20), 183 (100), 168 (25), 146 (16), 128 (17). Anal. Calcd for C12H11FN2: C, 71.27; H, 5.48. Found: C, 71.24; H, 5.61.
(E)-4-(2,3-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4m)
Procedure A. Yield 88%. Yellow crystals. Mp 132-133°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.50-7.47 (m, 1H), 7.45 (d, 2H, J=9.2Hz), 7.24 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.16-7.06 (m, 2H), 7.03 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 6.73 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 2.96 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 151.01 (dd, J=243.6Hz), 147.87 (dd, J=246.3Hz), 133.18 (d, J=5.3Hz), 128.69 (d, J=9.1Hz), 128.19, 124.95, 124.57 (d, J=7.6Hz), 124.53 (d, J=7.6Hz), 121.78 (t, J=3.0Hz), 114.65 (d, J=17.4Hz), 114.24 (t, J=3.8Hz), 112.37, 39.64. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (78), 243 (25), 214 (16), 195 (16). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.01; H, 5.71.
(E)-4-(2,4-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4n)
Procedure B. Yield 58%. Yellow crystals from acetonitrile. Mp 139–140°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.77-7.71 (m, 1H), 7.44 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 7.17 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.01 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.02-6.97 (m, 2H), 6.75 (d, 2H, J=9.2Hz), 2.98 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 161.64 (dd, J=245.2Hz), 159.99 (dd, J=248.9Hz, 248.2Hz), 150.87, 131.54 (dd, J=4.5Hz), 127.89, 125.34, 122.84 (dd, J=12.1Hz), 114.56 (t, J=1.6Hz), 112.43, 111.73 (dd, J=21.3Hz), 103.85 (t, J=26.5Hz, J=25.8Hz), 39.68. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (71), 243 (30), 215 (15), 195 (14). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.25; H, 5.77.
(E)-4-(2,5-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4o)
Procedure A Yield 77%. Yellow crystals. Mp 146–147°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.51-7.46 (m, 3H), 7.28 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.18-7.12 (m, 1H), 7.03 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 7.00-6.95 (m, 1H), 6.76 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 2.99 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 159.28 (dd, J=236.0Hz), 156.22 (dd, J=241.4Hz), 151.09, 133.04 (d, J=3.8Hz), 128.21, 124.94, 117.01 (d, J=25.8Hz), 116.92 (d, J=25.1Hz), 114.12 (d, J=25.1Hz), 114.03 (d, J=24.3Hz), 112.37, 112.12 (d, J=4.5Hz), 39.64. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (84), 243 (29), 215 (18), 195 (17). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.63; H, 5.90.
(E)-2-(2,6-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4p)
Procedure B. Yield 92%. Yellow oil. 1H NMR: δ 7.78 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 7.65 (dd, 1H, J=1.6Hz), 7.36-7.26 (m, 2H), 7.12-7.03 (m, 4H), 7.09 (d, 1H, J=17.2Hz), 2.74 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 161.10 (d, J=248.2Hz), 161.02 (d, J=248.2Hz), 152.77, 133.80 (t, J=8.3Hz, J=7.6Hz), 131.25, 129.19, 128.59 (t, J=11.4Hz, J=10.6Hz), 126.72, 122.65, 118.46, 115.31 (t, J=15.2Hz, J=15.9Hz), 113.84, 111.95 (d, J=19.7Hz), 111.89 (d, J=19.0Hz), 44.31. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (14), 132 (8). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.38; H, 5.79.
(E)-3-(2,6-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4q)
Procedure B. Yield 53%. Colorless crystals from hexane. Mp 69–71°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.38 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 7.33-7.26 (m, 1H), 7.19 (t, 1H, J=8.4Hz, J=8.0Hz), 7.11 (d, 1H, J=17.2Hz), 7.03 (dd, 2H, J=8.4 and 8.8Hz), 6.93-6.91 (m, 2H), 6.72-6.69 (m, 1H), 2.96 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 161.06 (d, J=248.2Hz), 160.98 (d, J=248.2Hz), 151.38, 138.03, 136.83 (t, J=7.6Hz, J=8.3Hz), 129.46, 128.70 (t, J=10.6Hz, J=11.4Hz), 114.87 (t, J=16Hz), 114.81, 114.09, 112.98, 111.94 (d, J=19.7Hz), 111.88 (d, J=19.0Hz), 111.21, 39.93. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (52), 239 (31), 238 (33), 223 (16), 222 (37). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.30; H, 5.78.
(E)-4-(2,6-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4r)
Procedure B. Yield 94%. Colorless crystals from hexane. Mp 112–113°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.45 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 7.35 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 7.27-7.20 (m, 1H), 7.01 (dd, 2H, J=8.4 and 8.8Hz), 6.91 (1H, d, J=16.8Hz), 6.75 (d, 2H, J=9.2Hz), 2.98 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 160.86 (d, J=247.4Hz), 160.78 (d, J=248.3Hz), 151.10, 135.99 (t, J=8.3Hz), 127.97, 127.57 (t, J=11.3Hz), 125.41, 115.50 (t, J=16.0Hz), 112.40, 111.82 (d, J=19.0Hz), 111.76 (d, J=19.0Hz), 109.73, 39.65. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (71), 243 (25), 195 (11). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.08; H, 5.79.
(E)-4-(2,6-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-diethylaniline (4s)
Procedure B. Yield 57%. Yellow crystals from hexane. Mp 70–71°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.43 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 7.34 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 7.27-7.20 (m, 1H), 7.01 (dd, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 6.89 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 6.72 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 3.43 (q, 4H, J=7.2Hz), 1.16 (t, 6H, J=7.2Hz). 13C NMR: δ 160.83 (d, J=246.7Hz), 160.75 (d, J=247.4Hz), 148.30, 136.07 (t, J=8.3Hz), 128.29, 127.37 (t, J=10.6Hz), 124.45, 115.62 (t, J=16.0Hz), 111.81 (d, J=19.0Hz), 111.74 (d, J=19.8Hz), 111.73, 109.07, 44.20, 12.20. MS: m/z (%) 287 (44), 272 (100), 244 (21), 243 (15). Anal. Calcd for C18H19F2N: C, 75.24; H, 6.66. Found: C, 75.12; H, 6.79.
(E)-4-(3,4-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4t)
Procedure A. Yield 59%. Yellow crystals from hexane. Mp 159–160°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.50-7.44 (m, 1H), 7.41 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.32-7.28 (m, 1H), 7.27-7.20 (m, 1H), 7.11 (d, 1H, J=16.0Hz), 6.92 (d, 1H, J=16.4Hz), 6.71 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 2.95 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 150.82, 150.56 (dd, J=243.9Hz), 150.50, 148.98 (dd, J=244.3Hz), 136.59, 130.55 (d, J=3.0Hz), 127.91, 125.16, 122.71 (d, J=6.1Hz), 122.68 (d, J=6.1Hz), 121.68 (d, J=2.3Hz), 117.49 (d, J=17.4Hz), 113.96 (d, J=17.5Hz), 112.43, 39.68. MS: m/z (%) 259 (100), 258 (82), 243 (36), 215 (22), 195 (16). Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.24; H, 5.79.
(E)-4-(3,5-Difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (4u)
Procedure A. Yield 51%. Yellow crystals. Mp 136–137°C. [lit.36 139–141°C]. Anal. Calcd for C16H15F2N: C, 74.11; H, 5.83. Found: C, 74.38; H, 5.70.
(E)-N,N-Dimethyl-4-(2,3,6-trifluorostyryl)aniline (4v)
Procedure B. Yield 45%. Light yellow crystals from hexane. Mp 91–92°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.48 (d, 2H, J=9.2Hz), 7.39 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 7.22-7.14 (m, 1H), 7.06-7.00 (m, 1H), 6.89 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 6.76 (d, 2H, J=8.0Hz), 3.00 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 157.35-154.83 (m, 1C), 151.31, 149.49-146.37 (m, 2C), 137.17 (t, J=8.4Hz), 128.23, 124.89, 117.43 (dd, J=17.4Hz, J=16.7Hz), 114.01 (dd, J=18.9Hz, J=19.8Hz), 112.33, 111.39-111.02 (m, 1C), 108.99, 39.59. MS: m/z (%) 277 (100), 276 (83), 261 (24), 214 (16), 213 (12). Anal. Calcd for C16H14F3N: C, 69.30; H, 5.09. Found: C, 69.50; H, 4.97.
(E)-N,N-Dimethyl-4-(2,4,6-trifluorostyryl)aniline (4w)
Procedure B. Yield 63%. Light yellow crystals from hexane. Mp 127–128°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.45 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.29 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 6.91 (t, 2H, J=9.2Hz, J=8.8Hz), 6.83 (d, 1H, J=16.8Hz), 6.75 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 2.99 (s, 6H). 13C NMR: δ 160.87 (dd, J=249.1Hz, J=248.9Hz), 160.72 (dd, J=249.0Hz), 151.09, 135.59 (t, J=7.7Hz, J=8.3Hz), 127.94, 125.24, 112.38, 108.80, 100.65 (dd, J=25.8Hz), 39.64. MS: m/z (%) 277 (100), 276 (75), 261 (29). Anal. Calcd for C16H14F3N: C, 69.30; H, 5.09. Found: C, 69.49; H, 4.99.
4-(2,6-Difluorophenethyl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (5r)
To 150 mg (0.58 mmol) of 4r in 10 mL of THF was added 50 mg of 10% Pd-C. The mixture was hydrogenated at 40 psi on a Parr shaker for 5 h. The mixture was filtered through Celite and chromatographed using 1:10 EtOAc:hexane to afford 110 mg (76%) of 5r: Colorless crystals from hexane. Mp 42–43°C. 1H NMR: δ 7.31-7.23 (m, 1H), 7.02 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 6.94 (t, 2H, J=8.4Hz, J=8.0Hz), 6.66 (d, 2H, J=8.4Hz), 2.90-2.89 (m, 2H), 2.85 (s, 6H), 2.77-2.73 (m, 2H). 13C NMR: δ 161.72 (d, J=243.7Hz), 161.63 (d, J=244.5Hz), 149.62, 128.98, 128.94, 128.15 (t, J=9.8Hz, J=10.7Hz), 117.36 (t, J=20.5Hz), 112.88, 111.25 (d, J=19.8Hz), 111.18 (d, J=19.0Hz), 40.10, 34.73, 24.75. MS: m/z (%) 261 (40), 134 (100), 118 (27), 91 (22). Anal. Calcd for C16H17F2N: C, 73.54; H, 6.56. Found: C, 73.53; H, 6.49.
Cell culture and transfection
HEK293T, HCT116 and SW480 cells were grown in DMEM medium (Mediatech) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. LS174T cells were grown in RPMI medium (Mediatech) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected using the calcium phosphate method as described previously 37.
Western blot
Western blot was performed as described previously 37. The following antibodies were used: β-catenin (Sigma, C2206), c-Myc (Epitomics, 1472-1), Axin2 (Cell Signaling, 2151), β-Actin (Sigma, A1978), TCF4 (Epitomics, 2114-1) and pygopus2 (Santa Cruz, sc-74878), Cyclin D1 (Cell signaling, 2926).
RT-PCR
LS174 cells were treated with DMSO or Wnt inhibitors. After 36h, RNA was isolated using the RNeasy kit (Qiagen). RT-PCR was performed as described previously 37. The following primers were used: β-actin: 5’-CAACCGCGAGAAGATGAC-3’, 5’-AGGAAGGCTGGAAGAGTG-3’; surivivin: 5’-CATTCGTCCGGTTGCGCTTTCC-3’, 5’-GCGCACTTTCTCCGCAGTTTCC-3’; c-Myc: 5’-TGGGCTGTGAGGAGGTTTG-3’, 5’-TATGTGGAGCGGCTTCTCG-3’. Axin2: 5’-CACCACCACCACCACCATTC-3’, 5’-GCATCCACTGCCAGACATCC-3’; TCF4: 5’-CACCACATCATACGCTACAC-3’, 5’- CGACCTTTGCTCTCATTTCC-3’; pygopus2: 5’-GGCCGGTCTGCAAATGAAG-3’, 5’-TCCACCTCCAGTGCTGTAG-3’; Lgr5: 5’-CCTGCTTGACTTTGAGGAAGAC-3’, 5’-ATGTTCACTGCTGCGATGAC-3’; CD44: 5’-CAGAATGGCTGATCATCTTG-3’, 5’-CAAATGCACCATTTCCTGAG-3’; Ki67: 5’-ACAGAGTGCTCAACAACTTC-3’, 5’-GCTTGCAGAGCATTTATCAG-3’.
Luciferase and cell proliferation assays
HEK293T cells were transiently transfected in a 12-well plate with 0.2µg of the Super8xTOPFlash reporter and 0.05µg of Renilla luciferase reporter. Culture medium was changed after 12h. After 6h, Cells were treated with DMSO or Wnt inhibitors for 12h, and then treated with 25mM LiCl or Wnt conditioned medium. After 12h, cells were harvested and luciferase activity measured by Dual-luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, Madison WI). All conditions were done in triplicate and each experiment was carried out at least two times. For cell proliferation assay, CRC cells were treated with DMSO or inhibitors for 2d and 4d. The cell numbers and viability were analyzed by Vi-Cell Cell Viability Analyzer.
In vivo studies
LS174 cells (2×106) were injected subcutaneously into both flanks of 6–8 week C57BL/6J athymic nude mice as previously described37. 4r was dissolved in corn oil. The mice were treated with 20mg/kg/day of 4r by ip injection (50µl/mouse). Control mice were treated with same volume of corn oil. The body weight and tumor growth were analyzed twice weekly for one month. Tumor size was measured using digital caliper. The tumor volume was calculated by the formula: V=1/2LW2 (mm3).
Immunofluorescence
Cells grown on cover glass were fixed by 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature. The cells were permeabilized with PBS containing 0.3% (w/v) Triton X-100 and blocked by 5% normal goat serum in PBS for 30 min. Anti- β-catenin antibody (1:300, Sigma, St. Louis, MO) was diluted in blocking solution and incubated with cells overnight. The cells were washed 3 times with PBS and further incubated with Alexa-488-labeled anti-rabbit IgG (1:500) diluted in PBS for 40 min. The cover glasses were washed, mounted on glass slides, viewed and photographed with an Olympus FW1000 confocal microscope.
Cells grown on cover glass were treated with fluorescent compounds for 2h, 6h, 12h and 24h respectively. Treated cells were fixed by 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature. Then cells were washed 3 times with PBS and mounted on glass slides, viewed under the fluorescence of 405nm-wavelength and photographed with an Olympus FW1000 confocal microscope.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Center for Clinical and Translational Science at University of Kentucky for CCTS Pilot Award. CL was supported by R01 DK071976 from the NIH. BME was supported by UK SPORE grant (P20 CA 150343). DSW was supported by the Office of the Vice President for Research and the Organic Synthesis Core Facility was supported by NIH Grant Number 2P20 RR020171 from the National Center for Research Resources.
Abbreviations
- CRC
colorectal cancer
- APC
adenomatous polyposis coli
- resveratrol
trans-resveratol or (E)-3,5, 4’-trihydroxystilbene
- 4r
(E)-4-(2,6-difluorostyryl)-N,N-dimethylaniline
Footnotes
Supplementary Material
Copies of the 1H and 13C NMR spectra for the compounds described in this paper are provided in the Supplementary Material.
References
- 1.Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.van Amerongen R, Nusse R. Towards an integrated view of Wnt signaling in development. Development. 2009;136:3205–3214. doi: 10.1242/dev.033910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Giles RH, van Es JH, Clevers H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1653:1–24. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(03)00005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159–170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1837–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Liu C, Kato Y, Zhang Z, Do VM, Yankner BA, He X. beta-Trcp couples beta-catenin phosphorylation-degradation and regulates Xenopus axis formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:6273–6278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH, Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X, He X. Control of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell. 2002;108:837–847. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00685-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H, Habas R, Okamura H, Woodgett J, He X. A dual-kinase mechanism for Wnt co-receptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature. 2005;438:873–877. doi: 10.1038/nature04185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zeng X, Huang H, Tamai K, Zhang X, Harada Y, Yokota C, Almeida K, Wang J, Doble B, Woodgett J, Wynshaw-Boris A, Hsieh JC, He X. Initiation of Wnt signaling: control of Wnt coreceptor Lrp6 phosphorylation/activation via frizzled, dishevelled and axin functions. Development. 2008;135:367–375. doi: 10.1242/dev.013540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yang J, Zhang W, Evans PM, Chen X, He X, Liu C. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) differentially regulates beta-catenin phosphorylation and ubiquitination in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17751–17757. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600831200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A, Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner S, Hild M, Shi X, Wilson CJ, Mickanin C, Myer V, Fazal A, Tomlinson R, Serluca F, Shao W, Cheng H, Shultz M, Rau C, Schirle M, Schlegl J, Ghidelli S, Fawell S, Lu C, Curtis D, Kirschner MW, Lengauer C, Finan PM, Tallarico JA, Bouwmeester T, Porter JA, Bauer A, Cong F. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature. 2009;461:614–620. doi: 10.1038/nature08356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan CW, Wei S, Hao W, Kilgore J, Williams NS, Roth MG, Amatruda JF, Chen C, Lum L. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5:100–107. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu C, He X. Destruction of a destructor: a new avenue for cancer therapeutics targeting the Wnt pathway. J Mol Cell Biol. 2:70–73. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjp040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Barker N, Clevers H. Mining the Wnt pathway for cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:997–1014. doi: 10.1038/nrd2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Garber K. Drugging the Wnt pathway: problems and progress. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:548–550. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Signorelli P, Ghidoni R. Resveratrol as an anticancer nutrient: molecular basis, open questions and promises. J Nutr Biochem. 2005;16:449–466. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Athar M, Back JH, Tang X, Kim KH, Kopelovich L, Bickers DR, Kim AL. Resveratrol: a review of preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007;224:274–283. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.12.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Suh N, Paul S, Hao X, Simi B, Xiao H, Rimando AM, Reddy BS. Pterostilbene, an active constituent of blueberries, suppresses aberrant crypt foci formation in the azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis model in rats. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:350–355. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vanamala J, Reddivari L, Radhakrishnan S, Tarver C. Resveratrol suppresses IGF-1 induced human colon cancer cell proliferation and elevates apoptosis via suppression of IGF-1R/Wnt and activation of p53 signaling pathways. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:238. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Roccaro AM, Leleu X, Sacco A, Moreau AS, Hatjiharissi E, Jia X, Xu L, Ciccarelli B, Patterson CJ, Ngo HT, Russo D, Vacca A, Dammacco F, Anderson KC, Ghobrial IM, Treon SP. Resveratrol exerts antiproliferative activity and induces apoptosis in Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1849–1858. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hope C, Planutis K, Planutiene M, Moyer MP, Johal KS, Woo J, Santoso C, Hanson JA, Holcombe RF. Low concentrations of resveratrol inhibit Wnt signal throughput in colon-derived cells: implications for colon cancer prevention. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008;52 Suppl 1:S52–S61. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pecere T, Gazzola MV, Mucignat C, Parolin C, Vecchia FD, Cavaggioni A, Basso G, Diaspro A, Salvato B, Carli M, Palu G. Aloe-emodin is a new type of anticancer agent with selective activity against neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2800–2804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chiang YJ, Hsiao SJ, Yver D, Cushman SW, Tessarollo L, Smith S, Hodes RJ. Tankyrase 1 and tankyrase 2 are essential but redundant for mouse embryonic development. PLoS One. 2008;3:e2639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Choi HY, Lim JE, Hong JH. Curcumin interrupts the interaction between the androgen receptor and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010;13:343–349. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2010.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim J, Zhang X, Rieger-Christ KM, Summerhayes IC, Wazer DE, Paulson KE, Yee AS. Suppression of Wnt signaling by the green tea compound (−)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG) in invasive breast cancer cells. Requirement of the transcriptional repressor HBP1. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10865–10875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513378200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Leow PC, Tian Q, Ong ZY, Yang Z, Ee PL. Antitumor activity of natural compounds, curcumin and PKF118-310, as Wnt/beta-catenin antagonists against human osteosarcoma cells. Invest New Drugs. 2010;28:766–782. doi: 10.1007/s10637-009-9311-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Paul S, DeCastro AJ, Lee HJ, Smolarek AK, So JY, Simi B, Wang CX, Zhou R, Rimando AM, Suh N. Dietary intake of pterostilbene, a constituent of blueberries, inhibits the betacatenin/ p65 downstream signaling pathway and colon carcinogenesis in rats. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:1272–1278. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhou H, Shang L, Li X, Zhang X, Gao G, Guo C, Chen B, Liu Q, Gong Y, Shao C. Resveratrol augments the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in promoting osteoblastic differentiation of multipotent mesenchymal cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:2953–2962. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang H, Zhou H, Zou Y, Liu Q, Guo C, Gao G, Shao C, Gong Y. Resveratrol modulates angiogenesis through the GSK3beta/beta-catenin/TCF-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;80:1386–1395. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.07.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, vandenBorn M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, Clevers H. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. doi: 10.1038/nature06196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Henry C, Vitrac X, Decendit A, Ennamany R, Krisa S, Merillon JM. Cellular uptake and efflux of trans-piceid and its aglycone trans-resveratrol on the apical membrane of human intestinal Caco-2 cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53:798–803. doi: 10.1021/jf048909e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gu B, Watanabe K, Dai X. Epithelial stem cells: an epigenetic and Wnt-centric perspective. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110:1279–1287. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Kuwata T, Hamano M, Okayasu I. Upregulation of TCF4 expression as a transcriptional target of beta-catenin/p300 complexes during trans-differentiation of endometrial carcinoma cells. Lab Invest. 2005;85:768–779. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Narender T, Papi Reddy K, Madhur G. Synthesis of (E)-stilbenes and (E,E)-1,4-diphenylbuta-1,3-diene promoted by boron trifluoride-diethyl ether complex. Synthesis. 2009;22:3791–3796. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gester S, Pietzsch J, Wuest FR. Synthesis of 18F-labelled stilbenes from 4-(18F)-fluorobenzaldehyde using the Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons reaction. J Label Compd Radiopharm. 2007;50:105–113. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Moran BW, Anderson FP, Devery A, Cloonan S, Butler WE, Varughese S, Draper SM, Kenny PT. Synthesis, structural characterisation and biological evaluation of fluorinated analogues of resveratrol. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:4510–4522. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang W, Chen X, Kato Y, Evans PM, Yuan S, Yang J, Rychahou PG, Yang VW, He X, Evers BM, Liu C. Novel cross talk of Kruppel-like factor 4 and beta-catenin regulates normal intestinal homeostasis and tumor repression. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:2055–2064. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2055-2064.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.